Difference between revisions of "Diffuse alveolar damage"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
(chg redirect) |
(split out) |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
# | '''Diffuse alveolar damage''', abbreviated '''DAD''', is a relatively common [[lung pathology]] that is grouped with the [[diffuse lung diseases]] and has several clinical correlates. | ||
==General== | |||
Etiology: | |||
*Abrupt hypoxemia with pulmonary infiltrates leading to epithelial cell and endothelial cell death not accompanied by cardiac failure.<ref name=Ref_PCPBoD8_364>{{Ref PCPBoD8|364}}</ref> | |||
DAD is the histologic correlate of: | |||
*Acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS). | |||
**[[AKA]] adult respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) to differentiate it from ''[[respiratory distress syndrome]]'' in infants. | |||
*Acute interstitial pneumonia (AIP). | |||
*Transfusion related acute lung injury (TRALI). | |||
The DDx is broad:<ref>{{Ref WMSP|91}}</ref> | |||
*Infection/sepsis. | |||
*Toxic (smoke, oxygen). | |||
*Drug (amiodarone, chemotherapy). | |||
*Trauma/shock. | |||
*Inflammatory. | |||
*Idiopathic. | |||
==Microscopic== | |||
Features:<ref name=Ref_Klatt103>{{Ref Klatt|103}}</ref><ref name=pmid16766248>{{Cite journal | last1 = Castro | first1 = CY. | title = ARDS and diffuse alveolar damage: a pathologist's perspective. | journal = Semin Thorac Cardiovasc Surg | volume = 18 | issue = 1 | pages = 13-9 | month = | year = 2006 | doi = 10.1053/j.semtcvs.2006.02.001 | PMID = 16766248 }}</ref> | |||
#Exudative: | |||
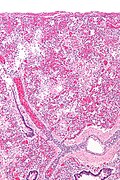
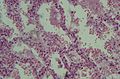
#*Hyaline membranes - '''key feature'''. | |||
#**Debris (pink crap) lines the alveolar spaces. | |||
#Proliferative: | |||
#*Interstitial thickening. | |||
#*Inflammation (lymphocytes). | |||
#*Hobnailing of alveolar lining cells (type 2 pneumocyte hyperplasia<ref>URL: [http://d3jonline.tripod.com/20-Pulmonary_II/Pathology_of_Interstitial_Lung_Diseases.htm http://d3jonline.tripod.com/20-Pulmonary_II/Pathology_of_Interstitial_Lung_Diseases.htm]. Accessed on: 22 February 2012.</ref>). | |||
#*Edema (link pink crap in the alveoli). | |||
#*[[Masson bodies]] in the airway. | |||
#*Hyaline material (usu. focal) - '''key feature'''. | |||
#Fibrotic: | |||
#*Interstitial inflammation. | |||
#*Fibrosis. | |||
DDx:<ref name=pmid16766248>{{Cite journal | last1 = Castro | first1 = CY. | title = ARDS and diffuse alveolar damage: a pathologist's perspective. | journal = Semin Thorac Cardiovasc Surg | volume = 18 | issue = 1 | pages = 13-9 | month = | year = 2006 | doi = 10.1053/j.semtcvs.2006.02.001 | PMID = 16766248 }}</ref> | |||
*[[Cryptogenic organizing pneumonia]] - especially for ''proliferative phase DAD''. | |||
*[[Bronchiolitis obliterans]]. | |||
===Images=== | |||
<gallery> | |||
Image:Hyaline membranes - low mag.jpg | Exudative phase DAD - low mag. (WC/Nephron) | |||
Image:Hyaline membranes - intermed mag.jpg | Exudative phase DAD - intermed. mag. (WC/Nephron) | |||
Image:Hyaline membranes - high mag.jpg | Exudative phase DAD - high mag. (WC/Nephron) | |||
Image:Hyaline membranes - very high mag.jpg | Exudative phase DAD - very high mag. (WC/Nephron) | |||
Image:ARDS.jpg | Exudative DAD (WC) | |||
</gallery> | |||
www: | |||
*[http://www.flickr.com/photos/pulmonary_pathology/4710141110/in/photostream/ Proliferative phase DAD - intermed. mag. (flickr.com/Yale Rosen)]. | |||
*[http://www.flickr.com/photos/pulmonary_pathology/4709499629/in/photostream/ Proliferative phase DAD - high mag. (flickr.com/Yale Rosen)]. | |||
==See also== | |||
*[[Diffuse lung diseases]]. | |||
==References== | |||
{{Reflist|2}} | |||
[[Category:Diagnosis]] | [[Category:Diagnosis]] | ||
[[Category:Diffuse lung diseases]] | |||
Revision as of 12:53, 18 April 2014
Diffuse alveolar damage, abbreviated DAD, is a relatively common lung pathology that is grouped with the diffuse lung diseases and has several clinical correlates.
General
Etiology:
- Abrupt hypoxemia with pulmonary infiltrates leading to epithelial cell and endothelial cell death not accompanied by cardiac failure.[1]
DAD is the histologic correlate of:
- Acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS).
- AKA adult respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) to differentiate it from respiratory distress syndrome in infants.
- Acute interstitial pneumonia (AIP).
- Transfusion related acute lung injury (TRALI).
The DDx is broad:[2]
- Infection/sepsis.
- Toxic (smoke, oxygen).
- Drug (amiodarone, chemotherapy).
- Trauma/shock.
- Inflammatory.
- Idiopathic.
Microscopic
- Exudative:
- Hyaline membranes - key feature.
- Debris (pink crap) lines the alveolar spaces.
- Hyaline membranes - key feature.
- Proliferative:
- Interstitial thickening.
- Inflammation (lymphocytes).
- Hobnailing of alveolar lining cells (type 2 pneumocyte hyperplasia[5]).
- Edema (link pink crap in the alveoli).
- Masson bodies in the airway.
- Hyaline material (usu. focal) - key feature.
- Fibrotic:
- Interstitial inflammation.
- Fibrosis.
DDx:[4]
- Cryptogenic organizing pneumonia - especially for proliferative phase DAD.
- Bronchiolitis obliterans.
Images
www:
- Proliferative phase DAD - intermed. mag. (flickr.com/Yale Rosen).
- Proliferative phase DAD - high mag. (flickr.com/Yale Rosen).
See also
References
- ↑ Mitchell, Richard; Kumar, Vinay; Fausto, Nelson; Abbas, Abul K.; Aster, Jon (2011). Pocket Companion to Robbins & Cotran Pathologic Basis of Disease (8th ed.). Elsevier Saunders. pp. 364. ISBN 978-1416054542.
- ↑ Humphrey, Peter A; Dehner, Louis P; Pfeifer, John D (2008). The Washington Manual of Surgical Pathology (1st ed.). Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. pp. 91. ISBN 978-0781765275.
- ↑ Klatt, Edward C. (2006). Robbins and Cotran Atlas of Pathology (1st ed.). Saunders. pp. 103. ISBN 978-1416002741.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 Castro, CY. (2006). "ARDS and diffuse alveolar damage: a pathologist's perspective.". Semin Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 18 (1): 13-9. doi:10.1053/j.semtcvs.2006.02.001. PMID 16766248.
- ↑ URL: http://d3jonline.tripod.com/20-Pulmonary_II/Pathology_of_Interstitial_Lung_Diseases.htm. Accessed on: 22 February 2012.