Difference between revisions of "Lung carcinoma with ALK rearrangement"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
(tweak) |
|||
| (26 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
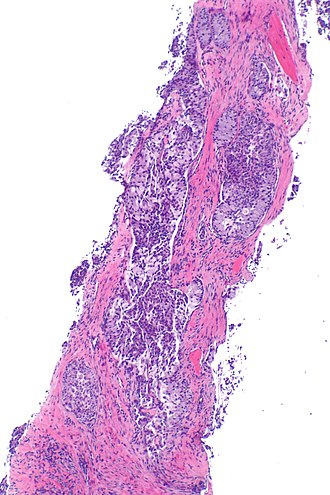
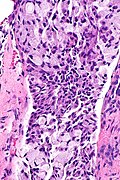
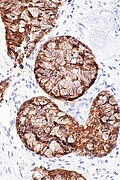
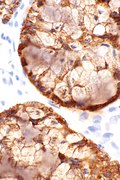
[[Image:ALK positive lung adenocarcinoma -- low mag.jpg|thumb|right|[[Micrograph]] showing ALK positive lung adenocarcinoma. [[H&E stain]].]] | |||
'''Lung carcinoma with ALK rearrangement''' is subset of [[lung adenocarcinoma]]. | '''Lung carcinoma with ALK rearrangement''' is subset of [[lung adenocarcinoma]]. | ||
==General== | ==General== | ||
ALK (anaplastic lymphoma (receptor tyrosine) kinase): | |||
*Approximately 1-5% non-small cell lung carcinoma.<ref name=pmid21753699>{{Cite journal | last1 = Yoshida | first1 = A. | last2 = Tsuta | first2 = K. | last3 = Nakamura | first3 = H. | last4 = Kohno | first4 = T. | last5 = Takahashi | first5 = F. | last6 = Asamura | first6 = H. | last7 = Sekine | first7 = I. | last8 = Fukayama | first8 = M. | last9 = Shibata | first9 = T. | title = Comprehensive histologic analysis of ALK-rearranged lung carcinomas. | journal = Am J Surg Pathol | volume = 35 | issue = 8 | pages = 1226-34 | month = Aug | year = 2011 | doi = 10.1097/PAS.0b013e3182233e06 | PMID = 21753699 }}</ref> | *Approximately 1-5% non-small cell lung carcinoma.<ref name=pmid21753699>{{Cite journal | last1 = Yoshida | first1 = A. | last2 = Tsuta | first2 = K. | last3 = Nakamura | first3 = H. | last4 = Kohno | first4 = T. | last5 = Takahashi | first5 = F. | last6 = Asamura | first6 = H. | last7 = Sekine | first7 = I. | last8 = Fukayama | first8 = M. | last9 = Shibata | first9 = T. | title = Comprehensive histologic analysis of ALK-rearranged lung carcinomas. | journal = Am J Surg Pathol | volume = 35 | issue = 8 | pages = 1226-34 | month = Aug | year = 2011 | doi = 10.1097/PAS.0b013e3182233e06 | PMID = 21753699 }}</ref> | ||
**Typically seen in nonsmokers and younger age patients. | |||
**Can be treated with ''[[crizotinib]]''.<ref name=pmid21475126>{{Cite journal | last1 = Crystal | first1 = AS. | last2 = Shaw | first2 = AT. | title = New targets in advanced NSCLC: EML4-ALK. | journal = Clin Adv Hematol Oncol | volume = 9 | issue = 3 | pages = 207-14 | month = Mar | year = 2011 | doi = | PMID = 21475126 }}</ref> | |||
***Resistance to [[ALK inhibitors]] may occur due mutations in kinase domain. | |||
***Ceritinib is indicated for tumor with acquired resistance to crizotinib.<ref>{{Cite journal | last1 = Shaw | first1 = AT. | last2 = Kim | first2 = DW. | last3 = Mehra | first3 = R. | last4 = Tan | first4 = DS. | last5 = Felip | first5 = E. | last6 = Chow | first6 = LQ. | last7 = Camidge | first7 = DR. | last8 = Vansteenkiste | first8 = J. | last9 = Sharma | first9 = S. | title = Ceritinib in ALK-rearranged non-small-cell lung cancer. | journal = N Engl J Med | volume = 370 | issue = 13 | pages = 1189-97 | month = Mar | year = 2014 | doi = 10.1056/NEJMoa1311107 | PMID = 24670165 }}</ref> | |||
*Testing in [[FFPE]] tissue requires ~100 cells.<ref name=pmid25806315>{{Cite journal | last1 = Popper | first1 = HH. | last2 = Tímár | first2 = J. | last3 = Ryska | first3 = A. | last4 = Olszewski | first4 = W. | title = Minimal requirements for the molecular testing of lung cancer. | journal = Transl Lung Cancer Res | volume = 3 | issue = 5 | pages = 301-4 | month = Oct | year = 2014 | doi = 10.3978/j.issn.2218-6751.2014.10.02 | PMID = 25806315 }}</ref> | |||
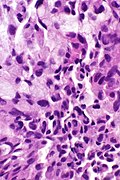
==Microscopic== | ==Microscopic== | ||
| Line 12: | Line 19: | ||
DDx: | DDx: | ||
*[[Adenocarcinoma of the lung]]. | *[[Adenocarcinoma of the lung]]. | ||
*[[Signet ring cell carcinoma]]. (?) | |||
*[[Mucinous carcinoma]]. (?) | |||
===Images=== | |||
<gallery> | |||
Image: ALK positive lung adenocarcinoma -- very low mag.jpg | ALK +ve lung adenoca - very low mag. (WC) | |||
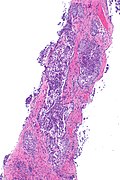
Image: ALK positive lung adenocarcinoma -- low mag.jpg | ALK +ve lung adenoca - low mag. (WC) | |||
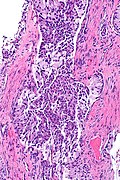
Image: ALK positive lung adenocarcinoma -- intermed mag.jpg | ALK +ve lung adenoca - intermed. mag. (WC) | |||
Image: ALK positive lung adenocarcinoma -- high mag.jpg | ALK +ve lung adenoca - high mag. (WC) | |||
Image: ALK positive lung adenocarcinoma -- very high mag.jpg | ALK +ve lung adenoca - very high mag. (WC) | |||
</gallery> | |||
====www==== | |||
*[http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3400179/figure/f1-cln_67p845/ Lung carcinoma with ALK rearrangement (nih.gov)].<ref name=pmid22892933>{{Cite journal | last1 = Lopes | first1 = LF. | last2 = Bacchi | first2 = CE. | title = Anaplastic lymphoma kinase gene rearrangement in non-small-cell lung cancer in a Brazilian population. | journal = Clinics (Sao Paulo) | volume = 67 | issue = 7 | pages = 845-7 | month = Jul | year = 2012 | doi = | PMID = 22892933 }}</ref> | |||
*[http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3731315/figure/pone-0069794-g002/ Lung carcinoma with ALK rearrangment (nih.gov)]<ref>{{Cite journal | last1 = Takamochi | first1 = K. | last2 = Takeuchi | first2 = K. | last3 = Hayashi | first3 = T. | last4 = Oh | first4 = S. | last5 = Suzuki | first5 = K. | title = A rational diagnostic algorithm for the identification of ALK rearrangement in lung cancer: a comprehensive study of surgically treated Japanese patients. | journal = PLoS One | volume = 8 | issue = 8 | pages = e69794 | month = | year = 2013 | doi = 10.1371/journal.pone.0069794 | PMID = 23936355 }}</ref> - [http://www.plosone.org/article/info:doi/10.1371/journal.pone.0069794.g002/largerimage high resolution (plosone.org)]. | |||
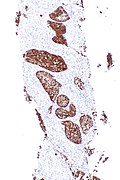
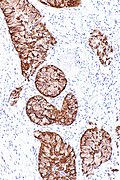
==IHC== | ==IHC== | ||
| Line 17: | Line 38: | ||
*p63 +ve. | *p63 +ve. | ||
*TTF-1 +ve. | *TTF-1 +ve. | ||
*ALK +ve.{{fact}} | |||
===Images=== | |||
<gallery> | |||
Image: ALK positive lung adenocarcinoma - ALK IHC -- very low mag.jpg | ALK +ve lung adenoca - very low mag. (WC) | |||
Image: ALK positive lung adenocarcinoma - ALK IHC -- low mag.jpg | ALK +ve lung adenoca - low mag. (WC) | |||
Image: ALK positive lung adenocarcinoma - ALK IHC -- intermed mag.jpg | ALK +ve lung adenoca - intermed. mag. (WC) | |||
Image: ALK positive lung adenocarcinoma - ALK IHC -- high mag.jpg | ALK +ve lung adenoca - high mag. (WC) | |||
Image: ALK positive lung adenocarcinoma - ALK IHC -- very high mag.jpg | ALK +ve lung adenoca - very high mag. (WC) | |||
</gallery> | |||
==Molecular== | ==Molecular== | ||
*EML4-ALK fusion -- inv(2)(p21p23).<ref name=pmid21245935>{{Cite journal | last1 = Li | first1 = Y. | last2 = Ye | first2 = X. | last3 = Liu | first3 = J. | last4 = Zha | first4 = J. | last5 = Pei | first5 = L. | title = Evaluation of EML4-ALK fusion proteins in non-small cell lung cancer using small molecule inhibitors. | journal = Neoplasia | volume = 13 | issue = 1 | pages = 1-11 | month = Jan | year = 2011 | doi = | PMID = 21245935 }}</ref> | *EML4-ALK fusion -- inv(2)(p21p23).<ref name=pmid21245935>{{Cite journal | last1 = Li | first1 = Y. | last2 = Ye | first2 = X. | last3 = Liu | first3 = J. | last4 = Zha | first4 = J. | last5 = Pei | first5 = L. | title = Evaluation of EML4-ALK fusion proteins in non-small cell lung cancer using small molecule inhibitors. | journal = Neoplasia | volume = 13 | issue = 1 | pages = 1-11 | month = Jan | year = 2011 | doi = | PMID = 21245935 }}</ref> | ||
**C-terminus of ALK protein fuses with N-terminus portion of partner protein. | |||
***ALK fusion leads to ligand-independent constitutive activation of important pathways in oncogenesis and tumor progression. | |||
Notes: | |||
*May be demonstrated with [[FISH]] or PCR looking for the a fusion transcript.<ref name=pmid23729361>{{Cite journal | last1 = Gainor | first1 = JF. | last2 = Varghese | first2 = AM. | last3 = Ou | first3 = SH. | last4 = Kabraji | first4 = S. | last5 = Awad | first5 = MM. | last6 = Katayama | first6 = R. | last7 = Pawlak | first7 = A. | last8 = Mino-Kenudson | first8 = M. | last9 = Yeap | first9 = BY. | title = ALK rearrangements are mutually exclusive with mutations in EGFR or KRAS: an analysis of 1,683 patients with non-small cell lung cancer. | journal = Clin Cancer Res | volume = 19 | issue = 15 | pages = 4273-81 | month = Aug | year = 2013 | doi = 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-13-0318 | PMID = 23729361 }}</ref> | |||
*ALK rearrangement does ''not'' occur with [[EGFR lung cancer|EGRF mutation]] ''or'' [[KRAS mutation]].<ref name=pmid23729361>{{Cite journal | last1 = Gainor | first1 = JF. | last2 = Varghese | first2 = AM. | last3 = Ou | first3 = SH. | last4 = Kabraji | first4 = S. | last5 = Awad | first5 = MM. | last6 = Katayama | first6 = R. | last7 = Pawlak | first7 = A. | last8 = Mino-Kenudson | first8 = M. | last9 = Yeap | first9 = BY. | title = ALK rearrangements are mutually exclusive with mutations in EGFR or KRAS: an analysis of 1,683 patients with non-small cell lung cancer. | journal = Clin Cancer Res | volume = 19 | issue = 15 | pages = 4273-81 | month = Aug | year = 2013 | doi = 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-13-0318 | PMID = 23729361 }}</ref> | |||
==See also== | ==See also== | ||
*[[Lung tumours]]. | *[[Lung tumours]]. | ||
*[[Lung carcinoma with EGFR mutation]]. | |||
*[[ALK translocation renal cell carcinoma]]. | |||
==References== | ==References== | ||
Latest revision as of 23:57, 17 March 2019
Lung carcinoma with ALK rearrangement is subset of lung adenocarcinoma.
General
ALK (anaplastic lymphoma (receptor tyrosine) kinase):
- Approximately 1-5% non-small cell lung carcinoma.[1]
- Typically seen in nonsmokers and younger age patients.
- Can be treated with crizotinib.[2]
- Resistance to ALK inhibitors may occur due mutations in kinase domain.
- Ceritinib is indicated for tumor with acquired resistance to crizotinib.[3]
- Testing in FFPE tissue requires ~100 cells.[4]
Microscopic
Features:[1]
- Adenocarcinoma - at least focally.
- Solid signet-ring cell pattern - common.
- Mucinous cribriform pattern - common.
DDx:
Images
www
- Lung carcinoma with ALK rearrangement (nih.gov).[5]
- Lung carcinoma with ALK rearrangment (nih.gov)[6] - high resolution (plosone.org).
IHC
Features:[1]
- p63 +ve.
- TTF-1 +ve.
- ALK +ve.[citation needed]
Images
Molecular
- EML4-ALK fusion -- inv(2)(p21p23).[7]
- C-terminus of ALK protein fuses with N-terminus portion of partner protein.
- ALK fusion leads to ligand-independent constitutive activation of important pathways in oncogenesis and tumor progression.
- C-terminus of ALK protein fuses with N-terminus portion of partner protein.
Notes:
- May be demonstrated with FISH or PCR looking for the a fusion transcript.[8]
- ALK rearrangement does not occur with EGRF mutation or KRAS mutation.[8]
See also
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 Yoshida, A.; Tsuta, K.; Nakamura, H.; Kohno, T.; Takahashi, F.; Asamura, H.; Sekine, I.; Fukayama, M. et al. (Aug 2011). "Comprehensive histologic analysis of ALK-rearranged lung carcinomas.". Am J Surg Pathol 35 (8): 1226-34. doi:10.1097/PAS.0b013e3182233e06. PMID 21753699.
- ↑ Crystal, AS.; Shaw, AT. (Mar 2011). "New targets in advanced NSCLC: EML4-ALK.". Clin Adv Hematol Oncol 9 (3): 207-14. PMID 21475126.
- ↑ Shaw, AT.; Kim, DW.; Mehra, R.; Tan, DS.; Felip, E.; Chow, LQ.; Camidge, DR.; Vansteenkiste, J. et al. (Mar 2014). "Ceritinib in ALK-rearranged non-small-cell lung cancer.". N Engl J Med 370 (13): 1189-97. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa1311107. PMID 24670165.
- ↑ Popper, HH.; Tímár, J.; Ryska, A.; Olszewski, W. (Oct 2014). "Minimal requirements for the molecular testing of lung cancer.". Transl Lung Cancer Res 3 (5): 301-4. doi:10.3978/j.issn.2218-6751.2014.10.02. PMID 25806315.
- ↑ Lopes, LF.; Bacchi, CE. (Jul 2012). "Anaplastic lymphoma kinase gene rearrangement in non-small-cell lung cancer in a Brazilian population.". Clinics (Sao Paulo) 67 (7): 845-7. PMID 22892933.
- ↑ Takamochi, K.; Takeuchi, K.; Hayashi, T.; Oh, S.; Suzuki, K. (2013). "A rational diagnostic algorithm for the identification of ALK rearrangement in lung cancer: a comprehensive study of surgically treated Japanese patients.". PLoS One 8 (8): e69794. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0069794. PMID 23936355.
- ↑ Li, Y.; Ye, X.; Liu, J.; Zha, J.; Pei, L. (Jan 2011). "Evaluation of EML4-ALK fusion proteins in non-small cell lung cancer using small molecule inhibitors.". Neoplasia 13 (1): 1-11. PMID 21245935.
- ↑ 8.0 8.1 Gainor, JF.; Varghese, AM.; Ou, SH.; Kabraji, S.; Awad, MM.; Katayama, R.; Pawlak, A.; Mino-Kenudson, M. et al. (Aug 2013). "ALK rearrangements are mutually exclusive with mutations in EGFR or KRAS: an analysis of 1,683 patients with non-small cell lung cancer.". Clin Cancer Res 19 (15): 4273-81. doi:10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-13-0318. PMID 23729361.