Difference between revisions of "Nodular hidradenoma"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
(split out) |
(→Microscopic: SqCC in DDX) |
||
| Line 21: | Line 21: | ||
DDx: | DDx: | ||
*[[Eccrine poroma]]. | *[[Eccrine poroma]]. | ||
*[[Squamous cell carcinoma]].<ref>{{cite journal |authors=Nakazato S, Yanagi T, Inamura Y, Kitamura S, Hata H, Shimizu H |title=A case of nodular hidradenoma of the auricle mimicking squamous cell carcinoma |journal=Eur J Dermatol |volume=26 |issue=4 |pages=409–10 |date=August 2016 |pmid=27350422 |doi=10.1684/ejd.2016.2810 |url=}}</ref> | |||
===Images=== | ===Images=== | ||
Revision as of 22:57, 25 November 2020
Nodular hidradenoma, also known as eccrine acrospiroma,[1] is a benign adnexal skin tumour.
General
- Benign adnexal tumour.[2]
Gross
Typical locations:[1]
- Scalp.
- Face.
- Trunk, anterior.
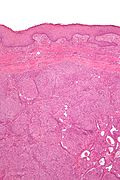
Microscopic
Features:[2]
- Well-circumscribed dermal lesions with:
- Back-to-back nests with a whorled appearance.
- Spaces between cells.
- Nuclei ovoid and centrally placed in the cell.
- No nucleolus.
- Cystic spaces with degenerated cells.
DDx:
Images
IHC
Features:[2]
- CAM5.2 +ve.
- AE1/AE3 +ve.
- EMA +ve.
- S100 -ve.
- Desmin -ve.
See also
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 Punia, RP.; Garg, S.; Bal, A.; Mohan, H. (2008). "Pigmented nodular hidradenoma masquerading as nodular malignant melanoma.". Dermatol Online J 14 (1): 15. PMID 18319032.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 Stratigos, AJ.; Olbricht, S.; Kwan, TH.; Bowers, KE. (Mar 1998). "Nodular hidradenoma. A report of three cases and review of the literature.". Dermatol Surg 24 (3): 387-91. PMID 9537017.
- ↑ Nakazato S, Yanagi T, Inamura Y, Kitamura S, Hata H, Shimizu H (August 2016). "A case of nodular hidradenoma of the auricle mimicking squamous cell carcinoma". Eur J Dermatol 26 (4): 409–10. doi:10.1684/ejd.2016.2810. PMID 27350422.