Difference between revisions of "C-cell hyperplasia"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
(→Gross) |
|||
| (5 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 13: | Line 13: | ||
| Molecular = | | Molecular = | ||
| IF = | | IF = | ||
| Gross = not apparent | | Gross = not apparent; mid portion of lobe to upper third of lobe | ||
| Grossing = | | Grossing = | ||
| Site = [[thyroid gland]] | | Site = [[thyroid gland]] | ||
| Assdx = | | Assdx = | ||
| Syndromes = [[Multiple endocrine neoplasia type 2A]] | | Syndromes = [[Multiple endocrine neoplasia type 2A]], [[Multiple endocrine neoplasia type 2B]] | ||
| Clinicalhx = | | Clinicalhx = +/-family history of thyroid cancer or MEN 2A or MEN 2B | ||
| Signs = | | Signs = +/-marfanoid habitus (seen in MEN 2B) | ||
| Symptoms = | | Symptoms = | ||
| Prevalence = uncommon | | Prevalence = uncommon | ||
| Line 27: | Line 27: | ||
| Prognosis = benign in itself | | Prognosis = benign in itself | ||
| Other = | | Other = | ||
| ClinDDx = | | ClinDDx = | ||
| Tx = prophylatic surgery | | Tx = prophylatic surgery | ||
}} | }} | ||
'''C-cell hyperplasia''' is a pathology of the [[thyroid gland]] and considered the precursor for [[medullary thyroid carcinoma]]. | '''C-cell hyperplasia''', abbreviated '''CCH''', is a pathology of the [[thyroid gland]] and considered the precursor for [[medullary thyroid carcinoma]]. | ||
==General== | ==General== | ||
*Screening for C-cell hyperplasia/[[medullary thyroid carcinoma]] done with ''serum calcitonin level''.<ref name=pmid19726541>{{cite journal |author=Machens A, Hoffmann F, Sekulla C, Dralle H |title=Importance of gender-specific calcitonin thresholds in screening for occult sporadic medullary thyroid cancer |journal=Endocr. Relat. Cancer |volume=16 |issue=4 |pages=1291–8 |year=2009 |month=December |pmid=19726541 |doi=10.1677/ERC-09-0136 |url=http://erc.endocrinology-journals.org/cgi/content/full/16/4/1291}}</ref> | *Screening for C-cell hyperplasia/[[medullary thyroid carcinoma]] done with ''serum calcitonin level''.<ref name=pmid19726541>{{cite journal |author=Machens A, Hoffmann F, Sekulla C, Dralle H |title=Importance of gender-specific calcitonin thresholds in screening for occult sporadic medullary thyroid cancer |journal=Endocr. Relat. Cancer |volume=16 |issue=4 |pages=1291–8 |year=2009 |month=December |pmid=19726541 |doi=10.1677/ERC-09-0136 |url=http://erc.endocrinology-journals.org/cgi/content/full/16/4/1291}}</ref> | ||
Associated with: | |||
*[[Multiple endocrine neoplasia type 2A]]<ref name=pmid21134882>{{Cite journal | last1 = Tyer | first1 = NM. | last2 = Braunstein | first2 = GD. | last3 = Frishberg | first3 = D. | title = Unusual case of multiple endocrine neoplasia type 2A syndrome without medullary thyroid carcinoma. | journal = Endocr Pract | volume = 17 | issue = 2 | pages = e4-7 | month = | year = | doi = 10.4158/EP10157.CR | PMID = 21134882 }}</ref> - may be found in specimen of a surgery done to exclude [[medullary thyroid carcinoma|MTC]] in the context of [[MEN 2A]].<ref name=pmid18976013>{{Cite journal | last1 = Etit | first1 = D. | last2 = Faquin | first2 = WC. | last3 = Gaz | first3 = R. | last4 = Randolph | first4 = G. | last5 = DeLellis | first5 = RA. | last6 = Pilch | first6 = BZ. | title = Histopathologic and clinical features of medullary microcarcinoma and C-cell hyperplasia in prophylactic thyroidectomies for medullary carcinoma: a study of 42 cases. | journal = Arch Pathol Lab Med | volume = 132 | issue = 11 | pages = 1767-73 | month = Nov | year = 2008 | doi = 10.1043/1543-2165-132.11.1767 | PMID = 18976013 }}</ref> | |||
*[[Multiple endocrine neoplasia type 2B]].<ref name=pmid20301434>{{Cite journal | last1 = Pagon | first1 = RA. | last2 = Adam | first2 = MP. | last3 = Ardinger | first3 = HH. | last4 = Wallace | first4 = SE. | last5 = Amemiya | first5 = A. | last6 = Bean | first6 = LJH. | last7 = Bird | first7 = TD. | last8 = Fong | first8 = CT. | last9 = Mefford | first9 = HC. | title = Multiple Endocrine Neoplasia Type 2 | journal = | volume = | issue = | pages = | month = | year = | doi = | PMID = 20301434 }}</ref> | |||
==Gross== | ==Gross== | ||
*Not visible. | *Not visible on gross. | ||
Location:<ref>URL: [http://www.cap.org/apps/docs/committees/cancer/cancer_protocols/2011/Thyroid_11protocol.pdf http://www.cap.org/apps/docs/committees/cancer/cancer_protocols/2011/Thyroid_11protocol.pdf]. Accessed on: 7 April 2012.</ref> | |||
*Mid portion of lobe to upper third of lobe. | |||
**Not at the poles. | |||
**Not in the isthmus. | |||
==Microscopic== | ==Microscopic== | ||
Features: | Features: | ||
*Definitions vary.<ref>Raphael S. 17 January 2011.</ref> | *Definitions vary.<ref>Raphael S. 17 January 2011.</ref> | ||
**One definition - either of the following:<ref name=pmid19726541>{{cite journal |author=Machens A, Hoffmann F, Sekulla C, Dralle H |title=Importance of gender-specific calcitonin thresholds in screening for occult sporadic medullary thyroid cancer |journal=Endocr. Relat. Cancer |volume=16 |issue=4 |pages=1291–8 |year=2009 |month=December |pmid=19726541 |doi=10.1677/ERC-09-0136 |url=http://erc.endocrinology-journals.org/cgi/content/full/16/4/1291}}</ref> | **One definition - either of the following:<ref name=pmid19726541>{{cite journal |author=Machens A, Hoffmann F, Sekulla C, Dralle H |title=Importance of gender-specific calcitonin thresholds in screening for occult sporadic medullary thyroid cancer |journal=Endocr. Relat. Cancer |volume=16 |issue=4 |pages=1291–8 |year=2009 |month=December |pmid=19726541 |doi=10.1677/ERC-09-0136 |url=http://erc.endocrinology-journals.org/cgi/content/full/16/4/1291}}</ref> | ||
| Line 88: | Line 91: | ||
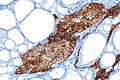
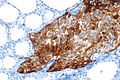
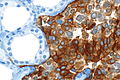
==IHC== | ==IHC== | ||
*Chromogranin A +ve. | *Chromogranin A +ve. | ||
*CEA +ve. | *[[CEA]] +ve. | ||
*Synaptophysin +ve. | *Synaptophysin +ve. | ||
Latest revision as of 17:56, 18 August 2022
| C-cell hyperplasia | |
|---|---|
| Diagnosis in short | |
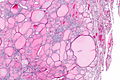
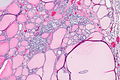
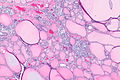
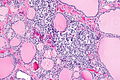
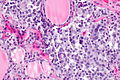
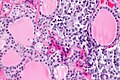
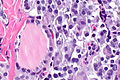
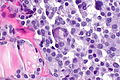
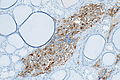
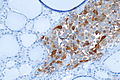
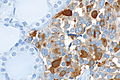
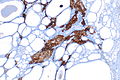
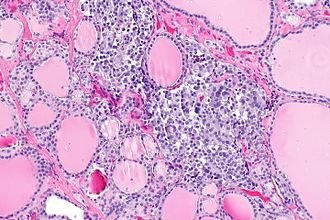 C-cell hyperplasia. H&E stain. | |
| LM DDx | medullary thyroid carcinoma |
| IHC | CEA +ve, chromogranin A +ve, synaptophysin +ve |
| Gross | not apparent; mid portion of lobe to upper third of lobe |
| Site | thyroid gland |
|
| |
| Syndromes | Multiple endocrine neoplasia type 2A, Multiple endocrine neoplasia type 2B |
|
| |
| Clinical history | +/-family history of thyroid cancer or MEN 2A or MEN 2B |
| Signs | +/-marfanoid habitus (seen in MEN 2B) |
| Prevalence | uncommon |
| Blood work | calcitonin level elevated |
| Prognosis | benign in itself |
| Treatment | prophylatic surgery |
C-cell hyperplasia, abbreviated CCH, is a pathology of the thyroid gland and considered the precursor for medullary thyroid carcinoma.
General
- Screening for C-cell hyperplasia/medullary thyroid carcinoma done with serum calcitonin level.[1]
Associated with:
- Multiple endocrine neoplasia type 2A[2] - may be found in specimen of a surgery done to exclude MTC in the context of MEN 2A.[3]
- Multiple endocrine neoplasia type 2B.[4]
Gross
- Not visible on gross.
Location:[5]
- Mid portion of lobe to upper third of lobe.
- Not at the poles.
- Not in the isthmus.
Microscopic
Features:
- Definitions vary.[6]
- One definition - either of the following:[1]
- >50 C-cells per low-power field (x100).
- This part of the definition suffers from LPFitis.
- "Medullary thyroid carcinoma confined to the thyroid gland and no larger than 10 mm in greatest dimension."
- >50 C-cells per low-power field (x100).
- Another definition:
- Invasion of the basement membrane with stromal reaction.
- A third definition:
- "Several clusters" of more than six C cells.
- One definition - either of the following:[1]
Images
www
- CCH - crappy B&W image (nature.com).[7]
- CCH - crappy B&W image (nature.com).
- CCH (forpath.org).[8]
- CCH (unibas.ch).
- Nodular CCH (unibas.ch).
IHC
- Chromogranin A +ve.
- CEA +ve.
- Synaptophysin +ve.
See also
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 Machens A, Hoffmann F, Sekulla C, Dralle H (December 2009). "Importance of gender-specific calcitonin thresholds in screening for occult sporadic medullary thyroid cancer". Endocr. Relat. Cancer 16 (4): 1291–8. doi:10.1677/ERC-09-0136. PMID 19726541. http://erc.endocrinology-journals.org/cgi/content/full/16/4/1291.
- ↑ Tyer, NM.; Braunstein, GD.; Frishberg, D.. "Unusual case of multiple endocrine neoplasia type 2A syndrome without medullary thyroid carcinoma.". Endocr Pract 17 (2): e4-7. doi:10.4158/EP10157.CR. PMID 21134882.
- ↑ Etit, D.; Faquin, WC.; Gaz, R.; Randolph, G.; DeLellis, RA.; Pilch, BZ. (Nov 2008). "Histopathologic and clinical features of medullary microcarcinoma and C-cell hyperplasia in prophylactic thyroidectomies for medullary carcinoma: a study of 42 cases.". Arch Pathol Lab Med 132 (11): 1767-73. doi:10.1043/1543-2165-132.11.1767. PMID 18976013.
- ↑ Pagon, RA.; Adam, MP.; Ardinger, HH.; Wallace, SE.; Amemiya, A.; Bean, LJH.; Bird, TD.; Fong, CT. et al. Multiple Endocrine Neoplasia Type 2. PMID 20301434.
- ↑ URL: http://www.cap.org/apps/docs/committees/cancer/cancer_protocols/2011/Thyroid_11protocol.pdf. Accessed on: 7 April 2012.
- ↑ Raphael S. 17 January 2011.
- ↑ Guyétant, S.; Josselin, N.; Savagner, F.; Rohmer, V.; Michalak, S.; Saint-André, JP. (Aug 2003). "C-cell hyperplasia and medullary thyroid carcinoma: clinicopathological and genetic correlations in 66 consecutive patients.". Mod Pathol 16 (8): 756-63. doi:10.1097/01.MP.0000081727.75778.0C. PMID 12920219.
- ↑ URL: http://www.forpath.org/workshops/0201/html/case_7.asp. Accessed on: 21 May 2013.