Difference between revisions of "Anaplastic astrocytoma"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
Jensflorian (talk | contribs) (to be continued) |
Jensflorian (talk | contribs) (continued - molecular data is still missing) |
||
| Line 7: | Line 7: | ||
WHO 2016 categorization combines morphology and genetics into following groups:<ref>{{Cite journal | last1 = Louis | first1 = DN. | last2 = Perry | first2 = A. | last3 = Reifenberger | first3 = G. | last4 = von Deimling | first4 = A. | last5 = Figarella-Branger | first5 = D. | last6 = Cavenee | first6 = WK. | last7 = Ohgaki | first7 = H. | last8 = Wiestler | first8 = OD. | last9 = Kleihues | first9 = P. | title = The 2016 World Health Organization Classification of Tumors of the Central Nervous System: a summary. | journal = Acta Neuropathol | volume = 131 | issue = 6 | pages = 803-20 | month = Jun | year = 2016 | doi = 10.1007/s00401-016-1545-1 | PMID = 27157931 }}</ref> | WHO 2016 categorization combines morphology and genetics into following groups:<ref>{{Cite journal | last1 = Louis | first1 = DN. | last2 = Perry | first2 = A. | last3 = Reifenberger | first3 = G. | last4 = von Deimling | first4 = A. | last5 = Figarella-Branger | first5 = D. | last6 = Cavenee | first6 = WK. | last7 = Ohgaki | first7 = H. | last8 = Wiestler | first8 = OD. | last9 = Kleihues | first9 = P. | title = The 2016 World Health Organization Classification of Tumors of the Central Nervous System: a summary. | journal = Acta Neuropathol | volume = 131 | issue = 6 | pages = 803-20 | month = Jun | year = 2016 | doi = 10.1007/s00401-016-1545-1 | PMID = 27157931 }}</ref> | ||
*Anaplastic astrocytoma, IDH-mutant (ICD-O: 9401/3). | *Anaplastic astrocytoma, IDH-mutant (ICD-O: 9401/3). | ||
*Anaplastic astrocytoma, IDH-wildtype (ICD-O: | *Anaplastic astrocytoma, IDH-wildtype (ICD-O: 9401/3). | ||
*Anaplastic astrocytoma,NOS (ICD-O: | *Anaplastic astrocytoma,NOS (ICD-O: 9401/3) - genetic data missing. | ||
==Radiology/Clinic== | ==Radiology/Clinic== | ||
| Line 16: | Line 16: | ||
*The majority are contrast-enhanching, T2 bright. | *The majority are contrast-enhanching, T2 bright. | ||
==Prognosis== | |||
*Overall prognosis is rather poor (average survival 2-3 years). | |||
*IDH-mutant tumors share a similiar prognosis to grade II IDH-mutant tumors.<ref>{{Cite journal | last1 = Reuss | first1 = DE. | last2 = Mamatjan | first2 = Y. | last3 = Schrimpf | first3 = D. | last4 = Capper | first4 = D. | last5 = Hovestadt | first5 = V. | last6 = Kratz | first6 = A. | last7 = Sahm | first7 = F. | last8 = Koelsche | first8 = C. | last9 = Korshunov | first9 = A. | title = IDH mutant diffuse and anaplastic astrocytomas have similar age at presentation and little difference in survival: a grading problem for WHO. | journal = Acta Neuropathol | volume = 129 | issue = 6 | pages = 867-73 | month = Jun | year = 2015 | doi = 10.1007/s00401-015-1438-8 | PMID = 25962792 }}</ref> | |||
*Anaplastic astrocytoma, IDH-wildtype perform worse than glioblastoma, IDH-mutant despite grading differences.<ref>{{Cite journal | last1 = Hartmann | first1 = C. | last2 = Hentschel | first2 = B. | last3 = Wick | first3 = W. | last4 = Capper | first4 = D. | last5 = Felsberg | first5 = J. | last6 = Simon | first6 = M. | last7 = Westphal | first7 = M. | last8 = Schackert | first8 = G. | last9 = Meyermann | first9 = R. | title = Patients with IDH1 wild type anaplastic astrocytomas exhibit worse prognosis than IDH1-mutated glioblastomas, and IDH1 mutation status accounts for the unfavorable prognostic effect of higher age: implications for classification of gliomas. | journal = Acta Neuropathol | volume = 120 | issue = 6 | pages = 707-18 | month = Dec | year = 2010 | doi = 10.1007/s00401-010-0781-z | PMID = 21088844 }}</ref> | |||
==Macroscopy== | ==Macroscopy== | ||
*No clear demarcation from white matter. | *No clear demarcation from white matter. | ||
| Line 21: | Line 26: | ||
*Softer consistency and opacity. | *Softer consistency and opacity. | ||
*No necrosis. | *No necrosis. | ||
==Histology== | |||
Features: <ref name=AFIP2007>{{Ref AFIP2007|34}}</ref> | |||
*Increased cellularity (compared to [[Diffuse Astrocytoma]]). | |||
**Specimens with low cellularity but plenty mitoses are also considered anaplastic. | |||
*Distinct nuclear atypia and pleomorphism. | |||
**May include multinucleated cells. | |||
*Cytoplasm highly variable (even within the same tumour). | |||
*Mitoses present (a single mitosis in a small specimen indicates a high-grade tumor). | |||
*Microcystic spaces of the background (none to extensive). | |||
*No necrosis, no vascular proliferations. | |||
**Except radiation necrosis after pretreatment. | |||
*Lymphocytic cuffing (mostly in gemistocytic type). | |||
*Rosenthal fibers usu. absent. | |||
<gallery> | |||
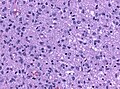
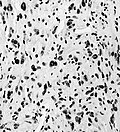
File:Mitoses_astro_III.jpg | Marked mitotic activity in anaplastic astrocytoma (WC/jensflorian). | |||
File:405551M-ANAPLASTIC_ASTROCYTOMA.jpg | Marked nuclear pleomorphism (AFIP). | |||
</gallery> | |||
==IHC== | |||
*[[GFAP]]+ve. | |||
*[[MAP2]]+ve (especially in cell processes). | |||
*Vimentin+ve (often perinuclear). | |||
*S-100+ve. | |||
*MIB-1: usu. 5-10& (overlaps with grade II tumors). | |||
*[[IDH-1]] (R132H)+ve in 60-70%. | |||
**'Note:'' This antibody does not detect other rare IDH1/2 mutations. | |||
*[[ATRX]] nuclear loss in 70%. | |||
==DDx== | |||
*[[Diffuse astrocytoma]] - absent or very low mitotic activity. | |||
*Anaplastic [[Oligoastrocytoma]], NOS - esp. when genetic data on IDH and LOH 1p/19q are lacking. | |||
*Anaplastic [[Oligodendroglioma]], when LOH 1p/19q is present. | |||
*[[Glioblastoma]] - vascular proliferations and / or necrosis. | |||
Revision as of 14:33, 19 May 2016
Anaplastic astrocytoma (AKA: high-grade astrocytoma) is a infiltrating neoplasm of the diffuse astrocytic and oligodendroglial tumor group occurring in the CNS white matter.
- Most common grade III WHO glioma in adults (peaks between 40-50 years).
- Approx 5% of all gliomas.[1]
- Usually shows progression to glioblastoma sooner or later.
WHO 2016 categorization combines morphology and genetics into following groups:[2]
- Anaplastic astrocytoma, IDH-mutant (ICD-O: 9401/3).
- Anaplastic astrocytoma, IDH-wildtype (ICD-O: 9401/3).
- Anaplastic astrocytoma,NOS (ICD-O: 9401/3) - genetic data missing.
Radiology/Clinic
- Mass effect.
- Seizures.
- Neurologic decifit.
- The majority are contrast-enhanching, T2 bright.
Prognosis
- Overall prognosis is rather poor (average survival 2-3 years).
- IDH-mutant tumors share a similiar prognosis to grade II IDH-mutant tumors.[3]
- Anaplastic astrocytoma, IDH-wildtype perform worse than glioblastoma, IDH-mutant despite grading differences.[4]
Macroscopy
- No clear demarcation from white matter.
- Invaded structures may appear enlarged.
- Softer consistency and opacity.
- No necrosis.
Histology
Features: [5]
- Increased cellularity (compared to Diffuse Astrocytoma).
- Specimens with low cellularity but plenty mitoses are also considered anaplastic.
- Distinct nuclear atypia and pleomorphism.
- May include multinucleated cells.
- Cytoplasm highly variable (even within the same tumour).
- Mitoses present (a single mitosis in a small specimen indicates a high-grade tumor).
- Microcystic spaces of the background (none to extensive).
- No necrosis, no vascular proliferations.
- Except radiation necrosis after pretreatment.
- Lymphocytic cuffing (mostly in gemistocytic type).
- Rosenthal fibers usu. absent.
IHC
- GFAP+ve.
- MAP2+ve (especially in cell processes).
- Vimentin+ve (often perinuclear).
- S-100+ve.
- MIB-1: usu. 5-10& (overlaps with grade II tumors).
- IDH-1 (R132H)+ve in 60-70%.
- 'Note: This antibody does not detect other rare IDH1/2 mutations.
- ATRX nuclear loss in 70%.
DDx
- Diffuse astrocytoma - absent or very low mitotic activity.
- Anaplastic Oligoastrocytoma, NOS - esp. when genetic data on IDH and LOH 1p/19q are lacking.
- Anaplastic Oligodendroglioma, when LOH 1p/19q is present.
- Glioblastoma - vascular proliferations and / or necrosis.
- ↑ Ohgaki, H.; Kleihues, P. (Jun 2005). "Population-based studies on incidence, survival rates, and genetic alterations in astrocytic and oligodendroglial gliomas.". J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 64 (6): 479-89. PMID 15977639.
- ↑ Louis, DN.; Perry, A.; Reifenberger, G.; von Deimling, A.; Figarella-Branger, D.; Cavenee, WK.; Ohgaki, H.; Wiestler, OD. et al. (Jun 2016). "The 2016 World Health Organization Classification of Tumors of the Central Nervous System: a summary.". Acta Neuropathol 131 (6): 803-20. doi:10.1007/s00401-016-1545-1. PMID 27157931.
- ↑ Reuss, DE.; Mamatjan, Y.; Schrimpf, D.; Capper, D.; Hovestadt, V.; Kratz, A.; Sahm, F.; Koelsche, C. et al. (Jun 2015). "IDH mutant diffuse and anaplastic astrocytomas have similar age at presentation and little difference in survival: a grading problem for WHO.". Acta Neuropathol 129 (6): 867-73. doi:10.1007/s00401-015-1438-8. PMID 25962792.
- ↑ Hartmann, C.; Hentschel, B.; Wick, W.; Capper, D.; Felsberg, J.; Simon, M.; Westphal, M.; Schackert, G. et al. (Dec 2010). "Patients with IDH1 wild type anaplastic astrocytomas exhibit worse prognosis than IDH1-mutated glioblastomas, and IDH1 mutation status accounts for the unfavorable prognostic effect of higher age: implications for classification of gliomas.". Acta Neuropathol 120 (6): 707-18. doi:10.1007/s00401-010-0781-z. PMID 21088844.
- ↑ Burger, P.C.; Scheithauer, B.W. (2007). Tumors of the Central Nervous System (Afip Atlas of Tumor Pathology) (4th ed.). Washington: American Registry of Pathology. pp. 34. ISBN 1933477016.