Difference between revisions of "Bullous diseases"
(→Pemphigoid gestationis: added a case) |
|||
| (37 intermediate revisions by one other user not shown) | |||
| Line 2: | Line 2: | ||
An introduction to skin pathology is in the ''[[dermatopathology]]'' article. An introduction to inflammatory skin lesions in the ''[[non-malignant skin disease]]'' article. | An introduction to skin pathology is in the ''[[dermatopathology]]'' article. An introduction to inflammatory skin lesions in the ''[[non-malignant skin disease]]'' article. | ||
Bullous disease of the [[lung]] is dealt with in ''[[lung bullae]]''. | |||
=Overview= | =Overview= | ||
| Line 7: | Line 9: | ||
===Subcorneal bullous disorders=== | ===Subcorneal bullous disorders=== | ||
DDx '''with''' acantholysis:<ref name=pmid18418089>{{cite journal |author=Brinster NK |title=Dermatopathology for the surgical pathologist: a pattern based approach to the diagnosis of inflammatory skin disorders (part I) |journal=Adv Anat Pathol |volume=15 |issue=2 |pages=76–96 |year=2008 |month=March |pmid=18418089 |doi=10.1097/PAP.0b013e3181664e8d |url=}}</ref> | DDx '''with''' acantholysis:<ref name=pmid18418089>{{cite journal |author=Brinster NK |title=Dermatopathology for the surgical pathologist: a pattern based approach to the diagnosis of inflammatory skin disorders (part I) |journal=Adv Anat Pathol |volume=15 |issue=2 |pages=76–96 |year=2008 |month=March |pmid=18418089 |doi=10.1097/PAP.0b013e3181664e8d |url=}}</ref> | ||
*[[Pemphigus | *[[Pemphigus foliaceus]]. | ||
*[[Bullous impetigo]]. | *[[Bullous impetigo]]. | ||
*[[ | *[[Staphylococcal scalded skin syndrome]]. | ||
DDx '''without''' acantholysis:DDx:<ref name=pmid18418089/> | DDx '''without''' acantholysis:DDx:<ref name=pmid18418089/> | ||
| Line 22: | Line 24: | ||
*[[Darier disease]]. | *[[Darier disease]]. | ||
*[[Grover disease]] (transient acantholytic dermatosis). | *[[Grover disease]] (transient acantholytic dermatosis). | ||
Memory device - ''PhD'' + ''Grover'' = '''P'''emphigus vulgaris, '''H'''ailey-Hailey, '''D'''arier, '''G'''rover. | |||
===Subepidermal bullous disorders=== | ===Subepidermal bullous disorders=== | ||
DDx:<ref name=pmid18418089/> | DDx:<ref name=pmid18418089/> | ||
*[[Bullous pemphigoid]]. | *[[Bullous pemphigoid]]. | ||
*Cicatricial pemphigoid. | *[[Cicatricial pemphigoid]]. | ||
*[[Porphyria cutanea tarda]]. | *[[Porphyria cutanea tarda]]. | ||
*Epidermolysis bullosa acquista. | *[[Epidermolysis bullosa acquista]]. | ||
*[[Dermatitis | *[[Dermatitis herpetiformis]]. | ||
*Linear IgA disease. | *Linear IgA disease. | ||
| Line 36: | Line 40: | ||
*Coma blister. | *Coma blister. | ||
*Bullous [[systemic lupus erythematosus]]. | *Bullous [[systemic lupus erythematosus]]. | ||
Mnemonic ''DELPHI'': | |||
*[[dermatitis herpetiformis|'''D'''ermatitis herpetiformis]]. | |||
*'''E'''pidermolysis bullosa acquisita. | |||
*Bullous '''l'''upus erythematosis. | |||
*'''P'''emphigoid, bullous. | |||
*'''H'''erpes gestationis (now called ''[[pemphigoid gestationis]]'') - rare autoimmune bullous dermatosis of pregnancy, not related to HSV.<ref>URL: [http://emedicine.medscape.com/article/1063499-overview http://emedicine.medscape.com/article/1063499-overview]. Accessed on: 23 September 2011.</ref> | |||
*Linear '''I'''gA disease. | |||
=Specific diseases= | =Specific diseases= | ||
==Pemphigus foliaceus== | |||
===General=== | |||
*Autoimmune disease.<ref name=pmid21605805>{{Cite journal | last1 = James | first1 = KA. | last2 = Culton | first2 = DA. | last3 = Diaz | first3 = LA. | title = Diagnosis and clinical features of pemphigus foliaceus. | journal = Dermatol Clin | volume = 29 | issue = 3 | pages = 405-12, viii | month = Jul | year = 2011 | doi = 10.1016/j.det.2011.03.012 | PMID = 21605805 }}</ref> | |||
**Autoantibodies against ''desmoglein 1'' only. | |||
Note: | |||
*[[Pemphigus vulgaris]] has autoantibodies against ''desmoglein 1'' and ''desmoglein 3''.<ref name=omim169615>{{OMIM|169615}}</ref> | |||
===Microscopic=== | |||
Features: | |||
*Subcorneal separation. | |||
*[[Acantholysis]]. | |||
**Separation of keratinocytes. | |||
DDx: | |||
*[[Staphylococcal scalded skin syndrome]]. | |||
*[[Bullous impetigo]]. | |||
===IF=== | |||
*Desmoglein 1 - abnormal. | |||
==Bullous pemphigoid== | ==Bullous pemphigoid== | ||
===General=== | ===General=== | ||
| Line 45: | Line 78: | ||
*Old people (60-80 year olds). | *Old people (60-80 year olds). | ||
Clinical | Clinical: | ||
*Extreme pruritis. | *Extreme pruritis. | ||
Etiology: | Etiology: | ||
*Antibodies to BPAG2. | *Antibodies to BPAG2 (a hemidesmosome protein).<ref name=Ref_PCPBoD8_607>{{Ref PCPBoD8|607}}</ref> | ||
Notes: | |||
*[[Pemphigus vulgaris]] = subepidermal. | |||
*[[Pemphigus foliaceus]] = intraepidermal. | |||
===Microscopic=== | ===Microscopic=== | ||
| Line 61: | Line 98: | ||
*Epidermis not affect, i.e. non-acantholytic. | *Epidermis not affect, i.e. non-acantholytic. | ||
*Linear Ig deposits along basement membrane. | *Linear Ig deposits along basement membrane. | ||
*Early changes may be that of a ''[[dermal perivascular lymphoeosinophilic infiltration]]''. | |||
Images: | Images: | ||
| Line 68: | Line 106: | ||
DDx: | DDx: | ||
*Bullous lupus. | *Bullous lupus. | ||
*[[Dermal perivascular lymphoeosinophilic infiltration]]. | |||
==Pemphigus vulgaris== | ==Pemphigus vulgaris== | ||
*[[AKA]] ''pemphigus''. | *[[AKA]] ''pemphigus''. | ||
===General=== | ===General=== | ||
*May lead to blindness. | |||
*Oral lesion is classically: ''first to show & last to go''. | |||
**Oral lesions usually precede the skin lesions. | |||
Classic presentation: | Classic presentation: | ||
*Mouth lesions. | *Mouth lesions. | ||
| Line 82: | Line 125: | ||
*Associated with [[thymoma]], myasthenia gravis, malignancy & D-penicillamine (used to Tx [[Wilson's disease]]). | *Associated with [[thymoma]], myasthenia gravis, malignancy & D-penicillamine (used to Tx [[Wilson's disease]]). | ||
*Middle age. | *Middle age. | ||
Etiology: | |||
*Autoimmune disease. | |||
**Antibodies against: ''desmoglein 1'' (DSG1)<ref name=omim125670>{{OMIM|125670}}</ref> and ''desmoglein 3'' (DSG3).<ref name=omim169615>{{OMIM|169615}}</ref> | |||
===Microscopic=== | ===Microscopic=== | ||
| Line 87: | Line 134: | ||
*Suprabasilar blistering. | *Suprabasilar blistering. | ||
DDx: Hailey-Hailey disease. | DDx: | ||
*[[Hailey-Hailey disease]]. | |||
*[[Darier disease]]. | |||
*[[Grover disease]]. | |||
Images: | Images: | ||
*[http://www.dermpedia.org/files/images/pemphigus_vulgaris_3.jpg PV (dermpedia.org)].<ref>URL: [http://www.dermpedia.org/baby-dermpedia-for-beginners/pemphigus-vulgaris http://www.dermpedia.org/baby-dermpedia-for-beginners/pemphigus-vulgaris]. Accessed on: 20 March 2011.</ref> | *[http://www.dermpedia.org/files/images/pemphigus_vulgaris_3.jpg PV (dermpedia.org)].<ref>URL: [http://www.dermpedia.org/baby-dermpedia-for-beginners/pemphigus-vulgaris http://www.dermpedia.org/baby-dermpedia-for-beginners/pemphigus-vulgaris]. Accessed on: 20 March 2011.</ref> | ||
*[http://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Pemphigus_vulgaris_-_intermed_mag.jpg Pemphigus vulgaris - intermed. mag. (WC)]. | |||
*[http://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Pemphigus_vulgaris_-_high_mag.jpg Pemphigus vulgaris - high mag. (WC)]. | |||
===IF=== | |||
*Desmoglein 1 | *Desmoglein 1 - abnormal. | ||
*Desmoglein 3 - abnormal. | |||
==Familial benign pemphigus== | ==Familial benign pemphigus== | ||
| Line 104: | Line 157: | ||
Clinical: | Clinical: | ||
*Chest. | *Chest. | ||
*Intertriginous regions | *Intertriginous regions (only) - where skin rubs together, e.g. skin folds of the breast, axilla. | ||
*Typically presents individual in their 30s and 40s.<ref name=emed_hailey/> | *Typically presents individual in their 30s and 40s.<ref name=emed_hailey/> | ||
| Line 110: | Line 163: | ||
Features: | Features: | ||
*Suprabasilar blistering. | *Suprabasilar blistering. | ||
*Acanthosis (thick epidermis). | *[[Acanthosis]] (thick epidermis). | ||
Notes: | Notes: | ||
| Line 168: | Line 221: | ||
Images: | Images: | ||
*[http://www.dermpedia.org/files/images/Image1_4.jpg Subepidermal blistering with thick vessels (dermpedia.org)]. | *[http://www.dermpedia.org/files/images/Image1_4.jpg Subepidermal blistering with thick vessels (dermpedia.org)]. | ||
==Epidermolysis bullosa acquisita== | |||
*Abbreviated ''EBA'' | |||
===General=== | |||
*Autoimmune disease. | |||
**Antibodies to collagen type VII.<ref>URL: [http://emedicine.medscape.com/article/1063083-overview http://emedicine.medscape.com/article/1063083-overview]. Accessed on: 25 September 2011.</ref> | |||
===Microscopic=== | |||
Features: | |||
*Subepidermal bullae. | |||
==Epidermolysis bullosa== | ==Epidermolysis bullosa== | ||
* | ===General=== | ||
*A group of inherited, bullous disorders. | |||
*Bullae form due to slight mechanical trauma. | |||
Three major groupings:<ref>URL: [http://emedicine.medscape.com/article/1062939-overview http://emedicine.medscape.com/article/1062939-overview]. Accessed on: 25 September 2011.</ref> | |||
#Epidermolysis bullosa simplex (intraepidermal disease). | |||
#Junctional epidermolysis bullosa (separation at DE junction; specifically central portion (lamina lucida)). | |||
#Dystrophic epidermolysis bullosa (separation at DE junction; specifically deep to lamina densa). | |||
===Microscopic=== | |||
Depends on subtype - either intraepidermal ''or'' subepidermal. | |||
==Grover disease== | ==Grover disease== | ||
*[[AKA]] transient acantholytic dermatosis. | *[[AKA]] ''transient acantholytic dermatosis''. | ||
===General=== | ===General=== | ||
* | *Cause not known. | ||
*Associated with sun damaged skin, hospitalization and fever.<ref name=pmid15068451>{{Cite journal | last1 = Quirk | first1 = CJ. | last2 = Heenan | first2 = PJ. | title = Grover's disease: 34 years on. | journal = Australas J Dermatol | volume = 45 | issue = 2 | pages = 83-6; quiz 87-8 | month = May | year = 2004 | doi = 10.1111/j.1440-0960.2004.054_1.x | PMID = 15068451 }}</ref> | |||
Clinical:<ref name=pmid16939188>{{Cite journal | last1 = Hanson | first1 = M. | last2 = Hsu | first2 = S. | title = Pruritic papules on the chest and back. Grover's disease. | journal = Am Fam Physician | volume = 74 | issue = 4 | pages = 641-2 | month = Aug | year = 2006 | doi = | PMID = 16939188 | url = http://www.aafp.org/afp/2006/0815/p641.html }}</ref> | |||
*Pruritis (itchy). | |||
*Usually self-limited. | |||
*Treatment for symptoms. | |||
===Gross=== | |||
*Usually small ~ 50% less than 2 mm.<ref name=pmid20526170>{{Cite journal | last1 = Fernández-Figueras | first1 = MT. | last2 = Puig | first2 = L. | last3 = Cannata | first3 = P. | last4 = Cuatrecases | first4 = M. | last5 = Quer | first5 = A. | last6 = Ferrándiz | first6 = C. | last7 = Ariza | first7 = A. | title = Grover disease: a reappraisal of histopathological diagnostic criteria in 120 cases. | journal = Am J Dermatopathol | volume = 32 | issue = 6 | pages = 541-9 | month = Aug | year = 2010 | doi = 10.1097/DAD.0b013e3181c80cf9 | PMID = 20526170 }}</ref> | |||
*Typically chest and back.<ref>{{Ref APBR|344 Q2</ref> | |||
===Microscopic=== | ===Microscopic=== | ||
| Line 183: | Line 267: | ||
*Acanthosis. | *Acanthosis. | ||
*Dyskeratosis. | *Dyskeratosis. | ||
DDx:<ref name=pmid10089990>{{Cite journal | last1 = Davis | first1 = MD. | last2 = Dinneen | first2 = AM. | last3 = Landa | first3 = N. | last4 = Gibson | first4 = LE. | title = Grover's disease: clinicopathologic review of 72 cases. | journal = Mayo Clin Proc | volume = 74 | issue = 3 | pages = 229-34 | month = Mar | year = 1999 | doi = 10.4065/74.3.229 | PMID = 10089990 }}</ref> | |||
#[[Pemphigus vulgaris]]. | |||
#[[Darier disease]]. | |||
====Images==== | |||
<gallery> | |||
Image:Transient acantholytic dermatosis - intermed mag.jpg | Grover disease - intermed. mag. (WC) | |||
Image:Transient_acantholytic_dermatosis_-_high_mag.jpg | Grover disease - high mag. (WC) | |||
Image:Transient_acantholytic_dermatosis_-_very_high_mag.jpg | Grover disease - very high mag. (WC) | |||
</gallery> | |||
==Acute generalized exanthematous pustulosis== | |||
*Abbreviated ''AGEP''. | |||
*[[AKA]] pustular drug eruption. | |||
===General=== | |||
*Drug reaction. | |||
Clinical DDx: | |||
*[[Erythema multiforme]]. | |||
*[[Stevens-Johnson syndrome]] (SJS) / [[toxic epidermal necrolysis]] (TEN). | |||
===Microscopic=== | |||
Features: | |||
*Superficial dermis separates from underlying tissue. (???) | |||
DDx: | |||
*[[Staphylococcal scalded skin syndrome]]. | |||
Images: | |||
*[http://www.dermpedia.org/case/acute-generalized-exanthematous-pustulosis AGEP (dermpedia.org)]. | |||
==Pemphigoid gestationis== | |||
*[[AKA]] ''gestational pemphigoid''. | |||
*Previously ''herpes gestationis''. | |||
===General=== | |||
*Autoimmune condition in pregnancy. | |||
**Autoantibodies against XVII collagen.<ref name=pmid21605810>{{Cite journal | last1 = Intong | first1 = LR. | last2 = Murrell | first2 = DF. | title = Pemphigoid gestationis: pathogenesis and clinical features. | journal = Dermatol Clin | volume = 29 | issue = 3 | pages = 447-52, ix | month = Jul | year = 2011 | doi = 10.1016/j.det.2011.03.002 | PMID = 21605810 }}</ref> | |||
**Fetus affected in ~5-10% of cases.<ref name=pmid17263216>{{Cite journal | last1 = Tunzi | first1 = M. | last2 = Gray | first2 = GR. | title = Common skin conditions during pregnancy. | journal = Am Fam Physician | volume = 75 | issue = 2 | pages = 211-8 | month = Jan | year = 2007 | doi = | PMID = 17263216 | URL = http://www.aafp.org/afp/2007/0115/p211.html }}</ref> | |||
*Rare - est. 1/50,000 pregnancies.<ref name=pmid18506459>{{Cite journal | last1 = Bedocs | first1 = PM. | last2 = Kumar | first2 = V. | last3 = Mahon | first3 = MJ. | title = Pemphigoid gestationis: a rare case and review. | journal = Arch Gynecol Obstet | volume = 279 | issue = 2 | pages = 235-8 | month = Feb | year = 2009 | doi = 10.1007/s00404-008-0687-3 | PMID = 18506459 }}</ref> | |||
Treatment: | |||
*Corticosteroids.<ref name=pmid21877502/> | |||
===Microscopic=== | |||
Features: | |||
*Subepidermal bullous disease.<ref>{{Cite journal | last1 = Kolanko | first1 = E. | last2 = Bickle | first2 = K. | last3 = Keehn | first3 = C. | last4 = Glass | first4 = LF. | title = Subepidermal blistering disorders: a clinical and histopathologic review. | journal = Semin Cutan Med Surg | volume = 23 | issue = 1 | pages = 10-8 | month = Mar | year = 2004 | doi = | PMID = 15095911 }}</ref> | |||
*Eosinophils - abundant. | |||
====Images==== | |||
<gallery> | |||
Image:Pemphigoid_gestationis_-_low_mag.jpg | PG - low mag. (WC) | |||
Image:Pemphigoid_gestationis_-_high_mag.jpg | PG - high mag. (WC) | |||
Image:Pemphigoid_gestationis_-_very_high_mag.jpg | PG - very high mag. (WC) | |||
</gallery> | |||
===IF=== | |||
*C3 linear pattern at DE junction - diagnostic.<ref name=pmid21877502>{{Cite journal | last1 = Campbell | first1 = SM. | last2 = Balazs | first2 = K. | last3 = Conroy | first3 = M. | title = Pemphigoid gestationis: a case report and review of the literature. | journal = Cutis | volume = 88 | issue = 1 | pages = 21-6 | month = Jul | year = 2011 | doi = | PMID = 21877502 }}</ref> | |||
==Bullous Arthropod Assault== | |||
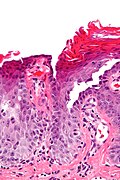
[[File:30MR17 dp sl 1.png|Bullous arthropod assault]] | |||
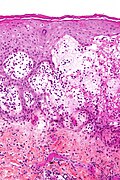
[[File:30MR17 dp sl 2.png|Bullous arthropod assault]] | |||
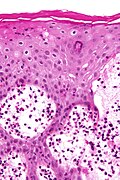
[[File:30MR17 dp sl 3.png|Bullous arthropod assault]]<br> | |||
Bullous arthropod assault. A. Beneath intraepidermal blistering lies superficial and deep inflammation with extension into fat. B. The vesicle shows spongiotic epidermis at base and multiple eosinophils. C. Eosinophils are prominent in dermal and adipose tissue inflammation. | |||
=See also= | =See also= | ||
Latest revision as of 18:20, 31 March 2017
Bullous diseases are a subset of the large inflammatory skin diseases category. Dermatopathologists help diagnose it.
An introduction to skin pathology is in the dermatopathology article. An introduction to inflammatory skin lesions in the non-malignant skin disease article.
Bullous disease of the lung is dealt with in lung bullae.
Overview
DDx based on type
Subcorneal bullous disorders
DDx with acantholysis:[1]
DDx without acantholysis:DDx:[1]
- Subcorneal pustular dermatosis (Sneddon-Wilkinson disease)
- Pustular psoriasis.
- Pustular drug eruption (acute generalized exanthematous pustulosis).
Suprabasilar bullous disorders
DDx:[1]
- Pemphigus vulgaris.
- Hailey-Hailey disease (benign familial pemphigus).
- Darier disease.
- Grover disease (transient acantholytic dermatosis).
Memory device - PhD + Grover = Pemphigus vulgaris, Hailey-Hailey, Darier, Grover.
Subepidermal bullous disorders
DDx:[1]
- Bullous pemphigoid.
- Cicatricial pemphigoid.
- Porphyria cutanea tarda.
- Epidermolysis bullosa acquista.
- Dermatitis herpetiformis.
- Linear IgA disease.
Others:
- Insect bite.
- Coma blister.
- Bullous systemic lupus erythematosus.
Mnemonic DELPHI:
- Dermatitis herpetiformis.
- Epidermolysis bullosa acquisita.
- Bullous lupus erythematosis.
- Pemphigoid, bullous.
- Herpes gestationis (now called pemphigoid gestationis) - rare autoimmune bullous dermatosis of pregnancy, not related to HSV.[2]
- Linear IgA disease.
Specific diseases
Pemphigus foliaceus
General
- Autoimmune disease.[3]
- Autoantibodies against desmoglein 1 only.
Note:
- Pemphigus vulgaris has autoantibodies against desmoglein 1 and desmoglein 3.[4]
Microscopic
Features:
- Subcorneal separation.
- Acantholysis.
- Separation of keratinocytes.
DDx:
IF
- Desmoglein 1 - abnormal.
Bullous pemphigoid
General
- Less serious than pemphigus vulgaris.
Epidemiology:
- Old people (60-80 year olds).
Clinical:
- Extreme pruritis.
Etiology:
- Antibodies to BPAG2 (a hemidesmosome protein).[5]
Notes:
- Pemphigus vulgaris = subepidermal.
- Pemphigus foliaceus = intraepidermal.
Microscopic
Features:[6]
- Subepidermal blisters.
- +/-Lymphocytes.
- +/-Eosinophils.
- +/-Neutrophils.
Notes:
- Epidermis not affect, i.e. non-acantholytic.
- Linear Ig deposits along basement membrane.
- Early changes may be that of a dermal perivascular lymphoeosinophilic infiltration.
Images:
DDx:
- Bullous lupus.
- Dermal perivascular lymphoeosinophilic infiltration.
Pemphigus vulgaris
- AKA pemphigus.
General
- May lead to blindness.
- Oral lesion is classically: first to show & last to go.
- Oral lesions usually precede the skin lesions.
Classic presentation:
- Mouth lesions.
- Non-pruritic.
Treatment:
- Prednisone then steroid sparing agent.
Epidemiology:
- Associated with thymoma, myasthenia gravis, malignancy & D-penicillamine (used to Tx Wilson's disease).
- Middle age.
Etiology:
Microscopic
Features:[10]
- Suprabasilar blistering.
DDx:
Images:
- PV (dermpedia.org).[11]
- Pemphigus vulgaris - intermed. mag. (WC).
- Pemphigus vulgaris - high mag. (WC).
IF
- Desmoglein 1 - abnormal.
- Desmoglein 3 - abnormal.
Familial benign pemphigus
- AKA Hailey-Hailey disease. Was described by two brothers - that's why it is Hailey-Hailey.[12]
General
- Genetic - autosomal dominant with incomplete penetration.[12]
- Desmosomal defect - due to mutation in the gene ATP2C1.[12]
Clinical:
- Chest.
- Intertriginous regions (only) - where skin rubs together, e.g. skin folds of the breast, axilla.
- Typically presents individual in their 30s and 40s.[12]
Microscopic
Features:
- Suprabasilar blistering.
- Acanthosis (thick epidermis).
Notes:
- Hair folicles spared.
DDx:
Dermatitis herpetiformis
General
- Associated with celiac sprue.
Clinical:
- Pruritis - intense.
Microscopic
Features:[13]
- Subepidermal blistering.
- Clusters of neurophils (microabscesses) - at tips of dermal papillae - key feature.
- Basal cell injury (vacuolization).
Notes:
- Immunofluorescence - IgA deposits at dermal papillae.
Images:
Porphyria cutanea tarda
General
Etiology:
- Genetic, autosomal dominant.
Treatment:
- D/C aggravating substances (see below) - phlebotomy, hydroxychloroquine if phlebotomy contraindicated.
Note:
- Fits into a larger category of porphyria.
Associations
Medications/substances:
Non-infection chronic conditions:
- DM.
Infections:
Gross
- In photoexposed areas subjected to trauma.
Microscopic
Features:[15]
- Subepidermal vesicles.
- Thickening of superficial dermal blood vessels.
Images:
Epidermolysis bullosa acquisita
- Abbreviated EBA
General
- Autoimmune disease.
- Antibodies to collagen type VII.[16]
Microscopic
Features:
- Subepidermal bullae.
Epidermolysis bullosa
General
- A group of inherited, bullous disorders.
- Bullae form due to slight mechanical trauma.
Three major groupings:[17]
- Epidermolysis bullosa simplex (intraepidermal disease).
- Junctional epidermolysis bullosa (separation at DE junction; specifically central portion (lamina lucida)).
- Dystrophic epidermolysis bullosa (separation at DE junction; specifically deep to lamina densa).
Microscopic
Depends on subtype - either intraepidermal or subepidermal.
Grover disease
- AKA transient acantholytic dermatosis.
General
- Cause not known.
- Associated with sun damaged skin, hospitalization and fever.[18]
Clinical:[19]
- Pruritis (itchy).
- Usually self-limited.
- Treatment for symptoms.
Gross
Microscopic
Features:[22]
- Subcorneal bullous disease.
- Acanthosis.
- Dyskeratosis.
DDx:[23]
Images
Acute generalized exanthematous pustulosis
- Abbreviated AGEP.
- AKA pustular drug eruption.
General
- Drug reaction.
Clinical DDx:
- Erythema multiforme.
- Stevens-Johnson syndrome (SJS) / toxic epidermal necrolysis (TEN).
Microscopic
Features:
- Superficial dermis separates from underlying tissue. (???)
DDx:
Images:
Pemphigoid gestationis
- AKA gestational pemphigoid.
- Previously herpes gestationis.
General
- Autoimmune condition in pregnancy.
- Rare - est. 1/50,000 pregnancies.[26]
Treatment:
- Corticosteroids.[27]
Microscopic
Features:
- Subepidermal bullous disease.[28]
- Eosinophils - abundant.
Images
IF
- C3 linear pattern at DE junction - diagnostic.[27]
Bullous Arthropod Assault


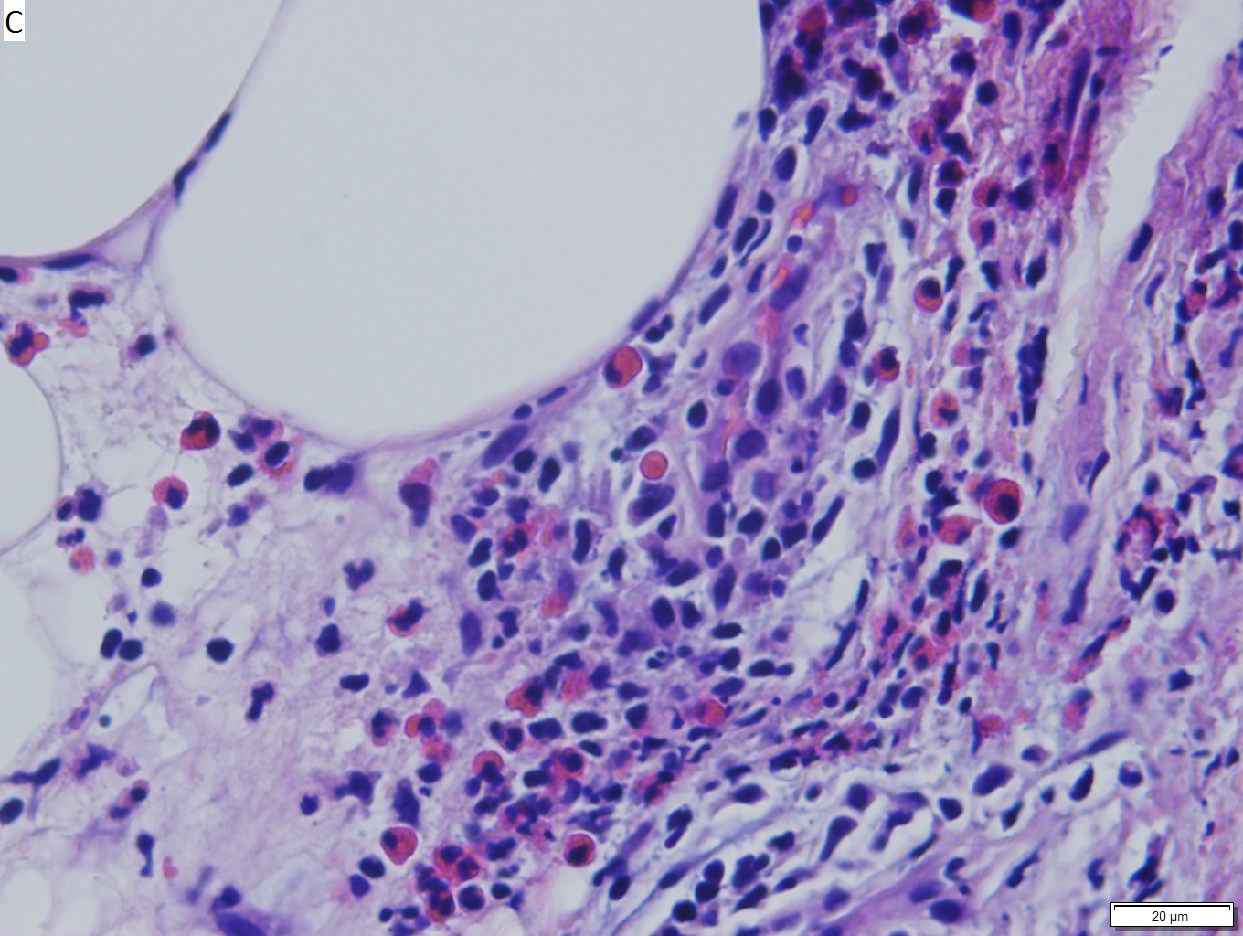
Bullous arthropod assault. A. Beneath intraepidermal blistering lies superficial and deep inflammation with extension into fat. B. The vesicle shows spongiotic epidermis at base and multiple eosinophils. C. Eosinophils are prominent in dermal and adipose tissue inflammation.
See also
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 Brinster NK (March 2008). "Dermatopathology for the surgical pathologist: a pattern based approach to the diagnosis of inflammatory skin disorders (part I)". Adv Anat Pathol 15 (2): 76–96. doi:10.1097/PAP.0b013e3181664e8d. PMID 18418089.
- ↑ URL: http://emedicine.medscape.com/article/1063499-overview. Accessed on: 23 September 2011.
- ↑ James, KA.; Culton, DA.; Diaz, LA. (Jul 2011). "Diagnosis and clinical features of pemphigus foliaceus.". Dermatol Clin 29 (3): 405-12, viii. doi:10.1016/j.det.2011.03.012. PMID 21605805.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 Online 'Mendelian Inheritance in Man' (OMIM) 169615
- ↑ Mitchell, Richard; Kumar, Vinay; Fausto, Nelson; Abbas, Abul K.; Aster, Jon (2011). Pocket Companion to Robbins & Cotran Pathologic Basis of Disease (8th ed.). Elsevier Saunders. pp. 607. ISBN 978-1416054542.
- ↑ Kumar, Vinay; Abbas, Abul K.; Fausto, Nelson; Aster, Jon (2009). Robbins and Cotran pathologic basis of disease (8th ed.). Elsevier Saunders. pp. 1195. ISBN 978-1416031215.
- ↑ URL: http://dermatology.cdlib.org/94/NYU/Feb2002/8.html. Accessed on: 20 March 2011.
- ↑ URL: http://missinglink.ucsf.edu/lm/DermatologyGlossary/bullous_pemphigoid.html. Accessed on: 20 March 2011.
- ↑ Online 'Mendelian Inheritance in Man' (OMIM) 125670
- ↑ Kumar, Vinay; Abbas, Abul K.; Fausto, Nelson; Aster, Jon (2009). Robbins and Cotran pathologic basis of disease (8th ed.). Elsevier Saunders. pp. 1193. ISBN 978-1416031215.
- ↑ URL: http://www.dermpedia.org/baby-dermpedia-for-beginners/pemphigus-vulgaris. Accessed on: 20 March 2011.
- ↑ 12.0 12.1 12.2 12.3 URL: http://emedicine.medscape.com/article/1063224-overview. Accessed on: 9 September 2011.
- ↑ Kumar, Vinay; Abbas, Abul K.; Fausto, Nelson; Aster, Jon (2009). Robbins and Cotran pathologic basis of disease (8th ed.). Elsevier Saunders. pp. 1196. ISBN 978-1416031215.
- ↑ URL: http://dermatology.cdlib.org/94/NYU/Nov2001/9.html. Accessed on: 21 March 2011.
- ↑ Kumar, Vinay; Abbas, Abul K.; Fausto, Nelson; Aster, Jon (2009). Robbins and Cotran pathologic basis of disease (8th ed.). Elsevier Saunders. pp. 1197. ISBN 978-1416031215.
- ↑ URL: http://emedicine.medscape.com/article/1063083-overview. Accessed on: 25 September 2011.
- ↑ URL: http://emedicine.medscape.com/article/1062939-overview. Accessed on: 25 September 2011.
- ↑ Quirk, CJ.; Heenan, PJ. (May 2004). "Grover's disease: 34 years on.". Australas J Dermatol 45 (2): 83-6; quiz 87-8. doi:10.1111/j.1440-0960.2004.054_1.x. PMID 15068451.
- ↑ Hanson, M.; Hsu, S. (Aug 2006). "Pruritic papules on the chest and back. Grover's disease.". Am Fam Physician 74 (4): 641-2. PMID 16939188. http://www.aafp.org/afp/2006/0815/p641.html.
- ↑ Fernández-Figueras, MT.; Puig, L.; Cannata, P.; Cuatrecases, M.; Quer, A.; Ferrándiz, C.; Ariza, A. (Aug 2010). "Grover disease: a reappraisal of histopathological diagnostic criteria in 120 cases.". Am J Dermatopathol 32 (6): 541-9. doi:10.1097/DAD.0b013e3181c80cf9. PMID 20526170.
- ↑ {{Ref APBR|344 Q2
- ↑ S. Sade. 8 September 2011.
- ↑ Davis, MD.; Dinneen, AM.; Landa, N.; Gibson, LE. (Mar 1999). "Grover's disease: clinicopathologic review of 72 cases.". Mayo Clin Proc 74 (3): 229-34. doi:10.4065/74.3.229. PMID 10089990.
- ↑ Intong, LR.; Murrell, DF. (Jul 2011). "Pemphigoid gestationis: pathogenesis and clinical features.". Dermatol Clin 29 (3): 447-52, ix. doi:10.1016/j.det.2011.03.002. PMID 21605810.
- ↑ Tunzi, M.; Gray, GR. (Jan 2007). "Common skin conditions during pregnancy.". Am Fam Physician 75 (2): 211-8. PMID 17263216.
- ↑ Bedocs, PM.; Kumar, V.; Mahon, MJ. (Feb 2009). "Pemphigoid gestationis: a rare case and review.". Arch Gynecol Obstet 279 (2): 235-8. doi:10.1007/s00404-008-0687-3. PMID 18506459.
- ↑ 27.0 27.1 Campbell, SM.; Balazs, K.; Conroy, M. (Jul 2011). "Pemphigoid gestationis: a case report and review of the literature.". Cutis 88 (1): 21-6. PMID 21877502.
- ↑ Kolanko, E.; Bickle, K.; Keehn, C.; Glass, LF. (Mar 2004). "Subepidermal blistering disorders: a clinical and histopathologic review.". Semin Cutan Med Surg 23 (1): 10-8. PMID 15095911.