Difference between revisions of "Gout"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
| Line 43: | Line 43: | ||
==Gross/radiology== | ==Gross/radiology== | ||
*Radiologically may mimic ''anconeus epitrochlearis'' muscle.<ref>URL: [http://radiology.casereports.net/index.php/rcr/article/viewArticle/57/213 http://radiology.casereports.net/index.php/rcr/article/viewArticle/57/213]. Accessed on: 7 August 2011.</ref> | *Radiologically may mimic ''anconeus epitrochlearis'' muscle.<ref>URL: [http://radiology.casereports.net/index.php/rcr/article/viewArticle/57/213 http://radiology.casereports.net/index.php/rcr/article/viewArticle/57/213]. Accessed on: 7 August 2011.</ref> | ||
DDx: | |||
*[[Epidermal inclusion cyst]]. (???) | |||
==Microscopic== | ==Microscopic== | ||
Revision as of 17:28, 16 April 2014
| Gout | |
|---|---|
| Diagnosis in short | |
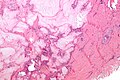
 Gouty tophus. H&E stain. | |
| Site | joints - classically large toe |
|
| |
| Symptoms | joint pain |
| Prevalence | common |
| Prognosis | benign |
Gout is a common benign affliction that can be disabling. It occasionally is seen by pathologists and can be grouped with conditions with crystals in body fluids.
General
- Classically afflicts the big toe - known as podagra.
Etiology:[1]
- Overproduction of uric acid ~ 10% of cases.
- Reduced excretion of uric acid ~ 90% of cases.
Gross/radiology
- Radiologically may mimic anconeus epitrochlearis muscle.[4]
DDx:
- Epidermal inclusion cyst. (???)
Microscopic
Features:[5]
- Tophi (advanced)
- Reactive granulomatous inflammation.
- Surrounds fluffy (cotton candy-like) material.
- Fibrotic synovium.
- Aggregates of urate crystals.
- Reactive granulomatous inflammation.
Images
www:
- Gouty tophus - A. xray, B. Diff-Quick, C. Pap smear, D. polarized light, E. H&E (archivesofpathology.org).
- Gout - several images (upmc.edu).
See also
References
- ↑ Mitchell, Richard; Kumar, Vinay; Fausto, Nelson; Abbas, Abul K.; Aster, Jon (2011). Pocket Companion to Robbins & Cotran Pathologic Basis of Disease (8th ed.). Elsevier Saunders. pp. 634. ISBN 978-1416054542.
- ↑ Online 'Mendelian Inheritance in Man' (OMIM) 607096
- ↑ Tin, A.; Woodward, OM.; Kao, WH.; Liu, CT.; Lu, X.; Nalls, MA.; Shriner, D.; Semmo, M. et al. (Oct 2011). "Genome-wide association study for serum urate concentrations and gout among African Americans identifies genomic risk loci and a novel URAT1 loss-of-function allele.". Hum Mol Genet 20 (20): 4056-68. doi:10.1093/hmg/ddr307. PMID 21768215.
- ↑ URL: http://radiology.casereports.net/index.php/rcr/article/viewArticle/57/213. Accessed on: 7 August 2011.
- ↑ URL: http://pathologyoutlines.com/joints.html#gout. Accessed on: 5 August 2011.