Difference between revisions of "Ductal carcinoma in situ"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
(+cat.) |
|||
| (2 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
# | '''Ductal carcinoma in situ''', abbreviated '''DCIS''', in a common type of [[non-invasive breast carcinoma]]. | ||
==General== | |||
*Diagnosis based on nuclear abnormalities ''and/or'' architecture. | |||
**Low-grade DCIS does '''not''' have a malignant cytology. | |||
*It is typically picked-up during radiologic screening. | |||
==Microscopic== | |||
Features: | |||
*Architectural changes: | |||
**Equal spacing of cells - "cookie cutter" look. | |||
**Cells line-up along lumen/glandular spaces - form "Roman briges". | |||
**Architecture suggestive of DCIS - see ''[[Subtypes of DCIS]]''. | |||
*Nuclear changes: | |||
**Nuclear enlargement - at least 2-3x size of [[RBC]] - '''key feature'''. | |||
***Compared to RBCs to grade DCIS - see ''[[Grading DCIS]]''. | |||
****Compare sizes of nuclei if you cannot find RBCs. | |||
**Nuclear pleomorphism - important feature. | |||
*+/-Mitoses. | |||
Note: | |||
*Apocrine changes of cytoplasm -- several sets of criteria exist -- any of the following: | |||
*#Nuclei should be ~4x RBC for low grade, 5x RBC for high grade.<ref>URL: [http://surgpathcriteria.stanford.edu/breast/dcis/apocrinedcis.html http://surgpathcriteria.stanford.edu/breast/dcis/apocrinedcis.html]. Accessed on: 4 August 2011.</ref> | |||
*#Nuclear enlargement of 3x +/- nucleolar enlargement.<ref name=pmid18171412/> | |||
*#Multiple nucleoli + nuclear size variation.<ref name=pmid18171412>{{Cite journal | last1 = O'Malley | first1 = FP. | last2 = Bane | first2 = A. | title = An update on apocrine lesions of the breast. | journal = Histopathology | volume = 52 | issue = 1 | pages = 3-10 | month = Jan | year = 2008 | doi = 10.1111/j.1365-2559.2007.02888.x | PMID = 18171412 }}</ref> | |||
===Subtypes of DCIS=== | |||
The subtypes are based on architecture. | |||
Note: | |||
*''Comedonecrosis'' used to be considered a separate subtype. [[Necrosis]] is seen most often in the context of ''solid ductal carcinoma in situ''. | |||
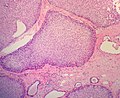
====Solid ductal carcinoma in situ==== | |||
Features: | |||
*Sheet of cells fills the duct | |||
*No spaces between cells. | |||
<gallery> | |||
Image:Breast DCIS Solid IntermediateGrade SNP.jpg|Breast - Ductal carcinoma in situ - Solid variant- Intermediate grade - Medium power (SKB) | |||
Image:Breast DCIS Solid SNP.jpg|Breast - Ductal carcinoma in situ - Solid variant- Intermediate grade - Low power (SKB) | |||
Image:Breast DCIS Solid PA.JPG|Breast - Ductal carcinoma in situ - Solid variant - Medium power (SKB) | |||
Image:Breast DCIS Comedonecrotic 2 PA.JPG|Breast - Ductal carcinoma in situ - Solid variant - Comedonecrosis (SKB) | |||
Image:Breast DCIS Comedonecrosis MP PA.JPG|Breast - Ductal carcinoma in situ - Solid variant - Comedonecrosis (SKB) | |||
</gallery> | |||
DDx: | |||
*[[LCIS]]. | |||
**May show dyscohesion | |||
**More monomorphic population of cells | |||
====Cribriform ductal carcinoma in situ==== | |||
Features: | |||
*Honeycomb-like appearance: circular holes. | |||
*"Cookie cutter" appearance/"punched-out" appearance/"Roman bridges" -- cells surround the circular holes. | |||
<gallery> | |||
Image:Breast DCIS Cribriform MP CTR.jpg|Breast - Ductal carcinoma in situ - cribriform varient - medium power (SKB) | |||
Image:Breast DCIS Cribriform PA.JPG|Breast - Ductal carcinoma in situ - cribriform varient - medium power (SKB) | |||
</gallery> | |||
DDx: | |||
*[[Collagenous spherulosis]]. | |||
*[[Adenoid cystic carcinoma of the breast]]. | |||
*Invasive cribriform carcinoma of the breast | |||
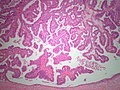
====Papillary ductal carcinoma in situ==== | |||
Features: | |||
*Papillae with fibrovascular cores. | |||
*Papillae lack a myoepithelial layer | |||
*Papillae are lined by atypical cells. | |||
*Papillae within a ductal space lined by myoepithelial cells. | |||
<gallery> | |||
Image:Breast DCIS PapillaryVariant LP PA.JPG|Breast - Ductal carcinoma in situ - Papillary variant - low power (SKB) | |||
Image:Breast DCIS Papillary PA.JPG|Breast - Ductal carcinoma in situ - Papillary variant - Medium power (SKB) | |||
</gallery> | |||
DDX: | |||
*[[Intraductal papilloma]] | |||
*Ductal carcinoma in situ arising within an intraductal papilloma | |||
*[[Intracystic papillary breast carcinoma]] | |||
*[[Invasive papillary breast carcinoma]] | |||
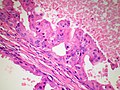
====Micropapillary ductal carcinoma in situ==== | |||
Features: | |||
*Small papillae without fibrovascular cores. | |||
*Have "drum stick" shape. | |||
DDx: | |||
*[[Gynecomastoid hyperplasia]]. | |||
<gallery> | |||
Image:Breast DCIS MicropapillaryType MP CTR.jpg|Breast - Ductal carcinoma in situ - micropapillary variant - Medium power - (SKB) | |||
Image:Breast DCIS Micropapillary SNP.jpg|Breast - Ductal carcinoma in situ - micropapillary variant - High power - (SKB) | |||
Image:Breast DCIS Apocrine PA.JPG|Breast - Ductal carcinoma in situ - Micropapillary type with apocrine features - High power - (SKB) | |||
</gallery> | |||
===Grading DCIS=== | |||
Graded 1-3 (low-high)<ref>URL: [http://surgpathcriteria.stanford.edu/breast/dcis/ http://surgpathcriteria.stanford.edu/breast/dcis/]. Accessed on: 4 August 2011.</ref> - compare lesional nuclei to one another. | |||
*Grade 1: | |||
**Nuclei 2-3x size of [[RBC]]. | |||
**No necrosis. | |||
*Grade 2: | |||
**Nuclei 2-3x size of RBC. | |||
**+/-[[Necrosis]]. | |||
*Grade 3: | |||
**Nuclei >3x size of RBC. | |||
**Necrosis usually present. | |||
Notes: | |||
*It is often hard to find RBCs when you want 'em. DCIS is pleomorphic. | |||
*If no RBCs are present to compare with compare the nuclei to one another. | |||
*If you see nuclei >3x larger than their neigbour you're ready to call DCIS Grade 3. | |||
===Size criteria for low-grade DCIS=== | |||
ADH is diagnosed if the lesion is small - specifically:<ref name=Ref_BP168>{{Ref BP|168}}</ref><ref>{{Ref DCHH|258}}</ref> | |||
# < Two membrane-bound spaces. | |||
# < 2 mm extent. ‡ | |||
The treatment is similar; ADH and DCIS are both excised. | |||
The differences are: | |||
*DCIS is cancer, i.e. this has life insurance implications. | |||
*Radiation treatment - DCIS is irradiated; ADH does ''not'' get radiation. | |||
Notes: | |||
* ‡ 3 mm is used in papillary lesions.{{fact}} | |||
===Micrometastasis in DCIS=== | |||
Micrometastasis in DCIS - not significant.<ref name=pmid14601079>{{Cite journal | last1 = Lara | first1 = JF. | last2 = Young | first2 = SM. | last3 = Velilla | first3 = RE. | last4 = Santoro | first4 = EJ. | last5 = Templeton | first5 = SF. | title = The relevance of occult axillary micrometastasis in ductal carcinoma in situ: a clinicopathologic study with long-term follow-up. | journal = Cancer | volume = 98 | issue = 10 | pages = 2105-13 | month = Nov | year = 2003 | doi = 10.1002/cncr.11761 | PMID = 14601079 }}</ref><ref name=pmid16569492>{{Cite journal | last1 = Broekhuizen | first1 = LN. | last2 = Wijsman | first2 = JH. | last3 = Peterse | first3 = JL. | last4 = Rutgers | first4 = EJ. | title = The incidence and significance of micrometastases in lymph nodes of patients with ductal carcinoma in situ and T1a carcinoma of the breast. | journal = Eur J Surg Oncol | volume = 32 | issue = 5 | pages = 502-6 | month = Jun | year = 2006 | doi = 10.1016/j.ejso.2006.02.006 | PMID = 16569492 }}</ref> | |||
==See also== | |||
*[[Non-invasive breast carcinoma]]. | |||
*[[Breast carcinoma with an extensive intraductal component]]. | |||
==References== | |||
{{Reflist|1}} | |||
[[Category:Diagnosis]] | [[Category:Diagnosis]] | ||
[[Category:Breast pathology]] | |||
Latest revision as of 21:40, 12 May 2016
Ductal carcinoma in situ, abbreviated DCIS, in a common type of non-invasive breast carcinoma.
General
- Diagnosis based on nuclear abnormalities and/or architecture.
- Low-grade DCIS does not have a malignant cytology.
- It is typically picked-up during radiologic screening.
Microscopic
Features:
- Architectural changes:
- Equal spacing of cells - "cookie cutter" look.
- Cells line-up along lumen/glandular spaces - form "Roman briges".
- Architecture suggestive of DCIS - see Subtypes of DCIS.
- Nuclear changes:
- Nuclear enlargement - at least 2-3x size of RBC - key feature.
- Compared to RBCs to grade DCIS - see Grading DCIS.
- Compare sizes of nuclei if you cannot find RBCs.
- Compared to RBCs to grade DCIS - see Grading DCIS.
- Nuclear pleomorphism - important feature.
- Nuclear enlargement - at least 2-3x size of RBC - key feature.
- +/-Mitoses.
Note:
- Apocrine changes of cytoplasm -- several sets of criteria exist -- any of the following:
Subtypes of DCIS
The subtypes are based on architecture.
Note:
- Comedonecrosis used to be considered a separate subtype. Necrosis is seen most often in the context of solid ductal carcinoma in situ.
Solid ductal carcinoma in situ
Features:
- Sheet of cells fills the duct
- No spaces between cells.
DDx:
- LCIS.
- May show dyscohesion
- More monomorphic population of cells
Cribriform ductal carcinoma in situ
Features:
- Honeycomb-like appearance: circular holes.
- "Cookie cutter" appearance/"punched-out" appearance/"Roman bridges" -- cells surround the circular holes.
DDx:
- Collagenous spherulosis.
- Adenoid cystic carcinoma of the breast.
- Invasive cribriform carcinoma of the breast
Papillary ductal carcinoma in situ
Features:
- Papillae with fibrovascular cores.
- Papillae lack a myoepithelial layer
- Papillae are lined by atypical cells.
- Papillae within a ductal space lined by myoepithelial cells.
DDX:
- Intraductal papilloma
- Ductal carcinoma in situ arising within an intraductal papilloma
- Intracystic papillary breast carcinoma
- Invasive papillary breast carcinoma
Micropapillary ductal carcinoma in situ
Features:
- Small papillae without fibrovascular cores.
- Have "drum stick" shape.
DDx:
Grading DCIS
Graded 1-3 (low-high)[3] - compare lesional nuclei to one another.
- Grade 1:
- Nuclei 2-3x size of RBC.
- No necrosis.
- Grade 2:
- Nuclei 2-3x size of RBC.
- +/-Necrosis.
- Grade 3:
- Nuclei >3x size of RBC.
- Necrosis usually present.
Notes:
- It is often hard to find RBCs when you want 'em. DCIS is pleomorphic.
- If no RBCs are present to compare with compare the nuclei to one another.
- If you see nuclei >3x larger than their neigbour you're ready to call DCIS Grade 3.
Size criteria for low-grade DCIS
ADH is diagnosed if the lesion is small - specifically:[4][5]
- < Two membrane-bound spaces.
- < 2 mm extent. ‡
The treatment is similar; ADH and DCIS are both excised.
The differences are:
- DCIS is cancer, i.e. this has life insurance implications.
- Radiation treatment - DCIS is irradiated; ADH does not get radiation.
Notes:
- ‡ 3 mm is used in papillary lesions.[citation needed]
Micrometastasis in DCIS
Micrometastasis in DCIS - not significant.[6][7]
See also
References
- ↑ URL: http://surgpathcriteria.stanford.edu/breast/dcis/apocrinedcis.html. Accessed on: 4 August 2011.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 O'Malley, FP.; Bane, A. (Jan 2008). "An update on apocrine lesions of the breast.". Histopathology 52 (1): 3-10. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2559.2007.02888.x. PMID 18171412.
- ↑ URL: http://surgpathcriteria.stanford.edu/breast/dcis/. Accessed on: 4 August 2011.
- ↑ O'Malley, Frances P.; Pinder, Sarah E. (2006). Breast Pathology: A Volume in Foundations in Diagnostic Pathology series (1st ed.). Churchill Livingstone. pp. 168. ISBN 978-0443066801.
- ↑ Tadrous, Paul.J. Diagnostic Criteria Handbook in Histopathology: A Surgical Pathology Vade Mecum (1st ed.). Wiley. pp. 258. ISBN 978-0470519035.
- ↑ Lara, JF.; Young, SM.; Velilla, RE.; Santoro, EJ.; Templeton, SF. (Nov 2003). "The relevance of occult axillary micrometastasis in ductal carcinoma in situ: a clinicopathologic study with long-term follow-up.". Cancer 98 (10): 2105-13. doi:10.1002/cncr.11761. PMID 14601079.
- ↑ Broekhuizen, LN.; Wijsman, JH.; Peterse, JL.; Rutgers, EJ. (Jun 2006). "The incidence and significance of micrometastases in lymph nodes of patients with ductal carcinoma in situ and T1a carcinoma of the breast.". Eur J Surg Oncol 32 (5): 502-6. doi:10.1016/j.ejso.2006.02.006. PMID 16569492.