Difference between revisions of "Germ cell neoplasia in situ"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
| (13 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 3: | Line 3: | ||
| Image = Intratubular germ cell neoplasia - 2 - very high mag.jpg | | Image = Intratubular germ cell neoplasia - 2 - very high mag.jpg | ||
| Width = | | Width = | ||
| Caption = | | Caption = GCNIS (left of image). [[H&E stain]]. | ||
| Synonyms = | | Synonyms = intratubular germ cell neoplasia (old term) | ||
| Micro = "large" round or polygonal nuclei, prominent nucleoli, clear cytoplasm, +/-cells (completely) fill the tubule | | Micro = "large" round or polygonal nuclei, prominent nucleoli, clear cytoplasm, +/-cells (completely) fill the tubule | ||
| Subtypes = undifferentiated, differentiated (intratubular seminoma, intratubular | | Subtypes = undifferentiated, differentiated (intratubular seminoma, intratubular non-seminoma) | ||
| LMDDx = [[seminoma]], [[embryonal carcinoma]], Sertoli cell-only syndrome | | LMDDx = [[seminoma]], [[embryonal carcinoma]], Sertoli cell-only syndrome, [[mixed germ cell tumour]] | ||
| Stains = | | Stains = | ||
| IHC = PLAP +ve, | | IHC = OCT4, PLAP +ve, D2-40 +ve | ||
| EM = | | EM = | ||
| Molecular = | | Molecular = | ||
| Line 30: | Line 30: | ||
| Tx = radiotherapy (?) | | Tx = radiotherapy (?) | ||
}} | }} | ||
''' | '''Germ cell neoplasia in situ''', abbreviated '''GCNIS''', is a premalignant lesion of the [[testis]]. | ||
It | It was previously known previously known as '''intratubular germ cell neoplasia''' (abbreviated '''ITGCN''') and '''testicular intraepithelial neoplasia'''.<ref name=pmid23293116 >{{Cite journal | last1 = Dieckmann | first1 = KP. | last2 = Wilken | first2 = S. | last3 = Loy | first3 = V. | last4 = Matthies | first4 = C. | last5 = Kleinschmidt | first5 = K. | last6 = Bedke | first6 = J. | last7 = Martinschek | first7 = A. | last8 = Souchon | first8 = R. | last9 = Pichlmeier | first9 = U. | title = Treatment of testicular intraepithelial neoplasia (intratubular germ cell neoplasia unspecified) with local radiotherapy or with platinum-based chemotherapy: a survey of the German Testicular Cancer Study Group. | journal = Ann Oncol | volume = 24 | issue = 5 | pages = 1332-7 | month = May | year = 2013 | doi = 10.1093/annonc/mds628 | PMID = 23293116 }}</ref><ref name=pmid26918959>{{Cite journal | last1 = Berney | first1 = DM. | last2 = Looijenga | first2 = L. | last3 = Idrees | first3 = M. | last4 = Oosterhuis | first4 = JW. | last5 = Rajpert-De Meyts | first5 = E. | last6 = Ulbright | first6 = TM. | last7 = Skakkebaek | first7 = NE. | title = Germ Cell Neoplasia In Situ (GCNIS). Evolution of the Current Nomenclature for Testicular Pre-invasive Germ Cell Malignancy. | journal = Histopathology | volume = | issue = | pages = | month = Feb | year = 2016 | doi = 10.1111/his.12958 | PMID = 26918959 }}</ref> | ||
==General== | ==General== | ||
| Line 38: | Line 38: | ||
*Not all germ cell tumours (GCTs) arise from ''intratubular germ cell neoplasia''. | *Not all germ cell tumours (GCTs) arise from ''intratubular germ cell neoplasia''. | ||
The following testicular GCTs do not arise from | The following testicular GCTs do not arise from GCNIS: | ||
*[[Spermatocytic | *[[Spermatocytic tumour]].<ref name=pmid2837162>{{cite journal |author=Müller J, Skakkebaek NE, Parkinson MC |title=The spermatocytic seminoma: views on pathogenesis |journal=Int. J. Androl. |volume=10 |issue=1 |pages=147–56 |year=1987 |month=February |pmid=3583416 |doi= |url=}}</ref> | ||
*[[Yolk sac tumour]]s (endodermal sinus tumour).<ref>{{cite journal |author=Manivel JC, Simonton S, Wold LE, Dehner LP |title=Absence of intratubular germ cell neoplasia in testicular yolk sac tumors in children. A histochemical and immunohistochemical study |journal=Arch. Pathol. Lab. Med. |volume=112 |issue=6 |pages=641–5 |year=1988 |month=June |pmid=2837162 |doi= |url=}}</ref> | *[[Yolk sac tumour]]s (endodermal sinus tumour).<ref>{{cite journal |author=Manivel JC, Simonton S, Wold LE, Dehner LP |title=Absence of intratubular germ cell neoplasia in testicular yolk sac tumors in children. A histochemical and immunohistochemical study |journal=Arch. Pathol. Lab. Med. |volume=112 |issue=6 |pages=641–5 |year=1988 |month=June |pmid=2837162 |doi= |url=}}</ref> | ||
*Teratoma.{{Fact}} | *Teratoma.{{Fact}} | ||
Classification:<ref name=pmid11900581/> | Classification:<ref name=pmid11900581/> | ||
*Undifferentiated | *Undifferentiated GCNIS. | ||
*Differentiated | *Differentiated GCNIS.<ref name=pmid17592271>{{Cite journal | last1 = Lau | first1 = SK. | last2 = Weiss | first2 = LM. | last3 = Chu | first3 = PG. | title = Association of intratubular seminoma and intratubular embryonal carcinoma with invasive testicular germ cell tumors. | journal = Am J Surg Pathol | volume = 31 | issue = 7 | pages = 1045-9 | month = Jul | year = 2007 | doi = 10.1097/PAS.0b013e31802b8712 | PMID = 17592271 }}</ref> | ||
**''Intratubular seminoma.'' | **''Intratubular seminoma.'' | ||
**''Intratubular non-seminoma''. | |||
Treatment: | Treatment: | ||
| Line 59: | Line 59: | ||
**Polygonal nuclei = squared-off nuclear membrane. | **Polygonal nuclei = squared-off nuclear membrane. | ||
*Prominent nucleoli - '''key feature'''. | *Prominent nucleoli - '''key feature'''. | ||
*Clear cytoplasm. | *Clear cytoplasm - '''important'''. | ||
*+/-Cells fill the tubule. | *+/-Cells fill the tubule. | ||
Note: | |||
*Sertoli cells may have a nucleolus... but they have eosinophilic ctyoplasm.{{fact}} | |||
DDx: | DDx: | ||
*Sertoli cell-only syndrome - Sertoli cells also have nucleoli, wind swept appearance.<ref>URL: [http://www.webpathology.com/image.asp?n=3&Case=28 http://www.webpathology.com/image.asp?n=3&Case=28]. Accessed on: 25 March 2013.</ref> | *Sertoli cell-only syndrome - Sertoli cells also have nucleoli, wind swept appearance.<ref>URL: [http://www.webpathology.com/image.asp?n=3&Case=28 http://www.webpathology.com/image.asp?n=3&Case=28]. Accessed on: 25 March 2013.</ref> | ||
*[[Seminoma]]. | *[[Seminoma]] - especially intratubular predominant growth pattern. | ||
*[[Embryonal carcinoma]]. | *[[Embryonal carcinoma]]. | ||
*[[Mixed germ cell tumour]]. | |||
===Images=== | ===Images=== | ||
====Case 1==== | |||
<gallery> | <gallery> | ||
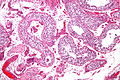
Image: Intratubular germ cell neoplasia - intermed mag.jpg | ITGCN - intermed. mag. | Image: Intratubular germ cell neoplasia - intermed mag.jpg | GCNIS (ITGCN) - intermed. mag. | ||
Image: Intratubular germ cell neoplasia - high mag.jpg | ITGCN - high mag. | Image: Intratubular germ cell neoplasia - high mag.jpg | GCNIS (ITGCN) - high mag. | ||
Image: Intratubular germ cell neoplasia - very high mag.jpg | ITGCN - very high mag. | Image: Intratubular germ cell neoplasia - very high mag.jpg | GCNIS (ITGCN) - very high mag. | ||
Image: Intratubular germ cell neoplasia - 2 - very high mag.jpg | ITGCN - very high mag. | Image: Intratubular germ cell neoplasia - 2 - very high mag.jpg | GCNIS (ITGCN) - very high mag. | ||
</gallery> | </gallery> | ||
====Case 2==== | |||
<gallery> | <gallery> | ||
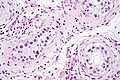
Image:Intratubular_germ_cell_neoplasia_high_mag_cropped.jpg | ITGCN - cropped. (WC/Nephron) | Image:Intratubular_germ_cell_neoplasia_high_mag_cropped.jpg | GCNIS (ITGCN) - cropped. (WC/Nephron) | ||
Image:Intratubular_germ_cell_neoplasia_high_mag.jpg | ITGCN. (WC/Nephron) | Image:Intratubular_germ_cell_neoplasia_high_mag.jpg | GCNIS (ITGCN). (WC/Nephron) | ||
</gallery> | </gallery> | ||
www | ====Case 3==== | ||
<gallery> | |||
Image: ITGCN and Sertoli cells only -- intermed mag.jpg | GCNIS (ITGCN) & SCO - intermed. mag. | |||
Image: ITGCN and Sertoli cells only -- high mag.jpg | GCNIS (ITGCN) & SCO - high mag. | |||
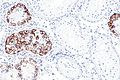
Image: ITGCN and Sertoli cells only - PLAP -- intermed mag.jpg | GCNIS (ITGCN) & SCO - intermed. mag. | |||
Image: ITGCN and Sertoli cells only - PLAP -- high mag.jpg | GCNIS (ITGCN) & SCO - high mag. | |||
Image: ITGCN and Sertoli cells only - PLAP -- very high mag.jpg | GCNIS (ITGCN) & SCO - very high mag. | |||
</gallery> | |||
====www==== | |||
*[http://www.webpathology.com/image.asp?case=30&n=1 ITGCN (webpathology.com)]. | *[http://www.webpathology.com/image.asp?case=30&n=1 ITGCN (webpathology.com)]. | ||
*[http://www.archivesofpathology.org/na101/home/literatum/publisher/pinnacle/journals/content/arpa/2002/15432165-126.4/0003-9985%282002%29126%3C0487%3Aiec%3E2.0.co%3B2/production/images/large/i1543-2165-126-4-487-f01.jpeg Intratubular embryonal carcinoma (archivesofpathology.org)].<ref name=pmid11900581/> | *[http://www.archivesofpathology.org/na101/home/literatum/publisher/pinnacle/journals/content/arpa/2002/15432165-126.4/0003-9985%282002%29126%3C0487%3Aiec%3E2.0.co%3B2/production/images/large/i1543-2165-126-4-487-f01.jpeg Intratubular embryonal carcinoma (archivesofpathology.org)].<ref name=pmid11900581/> | ||
| Line 84: | Line 99: | ||
==IHC== | ==IHC== | ||
===ISUP consensus=== | ===ISUP consensus=== | ||
ITGCN versus atypical intratubular germ cells:<ref name=pmid25025364>{{Cite journal | last1 = Amin | first1 = MB. | last2 = Epstein | first2 = JI. | last3 = Ulbright | first3 = TM. | last4 = Humphrey | first4 = PA. | last5 = Egevad | first5 = L. | last6 = Montironi | first6 = R. | last7 = Grignon | first7 = D. | last8 = Trpkov | first8 = K. | last9 = Lopez-Beltran | first9 = A. | title = Best practices recommendations in the application of immunohistochemistry in urologic pathology: report from the international society of urological pathology consensus conference. | journal = Am J Surg Pathol | volume = 38 | issue = 8 | pages = 1017-22 | month = Aug | year = 2014 | doi = 10.1097/PAS.0000000000000254 | PMID = 25025364 }}</ref> | GCNIS (ITGCN) versus atypical intratubular germ cells:<ref name=pmid25025364>{{Cite journal | last1 = Amin | first1 = MB. | last2 = Epstein | first2 = JI. | last3 = Ulbright | first3 = TM. | last4 = Humphrey | first4 = PA. | last5 = Egevad | first5 = L. | last6 = Montironi | first6 = R. | last7 = Grignon | first7 = D. | last8 = Trpkov | first8 = K. | last9 = Lopez-Beltran | first9 = A. | title = Best practices recommendations in the application of immunohistochemistry in urologic pathology: report from the international society of urological pathology consensus conference. | journal = Am J Surg Pathol | volume = 38 | issue = 8 | pages = 1017-22 | month = Aug | year = 2014 | doi = 10.1097/PAS.0000000000000254 | PMID = 25025364 }}</ref> | ||
*OCT4 +ve. | *OCT4 +ve. | ||
Alternates: | Alternates: | ||
*[[PLAP]] +ve.<ref>{{Cite journal | last1 = Schreiber | first1 = L. | last2 = Lifschitz-Mercer | first2 = B. | last3 = Paz | first3 = G. | last4 = Yavetz | first4 = H. | last5 = Elliott | first5 = DJ. | last6 = Kula | first6 = K. | last7 = Slowikowska-Hilczer | first7 = J. | last8 = Maymon | first8 = BB. | title = Double immunolabeling by the RBM and the PLAP markers for identifying intratubular (in situ) germ cell neoplasia of the testis. | journal = Int J Surg Pathol | volume = 11 | issue = 1 | pages = 17-20 | month = Jan | year = 2003 | doi = | PMID = 12598912 }}</ref> | *[[PLAP]] +ve.<ref name=pmid12598912>{{Cite journal | last1 = Schreiber | first1 = L. | last2 = Lifschitz-Mercer | first2 = B. | last3 = Paz | first3 = G. | last4 = Yavetz | first4 = H. | last5 = Elliott | first5 = DJ. | last6 = Kula | first6 = K. | last7 = Slowikowska-Hilczer | first7 = J. | last8 = Maymon | first8 = BB. | title = Double immunolabeling by the RBM and the PLAP markers for identifying intratubular (in situ) germ cell neoplasia of the testis. | journal = Int J Surg Pathol | volume = 11 | issue = 1 | pages = 17-20 | month = Jan | year = 2003 | doi = | PMID = 12598912 }}</ref> | ||
*D2-40 +ve. | *D2-40 +ve. | ||
===Others=== | ===Others=== | ||
Latest revision as of 04:41, 22 March 2016
| Germ cell neoplasia in situ | |
|---|---|
| Diagnosis in short | |
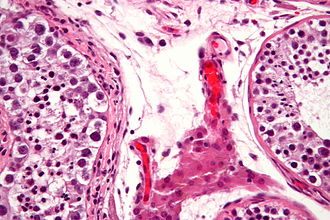 GCNIS (left of image). H&E stain. | |
|
| |
| Synonyms | intratubular germ cell neoplasia (old term) |
|
| |
| LM | "large" round or polygonal nuclei, prominent nucleoli, clear cytoplasm, +/-cells (completely) fill the tubule |
| Subtypes | undifferentiated, differentiated (intratubular seminoma, intratubular non-seminoma) |
| LM DDx | seminoma, embryonal carcinoma, Sertoli cell-only syndrome, mixed germ cell tumour |
| IHC | OCT4, PLAP +ve, D2-40 +ve |
| Site | testis |
|
| |
| Prognosis | premalignant |
| Treatment | radiotherapy (?) |
Germ cell neoplasia in situ, abbreviated GCNIS, is a premalignant lesion of the testis.
It was previously known previously known as intratubular germ cell neoplasia (abbreviated ITGCN) and testicular intraepithelial neoplasia.[1][2]
General
- Considered the precursor lesion for germ cell tumours.
- Not all germ cell tumours (GCTs) arise from intratubular germ cell neoplasia.
The following testicular GCTs do not arise from GCNIS:
- Spermatocytic tumour.[3]
- Yolk sac tumours (endodermal sinus tumour).[4]
- Teratoma.[citation needed]
Classification:[5]
- Undifferentiated GCNIS.
- Differentiated GCNIS.[6]
- Intratubular seminoma.
- Intratubular non-seminoma.
Treatment:
- Radiotherapy.[1]
Microscopic
- "Large" round or polygonal nuclei.
- Size in relation to normal often not defined.
- Rakheja et al. say >= 5x a lymphocyte for intratubular embryonal carcinoma.[5]
- Polygonal nuclei = squared-off nuclear membrane.
- Size in relation to normal often not defined.
- Prominent nucleoli - key feature.
- Clear cytoplasm - important.
- +/-Cells fill the tubule.
Note:
- Sertoli cells may have a nucleolus... but they have eosinophilic ctyoplasm.[citation needed]
DDx:
- Sertoli cell-only syndrome - Sertoli cells also have nucleoli, wind swept appearance.[9]
- Seminoma - especially intratubular predominant growth pattern.
- Embryonal carcinoma.
- Mixed germ cell tumour.
Images
Case 1
Case 2
Case 3
www
IHC
ISUP consensus
GCNIS (ITGCN) versus atypical intratubular germ cells:[10]
- OCT4 +ve.
Alternates:
Others
- CD117 +ve.
- Disputed: doesn't differentiate neoplastic from non-neoplastic according to Biermann et al.[12]
- OCT3/4 +ve.
See also
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 Dieckmann, KP.; Wilken, S.; Loy, V.; Matthies, C.; Kleinschmidt, K.; Bedke, J.; Martinschek, A.; Souchon, R. et al. (May 2013). "Treatment of testicular intraepithelial neoplasia (intratubular germ cell neoplasia unspecified) with local radiotherapy or with platinum-based chemotherapy: a survey of the German Testicular Cancer Study Group.". Ann Oncol 24 (5): 1332-7. doi:10.1093/annonc/mds628. PMID 23293116.
- ↑ Berney, DM.; Looijenga, L.; Idrees, M.; Oosterhuis, JW.; Rajpert-De Meyts, E.; Ulbright, TM.; Skakkebaek, NE. (Feb 2016). "Germ Cell Neoplasia In Situ (GCNIS). Evolution of the Current Nomenclature for Testicular Pre-invasive Germ Cell Malignancy.". Histopathology. doi:10.1111/his.12958. PMID 26918959.
- ↑ Müller J, Skakkebaek NE, Parkinson MC (February 1987). "The spermatocytic seminoma: views on pathogenesis". Int. J. Androl. 10 (1): 147–56. PMID 3583416.
- ↑ Manivel JC, Simonton S, Wold LE, Dehner LP (June 1988). "Absence of intratubular germ cell neoplasia in testicular yolk sac tumors in children. A histochemical and immunohistochemical study". Arch. Pathol. Lab. Med. 112 (6): 641–5. PMID 2837162.
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 5.2 Rakheja, D.; Hoang, MP.; Sharma, S.; Albores-Saavedra, J. (Apr 2002). "Intratubular embryonal carcinoma.". Arch Pathol Lab Med 126 (4): 487-90. doi:10.1043/0003-9985(2002)1260487:IEC2.0.CO;2. PMID 11900581. http://www.archivesofpathology.org/doi/full/10.1043/0003-9985(2002)126%3C0487:IEC%3E2.0.CO;2.
- ↑ Lau, SK.; Weiss, LM.; Chu, PG. (Jul 2007). "Association of intratubular seminoma and intratubular embryonal carcinoma with invasive testicular germ cell tumors.". Am J Surg Pathol 31 (7): 1045-9. doi:10.1097/PAS.0b013e31802b8712. PMID 17592271.
- ↑ URL: http://www.webpathology.com/image.asp?case=30&n=1. Accessed on: 18 May 2010.
- ↑ Gondos, B.; Migliozzi, JA. (Nov 1987). "Intratubular germ cell neoplasia.". Semin Diagn Pathol 4 (4): 292-303. PMID 3328244.
- ↑ URL: http://www.webpathology.com/image.asp?n=3&Case=28. Accessed on: 25 March 2013.
- ↑ Amin, MB.; Epstein, JI.; Ulbright, TM.; Humphrey, PA.; Egevad, L.; Montironi, R.; Grignon, D.; Trpkov, K. et al. (Aug 2014). "Best practices recommendations in the application of immunohistochemistry in urologic pathology: report from the international society of urological pathology consensus conference.". Am J Surg Pathol 38 (8): 1017-22. doi:10.1097/PAS.0000000000000254. PMID 25025364.
- ↑ Schreiber, L.; Lifschitz-Mercer, B.; Paz, G.; Yavetz, H.; Elliott, DJ.; Kula, K.; Slowikowska-Hilczer, J.; Maymon, BB. (Jan 2003). "Double immunolabeling by the RBM and the PLAP markers for identifying intratubular (in situ) germ cell neoplasia of the testis.". Int J Surg Pathol 11 (1): 17-20. PMID 12598912.
- ↑ Biermann, K.; Stoop, H.; Looijenga, L. (May 2012). "c-KIT protein expression does not discriminate neoplastic from non-neoplastic intratubular germ cells.". Histopathology 60 (6): 1017-9. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2559.2011.04157.x. PMID 22340755.