Difference between revisions of "Organizing pneumonia"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
(chg redirect) |
(split out) |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
#redirect [[Diffuse_lung_diseases#Organizing_pneumonia]] | #redirect [[Diffuse_lung_diseases#Organizing_pneumonia]] | ||
'''Organizing pneumonia''', abbreviated '''OP''', is a histologic pattern in [[lung pathology]]. | |||
==General== | |||
*Multiple causes, e.g. transplant rejection, infection. | |||
Clinical diagnoses:<ref name=Ref_WMSP91>{{Ref WMSP|91}}</ref> | |||
*[[Lung transplant pathology|Transplant rejection]]. | |||
*Cryptogenic organizing pneumonia (COP), [[AKA]] (idiopathic) bronchiolitis obliterans organizing pneumonia (BOOP). | |||
**Should '''not''' be confused with ''[[constrictive bronchiolitis]]'' (AKA ''[[bronchiolitis obliterans]]''). | |||
*[[Collagen vascular disease]]. | |||
*Toxic injury. | |||
*Infection. | |||
*Peri-tumor - in proximity to a space-occupying lesion (abscess, neoplasm). | |||
Note: | |||
*BOOP is used as a synonym for ''organizing pneumonia'' which has the long differential diagnosis above.<ref name=Ref_WMSP91>{{Ref WMSP|91}}</ref> | |||
**Confusingly, it may be used to refer to the idiopathic form of organizing pneumonia, now generally known as ''cryptogenic organizing pneumonia'' (COP). | |||
***In other words, strictly speaking, ''BOOP'' is '''not''' the same as ''COP''; idiopathic BOOP ''is'' COP. | |||
==Microscopic== | |||
Features:<ref name=Ref_Klatt110>{{Ref Klatt|110}}</ref> | |||
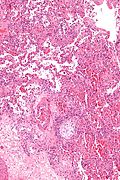
*Distal airway disease -- airways plugged with organizing exudate ("[[Masson bodies]]"). | |||
**"Organized exudate" = fluffy light-staining paucicellular regions with stellate cells (fibroblasts & immature connective tissue). | |||
*'''No''' hobnailing of pneumocytes. | |||
**Type 2 pneumocytes hyperplasia is absent. | |||
DDx: | |||
*[[Diffuse alveolar damage]], proliferative phase - has type 2 pneumoncyte hyperplasia. | |||
*[[Bronchiolitis obliterans]]. | |||
===Images=== | |||
<gallery> | |||
Image:Masson_body_-_intermed_mag.jpg | Masson body - intermed. mag. (WC/Nephron) | |||
Image:Masson_body_-_very_high_mag.jpg | Masson body - very high mag. (WC/Nephron) | |||
</gallery> | |||
www: | |||
*[http://150.59.224.157/pathology/system/data/image_data/11338411170518.jpg Masson body (150.59.224.157)].<ref>URL: [http://150.59.224.157/pathology/index.php?first_category_id=2&second_category_id=20 http://150.59.224.157/pathology/index.php?first_category_id=2&second_category_id=20]. Accessed on: 4 August 2011.</ref> | |||
*[http://casereports.bmj.com/content/2011/bcr.11.2010.3483.full BOOP (bmj.com)]. | |||
*[http://www.flickr.com/photos/pulmonary_pathology/4733384977/ Masson body (flickr.com)]. | |||
==See also== | |||
*[[Diffuse lung disease]]. | |||
*[[Pneumonia]]. | |||
==References== | |||
{{Reflist|2}} | |||
[[Category:Diagnosis]] | [[Category:Diagnosis]] | ||
[[Category:Diffuse lung diseases]] | |||
Revision as of 01:58, 31 May 2014
Redirect to:
Organizing pneumonia, abbreviated OP, is a histologic pattern in lung pathology.
General
- Multiple causes, e.g. transplant rejection, infection.
Clinical diagnoses:[1]
- Transplant rejection.
- Cryptogenic organizing pneumonia (COP), AKA (idiopathic) bronchiolitis obliterans organizing pneumonia (BOOP).
- Should not be confused with constrictive bronchiolitis (AKA bronchiolitis obliterans).
- Collagen vascular disease.
- Toxic injury.
- Infection.
- Peri-tumor - in proximity to a space-occupying lesion (abscess, neoplasm).
Note:
- BOOP is used as a synonym for organizing pneumonia which has the long differential diagnosis above.[1]
- Confusingly, it may be used to refer to the idiopathic form of organizing pneumonia, now generally known as cryptogenic organizing pneumonia (COP).
- In other words, strictly speaking, BOOP is not the same as COP; idiopathic BOOP is COP.
- Confusingly, it may be used to refer to the idiopathic form of organizing pneumonia, now generally known as cryptogenic organizing pneumonia (COP).
Microscopic
Features:[2]
- Distal airway disease -- airways plugged with organizing exudate ("Masson bodies").
- "Organized exudate" = fluffy light-staining paucicellular regions with stellate cells (fibroblasts & immature connective tissue).
- No hobnailing of pneumocytes.
- Type 2 pneumocytes hyperplasia is absent.
DDx:
- Diffuse alveolar damage, proliferative phase - has type 2 pneumoncyte hyperplasia.
- Bronchiolitis obliterans.
Images
www:
See also
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 Humphrey, Peter A; Dehner, Louis P; Pfeifer, John D (2008). The Washington Manual of Surgical Pathology (1st ed.). Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. pp. 91. ISBN 978-0781765275.
- ↑ Klatt, Edward C. (2006). Robbins and Cotran Atlas of Pathology (1st ed.). Saunders. pp. 110. ISBN 978-1416002741.
- ↑ URL: http://150.59.224.157/pathology/index.php?first_category_id=2&second_category_id=20. Accessed on: 4 August 2011.