Difference between revisions of "Squamous cell carcinoma"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search

m (→Invasion) |
(split out) |
||
| (48 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
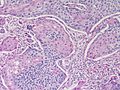
This article deal with '''squamous cell carcinoma''', also '''squamous carcinoma''', | [[Image:Esophageal_squamous_cell_carcinoma_-_a1_--_high_mag.jpg| thumb| Squamous cell carcinoma. [[H&E stain]]. (WC)]] | ||
This article deal with '''squamous cell carcinoma''', also '''squamous carcinoma''', a very common epithelial derived malignant neoplasm that can arise from many sites. It is commonly abbreviated '''[[SCC]]'''. | |||
=Sites= | =Sites= | ||
===Skin=== | ===Skin=== | ||
{{Main|Squamous cell carcinoma of the skin}} | |||
*A common [[Dermatologic_neoplasms#Squamous_cell_carcinoma|skin tumour]]. | *A common [[Dermatologic_neoplasms#Squamous_cell_carcinoma|skin tumour]]. | ||
===Head and neck=== | ===Head and neck=== | ||
{{Main|Squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck}} | |||
*Most common tumour of the [[head and neck pathology|head & neck]]. | *Most common tumour of the [[head and neck pathology|head & neck]]. | ||
**[[Tongue squamous cell carcinoma]] is dealt with separately. | |||
*''[[Nasopharyngeal carcinoma]]'' can be considered a variant SCC. | |||
*HPV-associated SCC is dealt with in ''[[HPV-associated head and neck squamous cell carcinoma]]''. | |||
====Tumour extent==== | |||
*There is no agreed upon measure of tumour extent (tumour thickness/depth of invasion)<ref name=pmid16240329>{{Cite journal | last1 = Pentenero | first1 = M. | last2 = Gandolfo | first2 = S. | last3 = Carrozzo | first3 = M. | title = Importance of tumor thickness and depth of invasion in nodal involvement and prognosis of oral squamous cell carcinoma: a review of the literature. | journal = Head Neck | volume = 27 | issue = 12 | pages = 1080-91 | month = Dec | year = 2005 | doi = 10.1002/hed.20275 | PMID = 16240329 }}</ref> - proposed measures:<ref>URL: [http://www.cap.org/apps/docs/committees/cancer/cancer_protocols/2011/LipOralCav_11protocol.pdf http://www.cap.org/apps/docs/committees/cancer/cancer_protocols/2011/LipOralCav_11protocol.pdf]. Accessed on: 3 April 2012.</ref> | |||
**"Tumour thickness" = perpendicular distance from mucosal surface to deepest point of invasion. | |||
**"Tumour depth" = perpendicular distance from epithelial basement membrane to deepest point of invasion. | |||
===Uterine cervix=== | ===Uterine cervix=== | ||
{{Main|Squamous cell carcinoma of the uterine cervix}} | |||
*Most common form of [[uterine cervix|cervical cancer]]. | *Most common form of [[uterine cervix|cervical cancer]]. | ||
===Vulva=== | ===Vulva=== | ||
*Most common form of [[vulva|vulvar cancer]]. | *Most common form of [[vulva|vulvar cancer]]. | ||
====Tumour extent==== | |||
Thickness is measured:<ref name=pmid18379417>{{Cite journal | last1 = Yoder | first1 = BJ. | last2 = Rufforny | first2 = I. | last3 = Massoll | first3 = NA. | last4 = Wilkinson | first4 = EJ. | title = Stage IA vulvar squamous cell carcinoma: an analysis of tumor invasive characteristics and risk. | journal = Am J Surg Pathol | volume = 32 | issue = 5 | pages = 765-72 | month = May | year = 2008 | doi = 10.1097/PAS.0b013e318159a2cb | PMID = 18379417 }}</ref><ref>URL: [http://www.cap.org/apps/docs/committees/cancer/cancer_protocols/2011/Vulva_11protocol.pdf http://www.cap.org/apps/docs/committees/cancer/cancer_protocols/2011/Vulva_11protocol.pdf]. Accessed on: 3 April 2012.</ref> | |||
*No kerinization present: mucosal surface to the deepest point of invasion. | |||
*Kerinization present: bottom of granular layer to the deepest point of invasion. | |||
===Lung=== | ===Lung=== | ||
{{Main|Squamous cell carcinoma of the lung}} | |||
*A common form of [[lung cancer]] that is associated with [[smoking]]. | *A common form of [[lung cancer]] that is associated with [[smoking]]. | ||
===Esophagus=== | |||
{{Main|Squamous cell carcinoma of the esophagus}} | |||
*Upper and middle esophagus. | |||
===Anus=== | |||
{{Main|Anal squamous cell carcinoma}} | |||
*Most common form of anal cancer. | |||
===Other sites=== | ===Other sites=== | ||
*[[Colorectal carcinoma|Colorectum]]. | *[[Colorectal carcinoma|Colorectum]]. | ||
*[[Squamous cell carcinoma of the penis]]. | |||
*[[Squamous cell carcinoma of the urinary bladder]]. | |||
=Microscopic= | =Microscopic= | ||
| Line 26: | Line 53: | ||
*Keratinizing type (KT). | *Keratinizing type (KT). | ||
**Worst prognosis. | **Worst prognosis. | ||
**More common than non-keratinizing type.<ref>URL: [http://www.cap.org/apps/docs/committees/cancer/cancer_protocols/2011/LipOralCav_11protocol.pdf http://www.cap.org/apps/docs/committees/cancer/cancer_protocols/2011/LipOralCav_11protocol.pdf]. Accessed on: 3 April 2012.</ref> | |||
*Undifferentiated type (UT). | *Undifferentiated type (UT). | ||
**Intermediate prognosis. | **Intermediate prognosis. | ||
**EBV association. | **EBV association. | ||
* | *Non-keratinizing type (NT). | ||
**Good prognosis. | **Good prognosis. | ||
**EBV association. | **EBV association. | ||
<gallery> | |||
Image:Anus SquamousCellCarcinoma SCC NonKeratinizing AIA SCCIS CTR.jpg |Anus Squamous Cell Carcinoma (Non Keratinizing)-(SKB) | |||
Image:Anus SquamousCellCarcinoma SCC NonKeratinizing MP4 CTR.jpg|Anus Squamous Cell Carcinoma (Non Keratinizing) -(SKB) | |||
Image:Anus SquamousCellCarcinoma SCC NonKeratinizing MP CTR.jpg|Anus Squamous Cell Carcinoma (Non Keratinizing) - (SKB) | |||
</gallery> | |||
Features based on classification:<ref name=Ref_Sternberg4_975>{{Ref Sternberg4|975}}</ref> | Features based on classification:<ref name=Ref_Sternberg4_975>{{Ref Sternberg4|975}}</ref> | ||
| Line 62: | Line 95: | ||
=Subtypes= | =Subtypes= | ||
There are several subtypes:<ref>URL: [http://www. | There are several subtypes:<ref>URL: [http://www.cap.org/apps/docs/committees/cancer/cancer_protocols/2011/LipOralCav_11protocol.pdf http://www.cap.org/apps/docs/committees/cancer/cancer_protocols/2011/LipOralCav_11protocol.pdf]. Accessed on: 3 April 2012.</ref> | ||
*Basaloid - poor prognosis, usu. diagnosed by recognition of typical SCC. | *[[Adenosquamous carcinoma]]. | ||
* | *Ancatholytic squamous cell carcinoma. | ||
*Verrucous - good prognosis, rare. | *[[Basaloid squamous cell carcinoma]] - poor prognosis, usu. diagnosed by recognition of typical SCC. | ||
*Papillary. | *Carcinoma cuniculatum. | ||
*Lymphoepithelial | *Verrucous carcinoma - good prognosis, rare. | ||
*Spindle cell | *Papillary squamous cell carcinoma. | ||
*Lymphoepithelial carcinoma - rare. | |||
*Spindle cell squamous carcinoma - a common spindle cell lesion of the H&N. | |||
==Carcinoma cuniculatum== | |||
===General=== | |||
*Rare. | |||
*Good prognosis.<ref name=pmid19625845>{{Cite journal | last1 = Kruse | first1 = AL. | last2 = Graetz | first2 = KW. | title = Carcinoma cuniculatum: a rare entity in the oral cavity. | journal = J Craniofac Surg | volume = 20 | issue = 4 | pages = 1270-2 | month = Jul | year = 2009 | doi = 10.1097/SCS.0b013e3181ace06b | PMID = 19625845 }}</ref> | |||
===Gross=== | |||
*Usually lower extremities. | |||
**Classically plantar aspect of foot.<ref name=pmid19625845/> | |||
===Microscopic=== | |||
Features: | |||
*Nests squamous epithelium with minimal atypia in the dermis - '''key feature'''. | |||
*Hyperkeratosis. | |||
*Parakeratosis. | |||
*Acanthosis. | |||
<!-- | |||
Image: | |||
*[http://www.cmaj.ca/content/177/3/249.2/F2.expansion.html Carcinoma cuniculatum (cmaj.ca)]. --> | |||
==Verrucous squamous cell carcinoma== | ==Verrucous squamous cell carcinoma== | ||
*[[AKA]] ''verrucous carcinoma''. | *[[AKA]] ''verrucous carcinoma''. | ||
{{Main|Verrucous carcinoma}} | |||
==Spindle cell squamous carcinoma== | |||
*[[AKA]] ''sarcomatoid squamous cell carcinoma''.<ref name=pmid18787630 >{{Cite journal | last1 = Hall | first1 = JM. | last2 = Saenger | first2 = JS. | last3 = Fadare | first3 = O. | title = Diagnostic utility of P63 and CD10 in distinguishing cutaneous spindle cell/sarcomatoid squamous cell carcinomas and atypical fibroxanthomas. | journal = Int J Clin Exp Pathol | volume = 1 | issue = 6 | pages = 524-30 | month = Mar | year = 2008 | doi = | PMID = 18787630 }}</ref> | |||
===General=== | ===General=== | ||
* | *Common spindle cell lesion of the head and neck. | ||
===Microscopic=== | ===Microscopic=== | ||
Feature: | |||
* | *Histomorphologic key to the diagnosis: finding a component of conventional squamous cell carcinoma. | ||
*Malignant spindle cell neoplasm. | |||
* | |||
DDx: | DDx: | ||
* | *Spindle cell [[melanoma]]. | ||
*Mesenchymal neoplasms - ''see [[spindle cell lesions]]''. | |||
== | ====Images==== | ||
<gallery> | |||
Image:SkinTumors-P5300131.JPG | Spindle cell squamous carcinoma. (WC) | |||
</gallery> | |||
IHC | ===IHC=== | ||
*Typically keratin -ve. | *Typically keratin -ve. | ||
*p63 +ve. | *p63 +ve. | ||
**Soft tissue tumour uncommonly positive.<ref name=pmid22031315>{{Cite journal | last1 = Jo | first1 = VY. | last2 = Fletcher | first2 = CD. | title = p63 immunohistochemical staining is limited in soft tissue tumors. | journal = Am J Clin Pathol | volume = 136 | issue = 5 | pages = 762-6 | month = Nov | year = 2011 | doi = 10.1309/AJCPXNUC7JZSKWEU | PMID = 22031315 }}</ref> | |||
==Basaloid squamous cell carcinoma== | |||
:''Should '''not''' be confused with [[basosquamous carcinoma]].'' | |||
== | ===General=== | ||
*May mimic ''[[adenoid cystic carcinoma]]''. | *May mimic ''[[adenoid cystic carcinoma]]''. | ||
*Classically base of tongue.<ref>URL: [http://www.biomedcentral.com/1471-2407/6/146 http://www.biomedcentral.com/1471-2407/6/146]. Accessed on: March 9, 2010.</ref> | *Classically base of [[tongue]].<ref>URL: [http://www.biomedcentral.com/1471-2407/6/146 http://www.biomedcentral.com/1471-2407/6/146]. Accessed on: March 9, 2010.</ref> | ||
*Typically poor prognosis. | *Typically poor prognosis. | ||
===Microscopic=== | |||
Features: | Features: | ||
* | *"Basaloid" cells - "blue" at low power. | ||
**Nests. | |||
***Basal pallisading. | |||
*+/-Keratinization - useful. | |||
*+/-Squamous dysplasia in overlying skin. | |||
*Conventional squamous cell carcinoma. | |||
DDx: | DDx: | ||
*Neuroendocrine tumour. | *[[Basal cell carcinoma]]. | ||
*[[Basosquamous carcinoma]]. | |||
*[[Neuroendocrine tumour]]. | |||
==Clear cell squamous cell carcinoma== | |||
===General=== | |||
*Very rare.<ref name=pmid23798842>{{Cite journal | last1 = Lawal | first1 = AO. | last2 = Adisa | first2 = AO. | last3 = Olajide | first3 = MA. | last4 = Olusanya | first4 = AA. | title = Clear cell variant of squamous cell carcinoma of skin: A report of a case. | journal = J Oral Maxillofac Pathol | volume = 17 | issue = 1 | pages = 110-2 | month = Jan | year = 2013 | doi = 10.4103/0973-029X.110697 | PMID = 23798842 }}</ref> | |||
===Microscopic=== | |||
Features: | |||
*Clear cytoplasm. | |||
====Images==== | |||
<gallery> | |||
Image: SkinTumors-P5290109.JPG | Clear cell SCC. (WC) | |||
</gallery> | |||
==Lymphoepithelial (squamous cell) carcinoma== | ==Lymphoepithelial (squamous cell) carcinoma== | ||
| Line 123: | Line 203: | ||
Images: see the ''[[LELC]]'' article. | Images: see the ''[[LELC]]'' article. | ||
=IHC= | |||
Features:<ref name=pmid20823766>{{Cite journal | last1 = Pereira | first1 = TC. | last2 = Share | first2 = SM. | last3 = Magalhães | first3 = AV. | last4 = Silverman | first4 = JF. | title = Can we tell the site of origin of metastatic squamous cell carcinoma? An immunohistochemical tissue microarray study of 194 cases. | journal = Appl Immunohistochem Mol Morphol | volume = 19 | issue = 1 | pages = 10-4 | month = Jan | year = 2011 | doi = 10.1097/PAI.0b013e3181ecaf1c | PMID = 20823766 }}</ref> | |||
*[[CK5/6]] +ve. | |||
*[[p63]] +ve. | |||
*K903 +ve. | |||
*[[p16]] +ve/-ve -- dependent on site, +ve favours non-lung SCC.<ref name=pmid20823766/> | |||
*[[p40]] +ve. | |||
Note: | |||
*Immunostains not particularly helpful for establishing primary site of squamous cell carcinoma. p16 may be helpful but is not definitive for non-lung SCC.<ref name=pmid20823766/> | |||
=See also= | =See also= | ||
*[[Adenocarcinoma]]. | |||
*[[Pseudoepitheliomatous hyperplasia]] - can mimic squamous cell carcinoma. | |||
*[[Basics]]. | *[[Basics]]. | ||
Latest revision as of 14:25, 19 March 2024

Squamous cell carcinoma. H&E stain. (WC)
This article deal with squamous cell carcinoma, also squamous carcinoma, a very common epithelial derived malignant neoplasm that can arise from many sites. It is commonly abbreviated SCC.
Sites
Skin
Main article: Squamous cell carcinoma of the skin
- A common skin tumour.
Head and neck
Main article: Squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck
- Most common tumour of the head & neck.
- Tongue squamous cell carcinoma is dealt with separately.
- Nasopharyngeal carcinoma can be considered a variant SCC.
- HPV-associated SCC is dealt with in HPV-associated head and neck squamous cell carcinoma.
Tumour extent
- There is no agreed upon measure of tumour extent (tumour thickness/depth of invasion)[1] - proposed measures:[2]
- "Tumour thickness" = perpendicular distance from mucosal surface to deepest point of invasion.
- "Tumour depth" = perpendicular distance from epithelial basement membrane to deepest point of invasion.
Uterine cervix
Main article: Squamous cell carcinoma of the uterine cervix
- Most common form of cervical cancer.
Vulva
- Most common form of vulvar cancer.
Tumour extent
- No kerinization present: mucosal surface to the deepest point of invasion.
- Kerinization present: bottom of granular layer to the deepest point of invasion.
Lung
Main article: Squamous cell carcinoma of the lung
- A common form of lung cancer that is associated with smoking.
Esophagus
Main article: Squamous cell carcinoma of the esophagus
- Upper and middle esophagus.
Anus
Main article: Anal squamous cell carcinoma
- Most common form of anal cancer.
Other sites
Microscopic
Classification
SCC is subdivided by the WHO into:[5]
- Keratinizing type (KT).
- Worst prognosis.
- More common than non-keratinizing type.[6]
- Undifferentiated type (UT).
- Intermediate prognosis.
- EBV association.
- Non-keratinizing type (NT).
- Good prognosis.
- EBV association.
Features based on classification:[5]
- KT subtype:
- Keratinization & intercellular bridges through-out most of the malignant lesion.
- UT:
- Non-distinct borders/syncytial pattern.
- Nucleoli.
- NT:
- Well-defined cell borders.
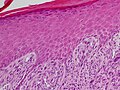
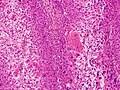
Invasive squamous cell carcinoma
Features:
- Eosinophilia.
- Extra large nuclei/bizarre nuclei.
- Inflammation (lymphocytes, plasma cells).
- Long rete ridges.
- Numerous beeds/blobs of epithelial cells that seem unlikely to be rete ridges.
Pitfalls:
- Tangential cuts.
- If you can trace the squamous cells from a gland to the surface it is less likely to be invasive cancer.
Notes on invasion:
- Nice review paper by Wenig.[7]
- See SCC of the cervix versus CIN III.
Image(s):
Subtypes
There are several subtypes:[8]
- Adenosquamous carcinoma.
- Ancatholytic squamous cell carcinoma.
- Basaloid squamous cell carcinoma - poor prognosis, usu. diagnosed by recognition of typical SCC.
- Carcinoma cuniculatum.
- Verrucous carcinoma - good prognosis, rare.
- Papillary squamous cell carcinoma.
- Lymphoepithelial carcinoma - rare.
- Spindle cell squamous carcinoma - a common spindle cell lesion of the H&N.
Carcinoma cuniculatum
General
- Rare.
- Good prognosis.[9]
Gross
- Usually lower extremities.
- Classically plantar aspect of foot.[9]
Microscopic
Features:
- Nests squamous epithelium with minimal atypia in the dermis - key feature.
- Hyperkeratosis.
- Parakeratosis.
- Acanthosis.
Verrucous squamous cell carcinoma
- AKA verrucous carcinoma.
Main article: Verrucous carcinoma
Spindle cell squamous carcinoma
General
- Common spindle cell lesion of the head and neck.
Microscopic
Feature:
- Histomorphologic key to the diagnosis: finding a component of conventional squamous cell carcinoma.
- Malignant spindle cell neoplasm.
DDx:
- Spindle cell melanoma.
- Mesenchymal neoplasms - see spindle cell lesions.
Images
IHC
- Typically keratin -ve.
- p63 +ve.
- Soft tissue tumour uncommonly positive.[11]
Basaloid squamous cell carcinoma
- Should not be confused with basosquamous carcinoma.
General
- May mimic adenoid cystic carcinoma.
- Classically base of tongue.[12]
- Typically poor prognosis.
Microscopic
Features:
- "Basaloid" cells - "blue" at low power.
- Nests.
- Basal pallisading.
- Nests.
- +/-Keratinization - useful.
- +/-Squamous dysplasia in overlying skin.
- Conventional squamous cell carcinoma.
DDx:
Clear cell squamous cell carcinoma
General
- Very rare.[13]
Microscopic
Features:
- Clear cytoplasm.
Images
Lymphoepithelial (squamous cell) carcinoma
- This is discussed in detail in the lymphoepithelioma-like carcinoma (LELC) article.
- In the head and neck this is a separate entity known as nasopharyngeal carcinoma.
General
Microscopic
Features:
- Malignant squamoid cells (eosinophilic cytoplasm, nuclear atypia).
- Abundant mononuclear inflammatory cells (plasma cells, lymphocytes).
Images: see the LELC article.
IHC
Features:[15]
- CK5/6 +ve.
- p63 +ve.
- K903 +ve.
- p16 +ve/-ve -- dependent on site, +ve favours non-lung SCC.[15]
- p40 +ve.
Note:
- Immunostains not particularly helpful for establishing primary site of squamous cell carcinoma. p16 may be helpful but is not definitive for non-lung SCC.[15]
See also
- Adenocarcinoma.
- Pseudoepitheliomatous hyperplasia - can mimic squamous cell carcinoma.
- Basics.
References
- ↑ Pentenero, M.; Gandolfo, S.; Carrozzo, M. (Dec 2005). "Importance of tumor thickness and depth of invasion in nodal involvement and prognosis of oral squamous cell carcinoma: a review of the literature.". Head Neck 27 (12): 1080-91. doi:10.1002/hed.20275. PMID 16240329.
- ↑ URL: http://www.cap.org/apps/docs/committees/cancer/cancer_protocols/2011/LipOralCav_11protocol.pdf. Accessed on: 3 April 2012.
- ↑ Yoder, BJ.; Rufforny, I.; Massoll, NA.; Wilkinson, EJ. (May 2008). "Stage IA vulvar squamous cell carcinoma: an analysis of tumor invasive characteristics and risk.". Am J Surg Pathol 32 (5): 765-72. doi:10.1097/PAS.0b013e318159a2cb. PMID 18379417.
- ↑ URL: http://www.cap.org/apps/docs/committees/cancer/cancer_protocols/2011/Vulva_11protocol.pdf. Accessed on: 3 April 2012.
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 Mills, Stacey E; Carter, Darryl; Greenson, Joel K; Oberman, Harold A; Reuter, Victor E (2004). Sternberg's Diagnostic Surgical Pathology (4th ed.). Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. pp. 975. ISBN 978-0781740517.
- ↑ URL: http://www.cap.org/apps/docs/committees/cancer/cancer_protocols/2011/LipOralCav_11protocol.pdf. Accessed on: 3 April 2012.
- ↑ Wenig BM (March 2002). "Squamous cell carcinoma of the upper aerodigestive tract: precursors and problematic variants". Mod. Pathol. 15 (3): 229–54. doi:10.1038/modpathol.3880520. PMID 11904340. http://www.nature.com/modpathol/journal/v15/n3/pdf/3880520a.pdf.
- ↑ URL: http://www.cap.org/apps/docs/committees/cancer/cancer_protocols/2011/LipOralCav_11protocol.pdf. Accessed on: 3 April 2012.
- ↑ 9.0 9.1 Kruse, AL.; Graetz, KW. (Jul 2009). "Carcinoma cuniculatum: a rare entity in the oral cavity.". J Craniofac Surg 20 (4): 1270-2. doi:10.1097/SCS.0b013e3181ace06b. PMID 19625845.
- ↑ Hall, JM.; Saenger, JS.; Fadare, O. (Mar 2008). "Diagnostic utility of P63 and CD10 in distinguishing cutaneous spindle cell/sarcomatoid squamous cell carcinomas and atypical fibroxanthomas.". Int J Clin Exp Pathol 1 (6): 524-30. PMID 18787630.
- ↑ Jo, VY.; Fletcher, CD. (Nov 2011). "p63 immunohistochemical staining is limited in soft tissue tumors.". Am J Clin Pathol 136 (5): 762-6. doi:10.1309/AJCPXNUC7JZSKWEU. PMID 22031315.
- ↑ URL: http://www.biomedcentral.com/1471-2407/6/146. Accessed on: March 9, 2010.
- ↑ Lawal, AO.; Adisa, AO.; Olajide, MA.; Olusanya, AA. (Jan 2013). "Clear cell variant of squamous cell carcinoma of skin: A report of a case.". J Oral Maxillofac Pathol 17 (1): 110-2. doi:10.4103/0973-029X.110697. PMID 23798842.
- ↑ Skinner, NE.; Horowitz, RI.; Majmudar, B. (Oct 2000). "Lymphoepithelioma-like carcinoma of the uterine cervix.". South Med J 93 (10): 1024-7. PMID 11147469.
- ↑ 15.0 15.1 15.2 Pereira, TC.; Share, SM.; Magalhães, AV.; Silverman, JF. (Jan 2011). "Can we tell the site of origin of metastatic squamous cell carcinoma? An immunohistochemical tissue microarray study of 194 cases.". Appl Immunohistochem Mol Morphol 19 (1): 10-4. doi:10.1097/PAI.0b013e3181ecaf1c. PMID 20823766.