Difference between revisions of "Polypectomy scar"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
(+so) |
m (re-arrange) |
||
| Line 12: | Line 12: | ||
*Polypectomy scar with adenocarcinoma. | *Polypectomy scar with adenocarcinoma. | ||
*Focal fibrosis due to other cause. | *Focal fibrosis due to other cause. | ||
===Images=== | ===Images=== | ||
| Line 23: | Line 20: | ||
</gallery> | </gallery> | ||
==Sign out== | |||
Should be signed in a non-commital way (e.g. "focal submucosal fibrosis") if no prior pathology is available/specimen is not labelled something like "old polypectomy site". | |||
==See also== | ==See also== | ||
*[[Polypectomy]]. | *[[Polypectomy]]. | ||
| Line 28: | Line 27: | ||
==References== | ==References== | ||
{{Reflist|1}} | {{Reflist|1}} | ||
[[Category:Diagnosis]] | [[Category:Diagnosis]] | ||
[[Category:Gastrointestinal pathology]] | [[Category:Gastrointestinal pathology]] | ||
Revision as of 14:07, 2 June 2020
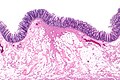
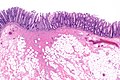
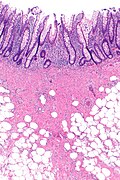
A polypectomy scar results from a polypectomy.
General
- Scar alone is difficult to differentiate from scar with cancer.[1]
Microscopic
Features:
- Focal submucosal fibrosis.
DDx:
- Polypectomy scar with adenocarcinoma.
- Focal fibrosis due to other cause.
Images
Sign out
Should be signed in a non-commital way (e.g. "focal submucosal fibrosis") if no prior pathology is available/specimen is not labelled something like "old polypectomy site".
See also
References
- ↑ "Narrow band imaging and white light endoscopy in the characterization of a polypectomy scar: A single-blind observational study". World J. Gastroenterol. 24 (45): 5179–5188. December 2018. doi:10.3748/wjg.v24.i45.5179. PMC 6288651. PMID 30568394. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6288651/.