Difference between revisions of "Organizing pneumonia"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
(→Images) |
|||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{ Infobox diagnosis | {{ Infobox diagnosis | ||
| Name = {{PAGENAME}} | | Name = {{PAGENAME}} | ||
| Image = | | Image = Organizing pneumonia -- low mag.jpg | ||
| Width = | | Width = | ||
| Caption = | | Caption = Organizing pneumonia. [[H&E stain]]. | ||
| Synonyms = | | Synonyms = | ||
| Micro = distal airway disease -- airways plugged with organizing exudate (fluffy light-staining paucicellular regions with stellate cells); no hobnailing of pneumocytes; type 2 pneumocytes hyperplasia is absent | | Micro = distal airway disease -- airways plugged with organizing exudate (fluffy light-staining paucicellular regions with stellate cells); no hobnailing of pneumocytes; type 2 pneumocytes hyperplasia is absent | ||
| Line 61: | Line 61: | ||
===Images=== | ===Images=== | ||
<gallery> | |||
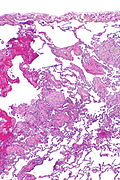
Image: Organizing pneumonia -- very low mag.jpg | OP - very low mag. (WC/Nephron) | |||
Image: Organizing pneumonia -- low mag.jpg | OP - low mag. (WC/Nephron) | |||
Image: Organizing pneumonia - alt -- low mag.jpg | OP - low mag. (WC/Nephron) | |||
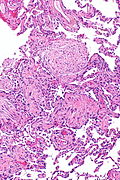
Image: Organizing pneumonia - alt - intermed mag.jpg | OP - intermed. mag. (WC/Nephron) | |||
Image: Organizing pneumonia -- intermed mag.jpg | OP - intermed. mag. (WC/Nephron) | |||
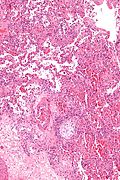
Image: Organizing pneumonia -- high mag.jpg | OP - high mag. (WC/Nephron) | |||
</gallery> | |||
===Masson body=== | |||
<gallery> | <gallery> | ||
Image:Masson_body_-_intermed_mag.jpg | Masson body - intermed. mag. (WC/Nephron) | Image:Masson_body_-_intermed_mag.jpg | Masson body - intermed. mag. (WC/Nephron) | ||
Revision as of 03:43, 27 March 2016
| Organizing pneumonia | |
|---|---|
| Diagnosis in short | |
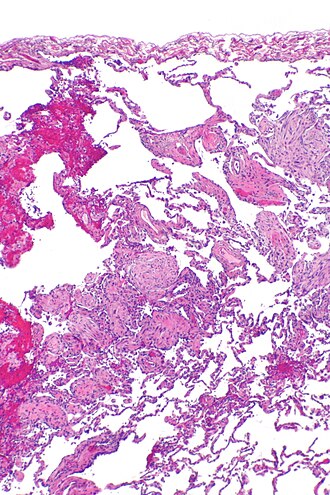 Organizing pneumonia. H&E stain. | |
|
| |
| LM | distal airway disease -- airways plugged with organizing exudate (fluffy light-staining paucicellular regions with stellate cells); no hobnailing of pneumocytes; type 2 pneumocytes hyperplasia is absent |
| LM DDx | diffuse alveolar damage (proliferative phase), bronchiolitis obliterans. |
| Site | lung - diffuse lung diseases |
|
| |
| Prevalence | uncommon |
| Prognosis | dependent on underlying cause |
| Clin. DDx | cryptogenic organizing pneumonia, transplant rejection, infection (pneumonia), collagen vascular disease, peri-tumour |
| Treatment | dependent on underlying cause |
Organizing pneumonia, abbreviated OP, is a histologic pattern in lung pathology. It fits into the larger category of diffuse lung diseases.
General
- Multiple causes, e.g. transplant rejection, infection.
Clinical diagnoses:[1]
- Transplant rejection.
- Cryptogenic organizing pneumonia (COP), AKA (idiopathic) bronchiolitis obliterans organizing pneumonia (BOOP).
- Should not be confused with constrictive bronchiolitis (AKA bronchiolitis obliterans).
- Collagen vascular disease.
- Toxic injury.
- Infection.
- Peri-tumour - in proximity to a space-occupying lesion (abscess, neoplasm).
Note:
- BOOP is used as a synonym for organizing pneumonia which has the long differential diagnosis above.[1]
- Confusingly, it may be used to refer to the idiopathic form of organizing pneumonia, now generally known as cryptogenic organizing pneumonia (COP).
- In other words, strictly speaking, BOOP is not the same as COP; idiopathic BOOP is COP.
- Confusingly, it may be used to refer to the idiopathic form of organizing pneumonia, now generally known as cryptogenic organizing pneumonia (COP).
Microscopic
Features:[2]
- Distal airway disease -- airways plugged with organizing exudate ("Masson bodies").
- "Organized exudate" = fluffy light-staining paucicellular regions with stellate cells (fibroblasts & immature connective tissue).
- No hobnailing of pneumocytes.
- Type 2 pneumocytes hyperplasia is absent.
DDx:
- Diffuse alveolar damage, proliferative phase - has type 2 pneumoncyte hyperplasia.
- Bronchiolitis obliterans.
Images
Masson body
www:
See also
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 Humphrey, Peter A; Dehner, Louis P; Pfeifer, John D (2008). The Washington Manual of Surgical Pathology (1st ed.). Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. pp. 91. ISBN 978-0781765275.
- ↑ Klatt, Edward C. (2006). Robbins and Cotran Atlas of Pathology (1st ed.). Saunders. pp. 110. ISBN 978-1416002741.