Difference between revisions of "Paraganglioma"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
(tweak) |
|||
| (23 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{ Infobox diagnosis | |||
| Name = {{PAGENAME}} | |||
| Image = Paraganglioma_-_very_high_mag.jpg | |||
| Width = | |||
| Caption = Paraganglioma. [[H&E stain]]. | |||
| Synonyms = | |||
| Micro = Zellballen (nests of cells), fibrovascular septae, salt-and-pepper nuclei, +/-hemorrhage (very common) | |||
| Subtypes = | |||
| LMDDx = [[neuroendocrine tumour]], [[pheochromocytoma]] (paraganglioma of the [[adrenal gland]]), [[gangliocytic paraganglioma]] | |||
| Stains = | |||
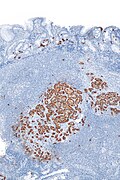
| IHC = chromogranin +ve, synaptophysin +ve, CD56 +ve | |||
| EM = | |||
| Molecular = | |||
| IF = | |||
| Gross = dusky colour | |||
| Grossing = | |||
| Site = abdomen (adrenal gland paraganglioma = pheochromocytoma), head and neck (carotid body tumour) | |||
| Assdx = | |||
| Syndromes = [[von Hippel Lindau]], hereditary paragangliomatosis, [[neurofibromatosis]] type 1 (von Recklinghausen disease), [[MEN 2A]], [[MEN 2B]], [[Carney-Stratakis syndrome]], [[Carney triad]] | |||
| Clinicalhx = | |||
| Signs = | |||
| Symptoms = | |||
| Prevalence = uncommon | |||
| Bloodwork = | |||
| Rads = | |||
| Endoscopy = | |||
| Prognosis = usually good, rarely malignant | |||
| Other = | |||
| ClinDDx = | |||
| Tx = | |||
}} | |||
'''Paraganglioma''' is a rare tumour arising from the paraganglion. A paraganglioma arising in the [[adrenal gland]] is known as a [[pheochromocytoma]]. | '''Paraganglioma''' is a rare tumour arising from the paraganglion. A paraganglioma arising in the [[adrenal gland]] is known as a [[pheochromocytoma]]. | ||
| Line 4: | Line 35: | ||
*Definition: tumour of paraganglion. | *Definition: tumour of paraganglion. | ||
**Can be sympathetic or parasympathetic. | **Can be sympathetic or parasympathetic. | ||
**Locations of paraganglia | |||
***Paravertebral (retroperitoneal) | |||
***Near the large blood vessels of the head and neck and base of skull | |||
***Scattered in other tissues | |||
*Most common paraganglioma = [[pheochromocytoma]].<ref name=Ref_EP_327>{{Ref EP|327}}</ref> | *Most common paraganglioma = [[pheochromocytoma]].<ref name=Ref_EP_327>{{Ref EP|327}}</ref> | ||
**Head & neck most common | **Sites relate to locations of paraganglia | ||
* | ****Head & neck most common - neck, ear, carotid body, base of skull | ||
****Retroperitoneal/abdomen | |||
****Bladder | |||
Special site names | |||
*Carotid body tumour = paraganglioma of carotid body - very vascular - right near a major artery. Don't stick a needle in it. | |||
*Glomus tympanicum tumor = paraganglioma of the middle ear - pulsitile tintinitis and conductive hearing loss. | |||
* | *Pheochromocytoma - basically a 'paraganglioma' in the adrenal medulla | ||
* | |||
* | |||
==Clinical== | ===Epidemiology=== | ||
*Rare. | |||
*Rarely malignant. | |||
Familial syndromes associated with paragangliomas:<ref name=Ref_EP328>{{Ref EP|328}}</ref> | |||
*[[von Hippel Lindau]]. | |||
*Hereditary paragangliomatosis. | |||
*[[Neurofibromatosis]] type 1 (von Recklinghausen disease). | |||
*[[MEN 2A]]. | |||
*[[MEN 2B]]. | |||
*[[Carney-Stratakis syndrome]] - [[GIST]]s and paraganglioma.<ref>{{Cite journal | last1 = Blay | first1 = JY. | last2 = Blomqvist | first2 = C. | last3 = Bonvalot | first3 = S. | last4 = Boukovinas | first4 = I. | last5 = Casali | first5 = PG. | last6 = De Alava | first6 = E. | last7 = Dei Tos | first7 = AP. | last8 = Dirksen | first8 = U. | last9 = Duffaud | first9 = F. | title = Gastrointestinal stromal tumors: ESMO Clinical Practice Guidelines for diagnosis, treatment and follow-up. | journal = Ann Oncol | volume = 23 Suppl 7 | issue = | pages = vii49-55 | month = Oct | year = 2012 | doi = 10.1093/annonc/mds252 | PMID = 22997454 | url = http://annonc.oxfordjournals.org/content/23/suppl_7/vii49.full }}</ref> | |||
*[[Succinate dehydrogenase|SDH]] mutation associated (SDHB, SDHC and SDHD).<ref name=pmid24523625>{{Cite journal | last1 = Lefebvre | first1 = M. | last2 = Foulkes | first2 = WD. | title = Pheochromocytoma and paraganglioma syndromes: genetics and management update. | journal = Curr Oncol | volume = 21 | issue = 1 | pages = e8-e17 | month = Feb | year = 2014 | doi = 10.3747/co.21.1579 | PMID = 24523625 }}</ref> | |||
Other associations - not proven to be genetic: | |||
*[[Carney triad]]. | |||
===Clinical=== | |||
*10% bilateral, multiple, familial, pediatric and malignant.<ref name=Ref_EP327>{{Ref EP|327}}</ref> | *10% bilateral, multiple, familial, pediatric and malignant.<ref name=Ref_EP327>{{Ref EP|327}}</ref> | ||
**''Not'' quite true... more than 10% are familial - see ''[[pheochromocytoma]]'' article. | |||
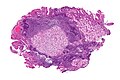
==Gross== | |||
*Dusky colour. | |||
Note: | |||
*''Pheo'' (in [[pheochromocytoma]]) is ''dusky''; ''chromo'' is ''colour''. | |||
Image: | |||
*[http://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Mediastinal_paraganglioma.jpg Mediastinal paraganglioma (WC/AFIP)]. | |||
==Microscopic== | ==Microscopic== | ||
Features:<ref>{{Ref EP|329-332}}</ref> | Features:<ref>{{Ref EP|329-332}}</ref> | ||
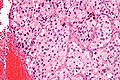
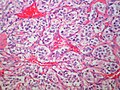
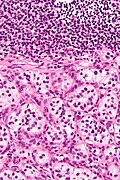
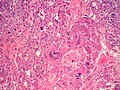
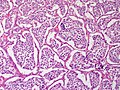
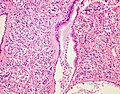
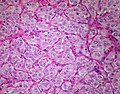
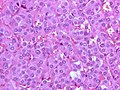
* | *Zellballen - nests of cells - '''key low power feature'''. | ||
**Zellballen | **Zellballen is "cell balls" in German. | ||
*Fibrovascular septae and sustentacular cells (structural support cell). | |||
*Finely granular cytoplasm (salt-and-pepper nuclei). | |||
*+/-Hemorrhage - very common. | |||
DDx: | |||
*[ | *[[Neuroendocrine tumour]] - nests surrounded by stroma/do not touch. | ||
*[[Pheochromocytoma]] - paraganglioma of the [[adrenal gland]]. | |||
*[[Gangliocytic paraganglioma]] - has schwannian component and ganglion cells, usu. [[duodenum]]. | |||
===Images=== | |||
Carotid body tumour: | |||
<gallery> | |||
Image:Carotid_body_tumour_2_intermed_mag.jpg | Paraganglioma - intermed. mag. (WC) | |||
Image:Carotid_body_tumour_2_high_mag.jpg | Paraganglioma - high mag. (WC) | |||
Image:Neck Paraganglioma HP CTR (2).jpg|Neck - Paraganglioma - nice Zeballen (SKB) | |||
Image:Neck Paraganglioma CarotidBody MP PA.JPG|Neck Paraganglioma - Carotid Body Tumor (SKB) | |||
Image:Neck Paraganglioma CarotidBody HP PA.JPG|Neck - Paraganglioma - Carotid Body Tumor (SKB) | |||
</gallery> | |||
Duodenal paraganglioma - uncommon location: | |||
<gallery> | |||
Image:Paraganglioma_-_low_mag.jpg | Paraganglioma - low mag. (WC) | |||
Image:Paraganglioma_-_very_high_mag.jpg | Paraganglioma - very high mag. (WC) | |||
Image:Paraganglioma_-_chromo_-_intermed_mag.jpg | Paraganglioma - chromogranin A - intermed. mag. (WC) | |||
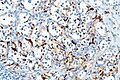
Image:Paraganglioma_-_s100_-_very_high_mag.jpg | Paraganglioma - S100 - very high mag. (WC) | |||
</gallery> | |||
Retroperitoneal paraganglioma | |||
<gallery> | |||
Image:Retroperitoneum Paraganglioma 2 MP PA.JPG|Retroperitoneum - Paraganglioma - Prominent vascular component (SKB) | |||
Image:Retroperitoneum Paraganglioma 2 HP PA.JPG|Retroperitoneum - Paraganglioma (SKB) | |||
Image:Retroperitoneum Paraganglioma HP PA.JPG|Retroperitoneum - Paraganglioma - florid atypia (SKB) | |||
Image:Retroperitoneum Paraganglioma MP CTR.jpg|Retroperitoneum - Paraganglioma - large nests (SKB) | |||
</gallery> | |||
Ear paraganglioma "Glomus Tympanicum" | |||
<gallery> | |||
Image:Ear Paraganglioma GlomusTympanicumTumor MP PA.JPG|Ear - Paraganglioma - Glomus Tympanicum Tumor (SKB) | |||
Image:Ear Paraganglioma GlomusTympanicumTumor HP 2 PA.JPG|Ear - Paraganglioma - Glomus Tympanicum Tumor (SKB) | |||
</gallery> | |||
Bladder | |||
<gallery> | |||
Image:Bladder Paraganglioma PA DSCN4717.JPG|Bladder - Paraganglioma - Presented as micturation syncope (SKB) | |||
</gallery> | |||
Other: | |||
<gallery> | |||
Image:Pheochromocytoma_high_mag.jpg | Pheochromocytoma - high mag. (WC) | |||
</gallery> | |||
www: | |||
*[http://path.upmc.edu/cases/case523.html Paraganglioma with gangliocytic differentiation - several images (upmc.edu)]. | |||
==IHC== | ==IHC== | ||
| Line 37: | Line 135: | ||
*Chromogranin +ve. | *Chromogranin +ve. | ||
*Synaptophysin +ve. | *Synaptophysin +ve. | ||
*S100 +/- | *S100 +ve/-ve (+ve in sustentacular cells, not tumor cells) | ||
*Cytokeratin -ve. | *Cytokeratin -ve. | ||
*EMA -ve. | *[[EMA]] -ve. | ||
**+ve in RCC. | **+ve in [[renal cell carcinoma|RCC]]. | ||
==EM== | |||
Features:<ref name=em_stuff>URL: [http://path.upmc.edu/cases/case408.html http://path.upmc.edu/cases/case408.html]. Accessed on: 16 January 2012.</ref> | |||
*Neurosecretory granules. | |||
**Electron dense core. | |||
**Typically perinuclear location. | |||
Image: | |||
*[http://path.upmc.edu/cases/case408/images/fig14.jpg Neurosecretory granules (upmc.edu)].<ref name=em_stuff>URL: [http://path.upmc.edu/cases/case408.html http://path.upmc.edu/cases/case408.html]. Accessed on: 16 January 2012.</ref> | |||
==Sign out== | |||
<pre> | |||
SOFT TISSUE, LEFT/RIGHT CAROTID BODY, EXCISION: | |||
- PARAGANGLIOMA (SIZE IN CM). | |||
- NEGATIVE RESECTION MARGIN. | |||
</pre> | |||
==See also== | ==See also== | ||
Latest revision as of 18:25, 29 March 2017
| Paraganglioma | |
|---|---|
| Diagnosis in short | |
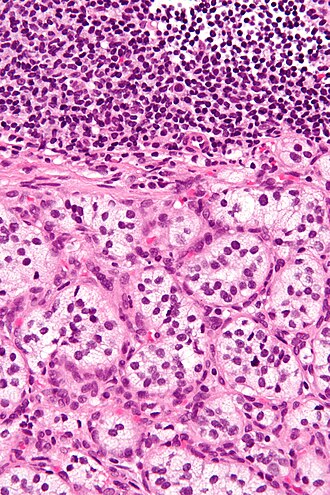 Paraganglioma. H&E stain. | |
|
| |
| LM | Zellballen (nests of cells), fibrovascular septae, salt-and-pepper nuclei, +/-hemorrhage (very common) |
| LM DDx | neuroendocrine tumour, pheochromocytoma (paraganglioma of the adrenal gland), gangliocytic paraganglioma |
| IHC | chromogranin +ve, synaptophysin +ve, CD56 +ve |
| Gross | dusky colour |
| Site | abdomen (adrenal gland paraganglioma = pheochromocytoma), head and neck (carotid body tumour) |
|
| |
| Syndromes | von Hippel Lindau, hereditary paragangliomatosis, neurofibromatosis type 1 (von Recklinghausen disease), MEN 2A, MEN 2B, Carney-Stratakis syndrome, Carney triad |
|
| |
| Prevalence | uncommon |
| Prognosis | usually good, rarely malignant |
Paraganglioma is a rare tumour arising from the paraganglion. A paraganglioma arising in the adrenal gland is known as a pheochromocytoma.
General
- Definition: tumour of paraganglion.
- Can be sympathetic or parasympathetic.
- Locations of paraganglia
- Paravertebral (retroperitoneal)
- Near the large blood vessels of the head and neck and base of skull
- Scattered in other tissues
- Most common paraganglioma = pheochromocytoma.[1]
- Sites relate to locations of paraganglia
- Head & neck most common - neck, ear, carotid body, base of skull
- Retroperitoneal/abdomen
- Bladder
- Sites relate to locations of paraganglia
Special site names
- Carotid body tumour = paraganglioma of carotid body - very vascular - right near a major artery. Don't stick a needle in it.
- Glomus tympanicum tumor = paraganglioma of the middle ear - pulsitile tintinitis and conductive hearing loss.
- Pheochromocytoma - basically a 'paraganglioma' in the adrenal medulla
Epidemiology
- Rare.
- Rarely malignant.
Familial syndromes associated with paragangliomas:[2]
- von Hippel Lindau.
- Hereditary paragangliomatosis.
- Neurofibromatosis type 1 (von Recklinghausen disease).
- MEN 2A.
- MEN 2B.
- Carney-Stratakis syndrome - GISTs and paraganglioma.[3]
- SDH mutation associated (SDHB, SDHC and SDHD).[4]
Other associations - not proven to be genetic:
Clinical
- 10% bilateral, multiple, familial, pediatric and malignant.[5]
- Not quite true... more than 10% are familial - see pheochromocytoma article.
Gross
- Dusky colour.
Note:
- Pheo (in pheochromocytoma) is dusky; chromo is colour.
Image:
Microscopic
Features:[6]
- Zellballen - nests of cells - key low power feature.
- Zellballen is "cell balls" in German.
- Fibrovascular septae and sustentacular cells (structural support cell).
- Finely granular cytoplasm (salt-and-pepper nuclei).
- +/-Hemorrhage - very common.
DDx:
- Neuroendocrine tumour - nests surrounded by stroma/do not touch.
- Pheochromocytoma - paraganglioma of the adrenal gland.
- Gangliocytic paraganglioma - has schwannian component and ganglion cells, usu. duodenum.
Images
Carotid body tumour:
Duodenal paraganglioma - uncommon location:
Retroperitoneal paraganglioma
Ear paraganglioma "Glomus Tympanicum"
Bladder
Other:
www:
IHC
Features:[7]
- Chromogranin +ve.
- Synaptophysin +ve.
- S100 +ve/-ve (+ve in sustentacular cells, not tumor cells)
- Cytokeratin -ve.
- EMA -ve.
- +ve in RCC.
EM
Features:[8]
- Neurosecretory granules.
- Electron dense core.
- Typically perinuclear location.
Image:
Sign out
SOFT TISSUE, LEFT/RIGHT CAROTID BODY, EXCISION: - PARAGANGLIOMA (SIZE IN CM). - NEGATIVE RESECTION MARGIN.
See also
References
- ↑ Thompson, Lester D. R. (2006). Endocrine Pathology: A Volume in Foundations in Diagnostic Pathology Series (1st ed.). Churchill Livingstone. pp. 327. ISBN 978-0443066856.
- ↑ Thompson, Lester D. R. (2006). Endocrine Pathology: A Volume in Foundations in Diagnostic Pathology Series (1st ed.). Churchill Livingstone. pp. 328. ISBN 978-0443066856.
- ↑ Blay, JY.; Blomqvist, C.; Bonvalot, S.; Boukovinas, I.; Casali, PG.; De Alava, E.; Dei Tos, AP.; Dirksen, U. et al. (Oct 2012). "Gastrointestinal stromal tumors: ESMO Clinical Practice Guidelines for diagnosis, treatment and follow-up.". Ann Oncol 23 Suppl 7: vii49-55. doi:10.1093/annonc/mds252. PMID 22997454. http://annonc.oxfordjournals.org/content/23/suppl_7/vii49.full.
- ↑ Lefebvre, M.; Foulkes, WD. (Feb 2014). "Pheochromocytoma and paraganglioma syndromes: genetics and management update.". Curr Oncol 21 (1): e8-e17. doi:10.3747/co.21.1579. PMID 24523625.
- ↑ Thompson, Lester D. R. (2006). Endocrine Pathology: A Volume in Foundations in Diagnostic Pathology Series (1st ed.). Churchill Livingstone. pp. 327. ISBN 978-0443066856.
- ↑ Thompson, Lester D. R. (2006). Endocrine Pathology: A Volume in Foundations in Diagnostic Pathology Series (1st ed.). Churchill Livingstone. pp. 329-332. ISBN 978-0443066856.
- ↑ Thompson, Lester D. R. (2006). Endocrine Pathology: A Volume in Foundations in Diagnostic Pathology Series (1st ed.). Churchill Livingstone. pp. 335. ISBN 978-0443066856.
- ↑ 8.0 8.1 URL: http://path.upmc.edu/cases/case408.html. Accessed on: 16 January 2012.