Difference between revisions of "Peptic duodenitis"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
m (Redirected page to Duodenum#Chronic duodenitis) |
|||
| (5 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
'''Peptic duodenitis''' is controversial type of [[chronic duodenitis]]. | |||
This article deals with that controversy and '''foveolar metaplasia of the duodenum'''. | |||
==General== | |||
*''Peptic duodenitis'' is a somewhat controversial type of [[chronic duodenitis]]. | |||
*Considered to be a consequence of [[peptic ulcer disease]] ([[Helicobacter gastritis]]). | |||
*One of the key components of the diagnosis is foveolar metaplasia and it is disputed that this is really due to Helicobacter. | |||
**Genta ''et al.'' consider gastric foveolar metaplasia a congenital lesion.<ref name=pmid20656325>{{Cite journal | last1 = Genta | first1 = RM. | last2 = Kinsey | first2 = RS. | last3 = Singhal | first3 = A. | last4 = Suterwala | first4 = S. | title = Gastric foveolar metaplasia and gastric heterotopia in the duodenum: no evidence of an etiologic role for Helicobacter pylori. | journal = Hum Pathol | volume = 41 | issue = 11 | pages = 1593-600 | month = Nov | year = 2010 | doi = 10.1016/j.humpath.2010.04.010 | PMID = 20656325 }}</ref> | |||
==Microscopic== | |||
Features:<ref name=Ref_GLP145>{{Ref GLP|145}}</ref> | |||
*Gastric foveolar metaplasia - '''key feature'''. | |||
*[[Brunner's gland hyperplasia]]. | |||
*+/-Inflammation - neutrophils.{{fact}} | |||
*Ulceration.{{fact}} | |||
DDx: | |||
*[[Chronic duodenitis]] not otherwise specified - no foveolar metaplasia, abundant plasma cells. | |||
*[[Acute duodenitis]]. | |||
*[[Brunner's gland hyperplasia]]. | |||
*[[Gastric heterotopia of the duodenum]]. | |||
*[[Helicobacter duodenitis]]. | |||
===Images=== | |||
<gallery> | |||
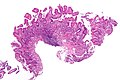
Image:Duodenum_with_foveolar_metaplasia_-_low_mag.jpg | Duodenum with foveolar metaplasia - low mag. (WC/Nephron) | |||
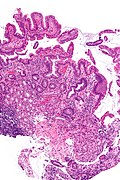
Image:Duodenum_with_foveolar_metaplasia_-_intermed_mag.jpg | Duodenum with foveolar metaplasia - intermed. mag. (WC/Nephron) | |||
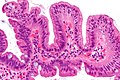
Image:Duodenum_with_foveolar_metaplasia_-_alt_-_very_high_mag.jpg | Duodenum with foveolar metaplasia - very high mag. (WC/Nephron) | |||
</gallery> | |||
==Stains== | |||
Foveolar metaplasia: | |||
*[[PAS stain]] +ve.<ref name=Ref_GLP145>{{Ref GLP|145}}</ref> | |||
*[[Mucicarmine stain]] +ve. | |||
==Sign out== | |||
===Foveolar metaplasia only=== | |||
<pre> | |||
DUODENUM, BIOPSY: | |||
- SMALL BOWEL MUCOSA WITH FOCAL GASTRIC FOVEOLAR METAPLASIA. | |||
- BRUNNER'S GLANDS NOT IDENTIFIED. | |||
- VILLI AND INTRAEPITHELIAL LYMPHOCYTES WITHIN NORMAL LIMITS (NEGATIVE FOR CELIAC DISEASE). | |||
- NEGATIVE FOR ACUTE DUODENITIS. | |||
- NEGATIVE FOR DYSPLASIA. | |||
</pre> | |||
<pre> | |||
DUODENUM, BIOPSY: | |||
- SMALL BOWEL MUCOSA WITH FOCAL GASTRIC FOVEOLAR METAPLASIA. | |||
- BRUNNER'S GLANDS NOT IDENTIFIED. | |||
- NEGATIVE FOR ACUTE DUODENITIS. | |||
- NEGATIVE FOR DYSPLASIA. | |||
</pre> | |||
===Chronic duodenitis=== | |||
<pre> | |||
Duodenum, Biopsy: | |||
- Small bowel mucosa with Brunner’s gland in the lamina propria and gastric foveolar metaplasia, consistent with chronic duodenitis. | |||
- NEGATIVE for acute duodenitis. | |||
- NEGATIVE for dysplasia and NEGATIVE for malignancy. | |||
</pre> | |||
<pre> | |||
DUODENUM, BIOPSY: | |||
- SMALL BOWEL MUCOSA WITH BRUNNER'S GLAND IN THE LAMINA PROPRIA AND | |||
GASTRIC FOVEOLAR METAPLASIA -- CONSISTENT WITH CHRONIC DUODENITIS. | |||
- NEGATIVE FOR ACUTE DUODENITIS. | |||
- NEGATIVE FOR MALIGNANCY. | |||
</pre> | |||
<pre> | |||
DUODENUM, BIOPSY: | |||
- SMALL BOWEL MUCOSA WITH PROMINENT BRUNNER'S GLANDS AND FOCAL GASTRIC | |||
FOVEOLAR METAPLASIA. | |||
- NEGATIVE FOR ACUTE INFLAMMATION. | |||
- NEGATIVE FOR DYSPLASIA. | |||
</pre> | |||
====Micro==== | |||
The sections show small bowel mucosa and a small amount of submucosa. Brunner's glands are abundant and found focally in the lamina propria. Gastric foveolar-type epithelium is identified. Intraepithelial neutrophils are not identified. | |||
The epithelium matures appropriately. There is no increase in intraepithelial lymphocytes. | |||
==See also== | |||
*[[Chronic duodenitis]]. | |||
*[[Gastric heterotopia of the duodenum]]. | |||
==References== | |||
{{Reflist|1}} | |||
[[Category:Duodenum]] | |||
[[Category:Diagnosis]] | [[Category:Diagnosis]] | ||
Latest revision as of 18:44, 5 February 2024
Peptic duodenitis is controversial type of chronic duodenitis.
This article deals with that controversy and foveolar metaplasia of the duodenum.
General
- Peptic duodenitis is a somewhat controversial type of chronic duodenitis.
- Considered to be a consequence of peptic ulcer disease (Helicobacter gastritis).
- One of the key components of the diagnosis is foveolar metaplasia and it is disputed that this is really due to Helicobacter.
- Genta et al. consider gastric foveolar metaplasia a congenital lesion.[1]
Microscopic
Features:[2]
- Gastric foveolar metaplasia - key feature.
- Brunner's gland hyperplasia.
- +/-Inflammation - neutrophils.[citation needed]
- Ulceration.[citation needed]
DDx:
- Chronic duodenitis not otherwise specified - no foveolar metaplasia, abundant plasma cells.
- Acute duodenitis.
- Brunner's gland hyperplasia.
- Gastric heterotopia of the duodenum.
- Helicobacter duodenitis.
Images
Stains
Foveolar metaplasia:
- PAS stain +ve.[2]
- Mucicarmine stain +ve.
Sign out
Foveolar metaplasia only
DUODENUM, BIOPSY: - SMALL BOWEL MUCOSA WITH FOCAL GASTRIC FOVEOLAR METAPLASIA. - BRUNNER'S GLANDS NOT IDENTIFIED. - VILLI AND INTRAEPITHELIAL LYMPHOCYTES WITHIN NORMAL LIMITS (NEGATIVE FOR CELIAC DISEASE). - NEGATIVE FOR ACUTE DUODENITIS. - NEGATIVE FOR DYSPLASIA.
DUODENUM, BIOPSY: - SMALL BOWEL MUCOSA WITH FOCAL GASTRIC FOVEOLAR METAPLASIA. - BRUNNER'S GLANDS NOT IDENTIFIED. - NEGATIVE FOR ACUTE DUODENITIS. - NEGATIVE FOR DYSPLASIA.
Chronic duodenitis
Duodenum, Biopsy: - Small bowel mucosa with Brunner’s gland in the lamina propria and gastric foveolar metaplasia, consistent with chronic duodenitis. - NEGATIVE for acute duodenitis. - NEGATIVE for dysplasia and NEGATIVE for malignancy.
DUODENUM, BIOPSY: - SMALL BOWEL MUCOSA WITH BRUNNER'S GLAND IN THE LAMINA PROPRIA AND GASTRIC FOVEOLAR METAPLASIA -- CONSISTENT WITH CHRONIC DUODENITIS. - NEGATIVE FOR ACUTE DUODENITIS. - NEGATIVE FOR MALIGNANCY.
DUODENUM, BIOPSY: - SMALL BOWEL MUCOSA WITH PROMINENT BRUNNER'S GLANDS AND FOCAL GASTRIC FOVEOLAR METAPLASIA. - NEGATIVE FOR ACUTE INFLAMMATION. - NEGATIVE FOR DYSPLASIA.
Micro
The sections show small bowel mucosa and a small amount of submucosa. Brunner's glands are abundant and found focally in the lamina propria. Gastric foveolar-type epithelium is identified. Intraepithelial neutrophils are not identified.
The epithelium matures appropriately. There is no increase in intraepithelial lymphocytes.
See also
References
- ↑ Genta, RM.; Kinsey, RS.; Singhal, A.; Suterwala, S. (Nov 2010). "Gastric foveolar metaplasia and gastric heterotopia in the duodenum: no evidence of an etiologic role for Helicobacter pylori.". Hum Pathol 41 (11): 1593-600. doi:10.1016/j.humpath.2010.04.010. PMID 20656325.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 Iacobuzio-Donahue, Christine A.; Montgomery, Elizabeth A. (2005). Gastrointestinal and Liver Pathology: A Volume in the Foundations in Diagnostic Pathology Series (1st ed.). Churchill Livingstone. pp. 145. ISBN 978-0443066573.