Difference between revisions of "Embryonal tumour with multilayered rosettes"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
Jensflorian (talk | contribs) (→Microscopy: +images) |
Jensflorian (talk | contribs) (→IHC: molecular update) |
||
| (3 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 3: | Line 3: | ||
==General== | ==General== | ||
* Extremely rare. | * Extremely rare. | ||
* Histologically WHO grade IV tumor. | |||
* ETMR historically had been termed CNS PNET. | * ETMR historically had been termed CNS PNET. | ||
* The WHO2016 CNS classification contains two groups: | * The WHO2016 CNS classification contains two groups: | ||
| Line 13: | Line 14: | ||
*[[Embryonal tumour with abundant neuropil and true rosettes]] <ref name=pmid23863344>{{Cite journal | last1 = Ceccom | first1 = J. | last2 = Bourdeaut | first2 = F. | last3 = Loukh | first3 = N. | last4 = Rigau | first4 = V. | last5 = Milin | first5 = S. | last6 = Takin | first6 = R. | last7 = Richer | first7 = W. | last8 = Uro-Coste | first8 = E. | last9 = Couturier | first9 = J. | title = Embryonal tumor with multilayered rosettes: diagnostic tools update and review of the literature. | journal = Clin Neuropathol | volume = 33 | issue = 1 | pages = 15-22 | month = | year = | doi = 10.5414/NP300636 | PMID = 23863344 }}</ref> | *[[Embryonal tumour with abundant neuropil and true rosettes]] <ref name=pmid23863344>{{Cite journal | last1 = Ceccom | first1 = J. | last2 = Bourdeaut | first2 = F. | last3 = Loukh | first3 = N. | last4 = Rigau | first4 = V. | last5 = Milin | first5 = S. | last6 = Takin | first6 = R. | last7 = Richer | first7 = W. | last8 = Uro-Coste | first8 = E. | last9 = Couturier | first9 = J. | title = Embryonal tumor with multilayered rosettes: diagnostic tools update and review of the literature. | journal = Clin Neuropathol | volume = 33 | issue = 1 | pages = 15-22 | month = | year = | doi = 10.5414/NP300636 | PMID = 23863344 }}</ref> | ||
*[[Ependymoblastoma]] <ref name=pmid19120373>{{Cite journal | last1 = Judkins | first1 = AR. | last2 = Ellison | first2 = DW. | title = Ependymoblastoma: dear, damned, distracting diagnosis, farewell!*. | journal = Brain Pathol | volume = 20 | issue = 1 | pages = 133-9 | month = Jan | year = 2010 | doi = 10.1111/j.1750-3639.2008.00253.x | PMID = 19120373 }}</ref> | *[[Ependymoblastoma]] <ref name=pmid19120373>{{Cite journal | last1 = Judkins | first1 = AR. | last2 = Ellison | first2 = DW. | title = Ependymoblastoma: dear, damned, distracting diagnosis, farewell!*. | journal = Brain Pathol | volume = 20 | issue = 1 | pages = 133-9 | month = Jan | year = 2010 | doi = 10.1111/j.1750-3639.2008.00253.x | PMID = 19120373 }}</ref> | ||
*[[Medulloepithelioma]]<ref>{{Cite journal | last1 = Korshunov | first1 = A. | last2 = Jakobiec | first2 = FA. | last3 = Eberhart | first3 = CG. | last4 = Hovestadt | first4 = V. | last5 = Capper | first5 = D. | last6 = Jones | first6 = DT. | last7 = Sturm | first7 = D. | last8 = Stagner | first8 = AM. | last9 = Edward | first9 = DP. | title = Comparative integrated molecular analysis of intraocular medulloepitheliomas and central nervous system embryonal tumors with multilayered rosettes confirms that they are distinct nosologic entities. | journal = Neuropathology | volume = 35 | issue = 6 | pages = 538-44 | month = Dec | year = 2015 | doi = 10.1111/neup.12227 | PMID = 26183384 }}</ref> | *[[Medulloepithelioma]] <ref>{{Cite journal | last1 = Korshunov | first1 = A. | last2 = Jakobiec | first2 = FA. | last3 = Eberhart | first3 = CG. | last4 = Hovestadt | first4 = V. | last5 = Capper | first5 = D. | last6 = Jones | first6 = DT. | last7 = Sturm | first7 = D. | last8 = Stagner | first8 = AM. | last9 = Edward | first9 = DP. | title = Comparative integrated molecular analysis of intraocular medulloepitheliomas and central nervous system embryonal tumors with multilayered rosettes confirms that they are distinct nosologic entities. | journal = Neuropathology | volume = 35 | issue = 6 | pages = 538-44 | month = Dec | year = 2015 | doi = 10.1111/neup.12227 | PMID = 26183384 }}</ref> | ||
| Line 42: | Line 43: | ||
File:Neuroblasts ependymoblastoma.jpg | ETMR, ganglion cells. | File:Neuroblasts ependymoblastoma.jpg | ETMR, ganglion cells. | ||
</gallery> | </gallery> | ||
DDx: | |||
*[[AT/RT]]. | |||
*[[Medulloblastoma]]. | |||
*[[Ependymoma]]. | |||
* CNS embryonal tumor, NOS. | |||
* Pediatric [[glioblastoma]]. | |||
==IHC== | ==IHC== | ||
| Line 56: | Line 64: | ||
File:MIB1 ependymoblastoma.jpg | MIB1 in ETMR rosettes. | File:MIB1 ependymoblastoma.jpg | MIB1 in ETMR rosettes. | ||
</gallery> | </gallery> | ||
==Molecular== | |||
*Chr 2 gain. | |||
*C19MC amplification. <ref>{{Cite journal | last1 = Spence | first1 = T. | last2 = Sin-Chan | first2 = P. | last3 = Picard | first3 = D. | last4 = Barszczyk | first4 = M. | last5 = Hoss | first5 = K. | last6 = Lu | first6 = M. | last7 = Kim | first7 = SK. | last8 = Ra | first8 = YS. | last9 = Nakamura | first9 = H. | title = CNS-PNETs with C19MC amplification and/or LIN28 expression comprise a distinct histogenetic diagnostic and therapeutic entity. | journal = Acta Neuropathol | volume = 128 | issue = 2 | pages = 291-303 | month = Aug | year = 2014 | doi = 10.1007/s00401-014-1291-1 | PMID = 24839957 }}</ref> | |||
*Some rare LIN28+ve cases without C19MC amplification may show DICER1 mutations.<ref>{{Cite journal | last1 = Uro-Coste | first1 = E. | last2 = Masliah-Planchon | first2 = J. | last3 = Siegfried | first3 = A. | last4 = Blanluet | first4 = M. | last5 = Lambo | first5 = S. | last6 = Kool | first6 = M. | last7 = Roujeau | first7 = T. | last8 = Boetto | first8 = S. | last9 = Palenzuela | first9 = G. | title = ETMR-like infantile cerebellar embryonal tumors in the extended morphologic spectrum of DICER1-related tumors. | journal = Acta Neuropathol | volume = 137 | issue = 1 | pages = 175-177 | month = Jan | year = 2019 | doi = 10.1007/s00401-018-1935-7 | PMID = 30446821 }}</ref> | |||
==See also== | ==See also== | ||
| Line 66: | Line 79: | ||
[[Category:Diagnosis]] | [[Category:Diagnosis]] | ||
[[Category:Neuropathology]] | [[Category:Neuropathology tumours]] | ||
Latest revision as of 09:09, 23 January 2019
Embryonal tumour with multilayered rosettes, abbreviated ETMR, is a very rare neuropathology embryonal tumour with aggressive behaviour.
General
- Extremely rare.
- Histologically WHO grade IV tumor.
- ETMR historically had been termed CNS PNET.
- The WHO2016 CNS classification contains two groups:
- Embryonal tumour with multilayered rosettes, C19MC-altered.
- Embryonal tumour with multilayered rosettes, NOS.
Note: ETMR is an umbrella term for tumors formerly known as:[1]
- Embryonal tumour with abundant neuropil and true rosettes [2]
- Ependymoblastoma [3]
- Medulloepithelioma [4]
Clinical presentation
- Usu. age <4 years.
- 70% supratentorial, 30% infratentorial.
- Raised intracranial pressure.
Imaging
- Usu. enhancing.
- Rarely cysts, calcifications.
- Widespread infiltration.
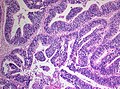
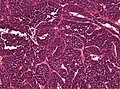
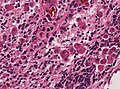
Microscopy
- Rosettes (often multilayered).
- Small cells.
- Fibrillar zones (neuropil-like areas).
- Neoplastic ganglion cells.
- Papillar and tubular growth (primitive neural tubes).
- PAS-positive membranes.
- Glial/neuronal maturation after treatment (rare).
DDx:
- AT/RT.
- Medulloblastoma.
- Ependymoma.
- CNS embryonal tumor, NOS.
- Pediatric glioblastoma.
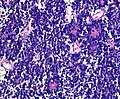
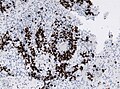
IHC
- LIN28+ve.
- Note: Some AT/RT may be focally +ve. [5]
- CD99: focally +ve.
- Synaptophysin: Neuropil-like areas +ve.
- GFAP: usu -ve.
- INI1 +ve.
- Mib1: 20-80%.
Molecular
- Chr 2 gain.
- C19MC amplification. [6]
- Some rare LIN28+ve cases without C19MC amplification may show DICER1 mutations.[7]
See also
References
- ↑ Korshunov, A.; Sturm, D.; Ryzhova, M.; Hovestadt, V.; Gessi, M.; Jones, DT.; Remke, M.; Northcott, P. et al. (Aug 2014). "Embryonal tumor with abundant neuropil and true rosettes (ETANTR), ependymoblastoma, and medulloepithelioma share molecular similarity and comprise a single clinicopathological entity.". Acta Neuropathol 128 (2): 279-89. doi:10.1007/s00401-013-1228-0. PMID 24337497.
- ↑ Ceccom, J.; Bourdeaut, F.; Loukh, N.; Rigau, V.; Milin, S.; Takin, R.; Richer, W.; Uro-Coste, E. et al. "Embryonal tumor with multilayered rosettes: diagnostic tools update and review of the literature.". Clin Neuropathol 33 (1): 15-22. doi:10.5414/NP300636. PMID 23863344.
- ↑ Judkins, AR.; Ellison, DW. (Jan 2010). "Ependymoblastoma: dear, damned, distracting diagnosis, farewell!*.". Brain Pathol 20 (1): 133-9. doi:10.1111/j.1750-3639.2008.00253.x. PMID 19120373.
- ↑ Korshunov, A.; Jakobiec, FA.; Eberhart, CG.; Hovestadt, V.; Capper, D.; Jones, DT.; Sturm, D.; Stagner, AM. et al. (Dec 2015). "Comparative integrated molecular analysis of intraocular medulloepitheliomas and central nervous system embryonal tumors with multilayered rosettes confirms that they are distinct nosologic entities.". Neuropathology 35 (6): 538-44. doi:10.1111/neup.12227. PMID 26183384.
- ↑ Rao, S.; Rajeswarie, RT.; Chickabasaviah Yasha, T.; Nandeesh, BN.; Arivazhagan, A.; Santosh, V. (Jul 2017). "LIN28A, a sensitive immunohistochemical marker for Embryonal Tumor with Multilayered Rosettes (ETMR), is also positive in a subset of Atypical Teratoid/Rhabdoid Tumor (AT/RT).". Childs Nerv Syst. doi:10.1007/s00381-017-3551-6. PMID 28744687.
- ↑ Spence, T.; Sin-Chan, P.; Picard, D.; Barszczyk, M.; Hoss, K.; Lu, M.; Kim, SK.; Ra, YS. et al. (Aug 2014). "CNS-PNETs with C19MC amplification and/or LIN28 expression comprise a distinct histogenetic diagnostic and therapeutic entity.". Acta Neuropathol 128 (2): 291-303. doi:10.1007/s00401-014-1291-1. PMID 24839957.
- ↑ Uro-Coste, E.; Masliah-Planchon, J.; Siegfried, A.; Blanluet, M.; Lambo, S.; Kool, M.; Roujeau, T.; Boetto, S. et al. (Jan 2019). "ETMR-like infantile cerebellar embryonal tumors in the extended morphologic spectrum of DICER1-related tumors.". Acta Neuropathol 137 (1): 175-177. doi:10.1007/s00401-018-1935-7. PMID 30446821.