Difference between revisions of "Gastric ulcer"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
(→Gross) |
|||
| (12 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 8: | Line 8: | ||
*[[Peptic ulcer disease]]. | *[[Peptic ulcer disease]]. | ||
**[[Helicobacter gastritis]]. | **[[Helicobacter gastritis]]. | ||
*[[Syphilis]].<ref name=pmid8343046>{{Cite journal | last1 = Fyfe | first1 = B. | last2 = Poppiti | first2 = RJ. | last3 = Lubin | first3 = J. | last4 = Robinson | first4 = MJ. | title = Gastric syphilis. Primary diagnosis by gastric biopsy: report of four cases. | journal = Arch Pathol Lab Med | volume = 117 | issue = 8 | pages = 820-3 | month = Aug | year = 1993 | doi = | PMID = 8343046 }}</ref> | |||
*Other causes. | |||
==Gross== | ==Gross== | ||
*Heaped (raised) edges - suggestive of [[gastric carcinoma|cancer]]. | *Heaped (raised) edges - suggestive of [[gastric carcinoma|cancer]]. | ||
*Punched-out appearance with flat edges - suggestive of benign. | *Punched-out appearance with flat edges - suggestive of benign. | ||
Notes: | |||
*The classical teaching is to biopsy the ulcer edge, as the dictum is: the cancer is there; this dictum may not be true.<ref name=pmid22469743>{{Cite journal | last1 = Lv | first1 = SX. | last2 = Gan | first2 = JH. | last3 = Ma | first3 = XG. | last4 = Wang | first4 = CC. | last5 = Chen | first5 = HM. | last6 = Luo | first6 = EP. | last7 = Huang | first7 = XP. | last8 = Wu | first8 = SH. | last9 = Qin | first9 = AL. | title = Biopsy from the base and edge of gastric ulcer healing or complete healing may lead to detection of gastric cancer earlier: an 8 years endoscopic follow-up study. | journal = Hepatogastroenterology | volume = 59 | issue = 115 | pages = 947-50 | month = May | year = 2012 | doi = 10.5754/hge10692 | PMID = 22469743 }}</ref> | |||
*''Ulcer with clean base'' refers to nothing "in" the ulcer (depression); these may be benign or malignant.<ref name=pmid25312052>{{cite journal |authors=Gielisse EA, Kuyvenhoven JP |title=Follow-up endoscopy for benign-appearing gastric ulcers has no additive value in detecting malignancy: It is time to individualise surveillance endoscopy |journal=Gastric Cancer |volume=18 |issue=4 |pages=803–9 |date=October 2015 |pmid=25312052 |doi=10.1007/s10120-014-0433-4 |url=}}</ref> | |||
**The term is within a popular classification of upper GI bleeding.<ref>URL: [https://www.endoscopy-campus.com/en/classifications/forrest-classification/ https://www.endoscopy-campus.com/en/classifications/forrest-classification/]. Accessed: 2022 January 11.</ref> | |||
===Images=== | |||
<gallery> | |||
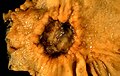
Image:Adenocarcinoma of the stomach.jpg | Malignant ulcer of the stomach. (WC) | |||
</gallery> | |||
==Microscopic== | |||
Features: | |||
*Loss of the (gastric) epithelium. | |||
*Vital reaction. | |||
**Marked (acute) inflammation. | |||
**Fibrin. | |||
===Images=== | |||
<gallery> | |||
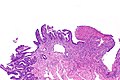
Image: Stomach ulcer -- low mag.jpg | SU - low mag. (WC) | |||
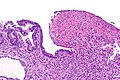
Image: Stomach ulcer -- intermed mag.jpg | SU - intermed. mag. (WC) | |||
</gallery> | |||
==Sign out== | ==Sign out== | ||
| Line 29: | Line 54: | ||
*[[Helicobacter gastritis]]. | *[[Helicobacter gastritis]]. | ||
*[[Gastric adenocarcinoma]]. | *[[Gastric adenocarcinoma]]. | ||
*[[Cameron lesion]]. | |||
==References== | |||
{{Reflist|1}} | |||
[[Category:Stomach]] | [[Category:Stomach]] | ||
[[Category:Diagnosis]] | [[Category:Diagnosis]] | ||
Latest revision as of 16:39, 11 January 2022
Gastric ulcer, also stomach ulcer, is pathology of the stomach that is evident grossly. It can be benign or malignant.
General
- May be benign or malignant.
Causes:
- Gastric carcinoma.
- Peptic ulcer disease.
- Syphilis.[1]
- Other causes.
Gross
- Heaped (raised) edges - suggestive of cancer.
- Punched-out appearance with flat edges - suggestive of benign.
Notes:
- The classical teaching is to biopsy the ulcer edge, as the dictum is: the cancer is there; this dictum may not be true.[2]
- Ulcer with clean base refers to nothing "in" the ulcer (depression); these may be benign or malignant.[3]
- The term is within a popular classification of upper GI bleeding.[4]
Images
Microscopic
Features:
- Loss of the (gastric) epithelium.
- Vital reaction.
- Marked (acute) inflammation.
- Fibrin.
Images
Sign out
Compatible with benign
A. STOMACH, BIOPSY: - GASTRIC ANTRAL-TYPE MUCOSA WITH EDEMA, FOCALLY PROMINENT SMOOTH MUSCLE, ACTIVATED FIBROBLASTS, A MILD INCREASE OF EOSINOPHILS, AND FIBRIN -- COMPATIBLE WITH NEARBY ULCER. - NEGATIVE FOR HELICOBACTOR-LIKE ORGANISMS. - NEGATIVE FOR INTESTINAL METAPLASIA. - NEGATIVE FOR DYSPLASIA AND NEGATIVE FOR MALIGNANCY.
See also
References
- ↑ Fyfe, B.; Poppiti, RJ.; Lubin, J.; Robinson, MJ. (Aug 1993). "Gastric syphilis. Primary diagnosis by gastric biopsy: report of four cases.". Arch Pathol Lab Med 117 (8): 820-3. PMID 8343046.
- ↑ Lv, SX.; Gan, JH.; Ma, XG.; Wang, CC.; Chen, HM.; Luo, EP.; Huang, XP.; Wu, SH. et al. (May 2012). "Biopsy from the base and edge of gastric ulcer healing or complete healing may lead to detection of gastric cancer earlier: an 8 years endoscopic follow-up study.". Hepatogastroenterology 59 (115): 947-50. doi:10.5754/hge10692. PMID 22469743.
- ↑ Gielisse EA, Kuyvenhoven JP (October 2015). "Follow-up endoscopy for benign-appearing gastric ulcers has no additive value in detecting malignancy: It is time to individualise surveillance endoscopy". Gastric Cancer 18 (4): 803–9. doi:10.1007/s10120-014-0433-4. PMID 25312052.
- ↑ URL: https://www.endoscopy-campus.com/en/classifications/forrest-classification/. Accessed: 2022 January 11.