Difference between revisions of "Diffuse idiopathic pulmonary neuroendocrine cell hyperplasia"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
(→General: link to MEN1) |
|||
| (3 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 6: | Line 6: | ||
*Usually women (15 of 19 cases<ref name=pmid17099078>{{Cite journal | last1 = Davies | first1 = SJ. | last2 = Gosney | first2 = JR. | last3 = Hansell | first3 = DM. | last4 = Wells | first4 = AU. | last5 = du Bois | first5 = RM. | last6 = Burke | first6 = MM. | last7 = Sheppard | first7 = MN. | last8 = Nicholson | first8 = AG. | title = Diffuse idiopathic pulmonary neuroendocrine cell hyperplasia: an under-recognised spectrum of disease. | journal = Thorax | volume = 62 | issue = 3 | pages = 248-52 | month = Mar | year = 2007 | doi = 10.1136/thx.2006.063065 | PMID = 17099078 }}</ref>). | *Usually women (15 of 19 cases<ref name=pmid17099078>{{Cite journal | last1 = Davies | first1 = SJ. | last2 = Gosney | first2 = JR. | last3 = Hansell | first3 = DM. | last4 = Wells | first4 = AU. | last5 = du Bois | first5 = RM. | last6 = Burke | first6 = MM. | last7 = Sheppard | first7 = MN. | last8 = Nicholson | first8 = AG. | title = Diffuse idiopathic pulmonary neuroendocrine cell hyperplasia: an under-recognised spectrum of disease. | journal = Thorax | volume = 62 | issue = 3 | pages = 248-52 | month = Mar | year = 2007 | doi = 10.1136/thx.2006.063065 | PMID = 17099078 }}</ref>). | ||
*Typically non-smokers (16 of 19 cases<ref name=pmid17099078/>). | *Typically non-smokers (16 of 19 cases<ref name=pmid17099078/>). | ||
*DIPNECH has been described in the context of [[multiple endocrine neoplasia 1]].<ref name=pmid17099078/> | |||
Clinical:<ref name=pmid26112453>{{Cite journal | last1 = Chauhan | first1 = A. | last2 = Ramirez | first2 = RA. | title = Diffuse Idiopathic Pulmonary Neuroendocrine Cell Hyperplasia (DIPNECH) and the Role of Somatostatin analogs: A Case Series. | journal = Lung | volume = | issue = | pages = | month = Jun | year = 2015 | doi = 10.1007/s00408-015-9754-2 | PMID = 26112453 }}</ref> | Clinical:<ref name=pmid26112453>{{Cite journal | last1 = Chauhan | first1 = A. | last2 = Ramirez | first2 = RA. | title = Diffuse Idiopathic Pulmonary Neuroendocrine Cell Hyperplasia (DIPNECH) and the Role of Somatostatin analogs: A Case Series. | journal = Lung | volume = | issue = | pages = | month = Jun | year = 2015 | doi = 10.1007/s00408-015-9754-2 | PMID = 26112453 }}</ref> | ||
| Line 22: | Line 23: | ||
Notes: | Notes: | ||
*The ''Marchevsky and Walts'' definition is not universally accepted. | *The ''Marchevsky and Walts'' definition is not universally accepted. | ||
*WHO definition is vague. | *[[World Health Organization]] (WHO) definition is vague. | ||
==Gross== | ==Gross== | ||
| Line 28: | Line 29: | ||
DDx: | DDx: | ||
*[[lung metastasis|Metastases]]. | *[[lung metastasis|Metastases to the lung]]. | ||
==Microscopic== | ==Microscopic== | ||
Latest revision as of 07:05, 11 September 2018

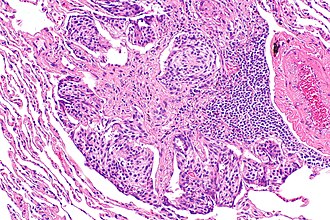
A carcinoid tumourlet, as may be seen in the context of DIPNECH. (WC/Nephron)
Diffuse idiopathic pulmonary neuroendocrine cell hyperplasia, abbreviated DIPNECH, is an uncommon lung pathology that is considered pre-neoplastic by the WHO.[1]
General
- Rare - less than 50 reported based on a 2010 paper.[2]
- Usually women (15 of 19 cases[3]).
- Typically non-smokers (16 of 19 cases[3]).
- DIPNECH has been described in the context of multiple endocrine neoplasia 1.[3]
Clinical:[4]
- Typical patient in 60s.
- Cough.
Treatment:
- Somatostatin analogs[4] - improves cough.
Criteria
Marchevsky and Walts criteria - both 1 & 2 are required:[5]
- Three or more separate small airways pulmonary neuroendocrine cell clusters.
- Each cluster should have five or more pulmonary neuroendocrine cells.
- Three or more carcinoid tumourlets.
Notes:
- The Marchevsky and Walts definition is not universally accepted.
- World Health Organization (WHO) definition is vague.
Gross
- Multiple small pulmonary nodules.[1]
DDx:
Microscopic
See also
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 Wirtschafter, E.; Walts, AE.; Liu, ST.; Marchevsky, AM. (Jun 2015). "Diffuse Idiopathic Pulmonary Neuroendocrine Cell Hyperplasia of the Lung (DIPNECH): Current Best Evidence.". Lung. doi:10.1007/s00408-015-9755-1. PMID 26104490.
- ↑ Tippett, VM.; Wathen, CG. (2010). "Diffuse idiopathic neuroendocrine cell hyperplasia: an unusual cause of breathlessness and pulmonary nodules.". BMJ Case Rep 2010. doi:10.1136/bcr.05.2010.3006. PMID 22798306.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 Davies, SJ.; Gosney, JR.; Hansell, DM.; Wells, AU.; du Bois, RM.; Burke, MM.; Sheppard, MN.; Nicholson, AG. (Mar 2007). "Diffuse idiopathic pulmonary neuroendocrine cell hyperplasia: an under-recognised spectrum of disease.". Thorax 62 (3): 248-52. doi:10.1136/thx.2006.063065. PMID 17099078.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 Chauhan, A.; Ramirez, RA. (Jun 2015). "Diffuse Idiopathic Pulmonary Neuroendocrine Cell Hyperplasia (DIPNECH) and the Role of Somatostatin analogs: A Case Series.". Lung. doi:10.1007/s00408-015-9754-2. PMID 26112453.
- ↑ Marchevsky, AM.; Walts, AE. (Nov 2015). "Diffuse idiopathic pulmonary neuroendocrine cell hyperplasia (DIPNECH).". Semin Diagn Pathol 32 (6): 438-44. doi:10.1053/j.semdp.2015.08.002. PMID 26472691.