Difference between revisions of "Testicular adrenal rest tumour"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
(→IHC) |
|||
| (13 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
'''Testicular adrenal rest tumour''', abbreviated '''TART''', is a rare tumour associated with increased ACTH, typically seen in the context of congenital adrenal hyperplasia.<ref name=pmid24967019>{{Cite journal | last1 = Olpin | first1 = JD. | last2 = Witt | first2 = B. | title = Testicular adrenal rest tumors in a patient with congenital adrenal hyperplasia. | journal = J Radiol Case Rep | volume = 8 | issue = 2 | pages = 46-53 | month = Feb | year = 2014 | doi = 10.3941/jrcr.v8i2.1489 | PMID = 24967019 }}</ref> | {{ Infobox diagnosis | ||
| Name = {{PAGENAME}} | |||
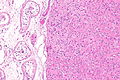
| Image = Testicular adrenal rest tumour -- intermed. mag.jpg | |||
| Width = | |||
| Caption = Testicular adrenal rest tumour. [[H&E stain]]. | |||
| Synonyms = | |||
| Micro = nests of eosinophilic cells interspersed with thin bands of fibrous tissue, mild (endocrine) [[nuclear atypia]] | |||
| Subtypes = | |||
| LMDDx = [[Leydig cell tumour]], [[adrenal cortical rest]] | |||
| Stains = | |||
| IHC = melan A +ve | |||
| EM = | |||
| Molecular = | |||
| IF = | |||
| Gross = | |||
| Grossing = | |||
| Site = [[testis]] | |||
| Assdx = congenital adrenal hyperplasia | |||
| Syndromes = | |||
| Clinicalhx = | |||
| Signs = testicular masses (bilateral) | |||
| Symptoms = | |||
| Prevalence = extremely rare | |||
| Bloodwork = serum ACTH elevated | |||
| Rads = | |||
| Endoscopy = | |||
| Prognosis = benign | |||
| Other = | |||
| ClinDDx = other testicular masses | |||
| Tx = | |||
}} | |||
'''Testicular adrenal rest tumour''', abbreviated '''TART''', is a rare tumour associated with increased adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH), typically seen in the context of congenital adrenal hyperplasia.<ref name=pmid24967019>{{Cite journal | last1 = Olpin | first1 = JD. | last2 = Witt | first2 = B. | title = Testicular adrenal rest tumors in a patient with congenital adrenal hyperplasia. | journal = J Radiol Case Rep | volume = 8 | issue = 2 | pages = 46-53 | month = Feb | year = 2014 | doi = 10.3941/jrcr.v8i2.1489 | PMID = 24967019 }}</ref> | |||
==General== | ==General== | ||
*Very rare. | *Very rare. | ||
*Benign.<ref name=pmid25485724>{{Cite journal | last1 = Smeets | first1 = EE. | last2 = Span | first2 = PN. | last3 = van Herwaarden | first3 = AE. | last4 = Wevers | first4 = RA. | last5 = Hermus | first5 = AR. | last6 = Sweep | first6 = FC. | last7 = Claahsen-van der Grinten | first7 = HL. | title = Molecular characterization of testicular adrenal rest tumors in congenital adrenal hyperplasia: lesions with both adrenocortical and Leydig cell features. | journal = J Clin Endocrinol Metab | volume = 100 | issue = 3 | pages = E524-30 | month = Mar | year = 2015 | doi = 10.1210/jc.2014-2036 | PMID = 25485724 }}</ref> | |||
*May overlap with [[Leydig cell tumour]] - see ''molecular'' section. | |||
*Associated with ''congenital adrenal hyperplasia'' (abbreviated ''CAH''). | |||
**Due to mutation in CYP21A2.<ref name=pmid19531083>{{Cite journal | last1 = Mouritsen | first1 = A. | last2 = Jørgensen | first2 = N. | last3 = Main | first3 = KM. | last4 = Schwartz | first4 = M. | last5 = Juul | first5 = A. | title = Testicular adrenal rest tumours in boys, adolescents and adult men with congenital adrenal hyperplasia may be associated with the CYP21A2 mutation. | journal = Int J Androl | volume = 33 | issue = 3 | pages = 521-7 | month = Jun | year = 2010 | doi = 10.1111/j.1365-2605.2009.00967.x | PMID = 19531083 }}</ref> | |||
**TART prevalence increases with age - one study suggests moderate prevalance at age 10, increasing to 100% of individuals with CAH over 16 years of age.<ref>{{Cite journal | last1 = Claahsen-van der Grinten | first1 = HL. | last2 = Dehzad | first2 = F. | last3 = Kamphuis-van Ulzen | first3 = K. | last4 = de Korte | first4 = CL. | title = Increased prevalence of testicular adrenal rest tumours during adolescence in congenital adrenal hyperplasia. | journal = Horm Res Paediatr | volume = 82 | issue = 4 | pages = 238-44 | month = | year = 2014 | doi = 10.1159/000365570 | PMID = 25195868 }}</ref> | |||
Clinical: | Clinical: | ||
| Line 17: | Line 53: | ||
DDx: | DDx: | ||
*[[Leydig cell tumour]] - history different. | *[[Leydig cell tumour]] - history different. | ||
*[[Adrenal cortical rest]] - architecture different, not a sizable mass lesion and not bilateral.{{fact}} | |||
===Images=== | ===Images=== | ||
====www==== | |||
*[http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4037253/figure/f4-jrcr-8-2-46/ TART (nih.gov)]. | *[http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4037253/figure/f4-jrcr-8-2-46/ TART (nih.gov)]. | ||
====Case==== | |||
<gallery> | |||
Image: Testicular adrenal rest tumour -- low mag.jpg | TART - low mag. (WC) | |||
Image: Testicular adrenal rest tumour -- intermed. mag.jpg | Image: Testicular adrenal rest tumour -- high mag.jpg | TART - high mag. (WC) | |||
Image: Testicular adrenal rest tumour - alt -- intermed. mag.jpg | TART - intermed. mag. (WC) | |||
Image: Testicular adrenal rest tumour -- high mag.jpg | TART - high mag. (WC) | |||
Image: Testicular adrenal rest tumour -- very high mag.jpg | TART - very high mag. (WC) | |||
Image: Testicular adrenal rest tumour - alt -- high mag.jpg | TART - high mag. (WC) | |||
Image: Testicular adrenal rest tumour - alt -- very high mag.jpg | TART - very high mag. (WC) | |||
</gallery> | |||
==IHC== | ==IHC== | ||
*Melan A +ve.<ref name=pmid20951518>{{Cite journal | last1 = Mizukami | first1 = H. | last2 = Hamamatsu | first2 = A. | last3 = Mori | first3 = S. | last4 = Hara | first4 = S. | last5 = Kuroda | first5 = M. | last6 = Nagai | first6 = T. | last7 = Fukunaga | first7 = T. | title = Autopsy and genetic diagnosis of 21-hydroxylase deficiency with bilateral testicular tumors in a case under no medication for over one year. | journal = Forensic Sci Int | volume = 206 | issue = 1-3 | pages = e71-5 | month = Mar | year = 2011 | doi = 10.1016/j.forsciint.2010.09.017 | PMID = 20951518 }}</ref> | *Melan A +ve.<ref name=pmid20951518>{{Cite journal | last1 = Mizukami | first1 = H. | last2 = Hamamatsu | first2 = A. | last3 = Mori | first3 = S. | last4 = Hara | first4 = S. | last5 = Kuroda | first5 = M. | last6 = Nagai | first6 = T. | last7 = Fukunaga | first7 = T. | title = Autopsy and genetic diagnosis of 21-hydroxylase deficiency with bilateral testicular tumors in a case under no medication for over one year. | journal = Forensic Sci Int | volume = 206 | issue = 1-3 | pages = e71-5 | month = Mar | year = 2011 | doi = 10.1016/j.forsciint.2010.09.017 | PMID = 20951518 }}</ref> | ||
*CD56 +ve.<ref name=pmid23984262>{{Cite journal | last1 = Ali | first1 = HH. | last2 = Samkari | first2 = A. | last3 = Arabi | first3 = H. | title = Testicular adrenal rest "tumor" or Leydig cell tumor? A report of a challenging case with literature review. | journal = Avicenna J Med | volume = 3 | issue = 1 | pages = 15-9 | month = Jan | year = 2013 | doi = 10.4103/2231-0770.112789 | PMID = 23984262 }}</ref> | |||
*AR -ve.<ref name=pmid23984262/> | |||
==Molecular== | |||
*Molecular characteristics are in keeping with [[adrenal gland|adrenal tissue]]; however, some Leydig cell markers active.<ref name=pmid25485724>{{Cite journal | last1 = Smeets | first1 = EE. | last2 = Span | first2 = PN. | last3 = van Herwaarden | first3 = AE. | last4 = Wevers | first4 = RA. | last5 = Hermus | first5 = AR. | last6 = Sweep | first6 = FC. | last7 = Claahsen-van der Grinten | first7 = HL. | title = Molecular characterization of testicular adrenal rest tumors in congenital adrenal hyperplasia: lesions with both adrenocortical and Leydig cell features. | journal = J Clin Endocrinol Metab | volume = 100 | issue = 3 | pages = E524-30 | month = Mar | year = 2015 | doi = 10.1210/jc.2014-2036 | PMID = 25485724 }}</ref> | |||
*Mutation in CYP21A2 causative of congenital adrenal hyperplasia.<ref name=pmid19531083/> | |||
==See also== | ==See also== | ||
| Line 28: | Line 83: | ||
==References== | ==References== | ||
{{Reflist| | {{Reflist|2}} | ||
[[Category:Diagnosis]] | [[Category:Diagnosis]] | ||
[[Category:Testis]] | [[Category:Testis]] | ||
Latest revision as of 21:51, 25 May 2016
| Testicular adrenal rest tumour | |
|---|---|
| Diagnosis in short | |
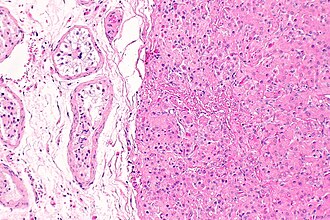 Testicular adrenal rest tumour. H&E stain. | |
|
| |
| LM | nests of eosinophilic cells interspersed with thin bands of fibrous tissue, mild (endocrine) nuclear atypia |
| LM DDx | Leydig cell tumour, adrenal cortical rest |
| IHC | melan A +ve |
| Site | testis |
|
| |
| Associated Dx | congenital adrenal hyperplasia |
| Signs | testicular masses (bilateral) |
| Prevalence | extremely rare |
| Blood work | serum ACTH elevated |
| Prognosis | benign |
| Clin. DDx | other testicular masses |
Testicular adrenal rest tumour, abbreviated TART, is a rare tumour associated with increased adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH), typically seen in the context of congenital adrenal hyperplasia.[1]
General
- Very rare.
- Benign.[2]
- May overlap with Leydig cell tumour - see molecular section.
- Associated with congenital adrenal hyperplasia (abbreviated CAH).
Clinical:
- Serum ACTH elevated.
Gross
- Bilateral testicular masses.
Microscopic
Features:
- Nests of eosinophilic cells interspersed with thin bands of fibrous tissue.
- Mild (endocrine) nuclear atypia.
DDx:
- Leydig cell tumour - history different.
- Adrenal cortical rest - architecture different, not a sizable mass lesion and not bilateral.[citation needed]
Images
www
Case
IHC
Molecular
- Molecular characteristics are in keeping with adrenal tissue; however, some Leydig cell markers active.[2]
- Mutation in CYP21A2 causative of congenital adrenal hyperplasia.[3]
See also
References
- ↑ Olpin, JD.; Witt, B. (Feb 2014). "Testicular adrenal rest tumors in a patient with congenital adrenal hyperplasia.". J Radiol Case Rep 8 (2): 46-53. doi:10.3941/jrcr.v8i2.1489. PMID 24967019.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 Smeets, EE.; Span, PN.; van Herwaarden, AE.; Wevers, RA.; Hermus, AR.; Sweep, FC.; Claahsen-van der Grinten, HL. (Mar 2015). "Molecular characterization of testicular adrenal rest tumors in congenital adrenal hyperplasia: lesions with both adrenocortical and Leydig cell features.". J Clin Endocrinol Metab 100 (3): E524-30. doi:10.1210/jc.2014-2036. PMID 25485724.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 Mouritsen, A.; Jørgensen, N.; Main, KM.; Schwartz, M.; Juul, A. (Jun 2010). "Testicular adrenal rest tumours in boys, adolescents and adult men with congenital adrenal hyperplasia may be associated with the CYP21A2 mutation.". Int J Androl 33 (3): 521-7. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2605.2009.00967.x. PMID 19531083.
- ↑ Claahsen-van der Grinten, HL.; Dehzad, F.; Kamphuis-van Ulzen, K.; de Korte, CL. (2014). "Increased prevalence of testicular adrenal rest tumours during adolescence in congenital adrenal hyperplasia.". Horm Res Paediatr 82 (4): 238-44. doi:10.1159/000365570. PMID 25195868.
- ↑ Mizukami, H.; Hamamatsu, A.; Mori, S.; Hara, S.; Kuroda, M.; Nagai, T.; Fukunaga, T. (Mar 2011). "Autopsy and genetic diagnosis of 21-hydroxylase deficiency with bilateral testicular tumors in a case under no medication for over one year.". Forensic Sci Int 206 (1-3): e71-5. doi:10.1016/j.forsciint.2010.09.017. PMID 20951518.
- ↑ 6.0 6.1 Ali, HH.; Samkari, A.; Arabi, H. (Jan 2013). "Testicular adrenal rest "tumor" or Leydig cell tumor? A report of a challenging case with literature review.". Avicenna J Med 3 (1): 15-9. doi:10.4103/2231-0770.112789. PMID 23984262.