Difference between revisions of "Emphysema"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
| Line 5: | Line 5: | ||
| Caption = Emphysematous changes. [[H&E stain]]. | | Caption = Emphysematous changes. [[H&E stain]]. | ||
| Synonyms = | | Synonyms = | ||
| Micro = | | Micro = alveoli too large, thin septa (no interstitial thickening) | ||
| Subtypes = | | Subtypes = centriacinar (centrilobular) emphysema, panacinar (panlobular) emphysema, | ||
distal (paraseptal) acinar emphysema, irregular emphysema | |||
| LMDDx = | | LMDDx = | ||
| Stains = | | Stains = | ||
| Line 18: | Line 19: | ||
| Assdx = +/-pneumothorax | | Assdx = +/-pneumothorax | ||
| Syndromes = [[Alpha-1 antitrypsin deficiency]], others | | Syndromes = [[Alpha-1 antitrypsin deficiency]], others | ||
| Clinicalhx = [[smoking]] | | Clinicalhx = +/-[[smoking]] | ||
| Signs = barrel chest | | Signs = barrel chest | ||
| Symptoms = shortness of breath | | Symptoms = shortness of breath | ||
Revision as of 18:06, 14 April 2014
| Emphysema | |
|---|---|
| Diagnosis in short | |
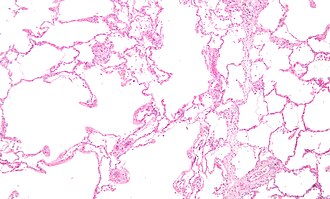 Emphysematous changes. H&E stain. | |
|
| |
| LM | alveoli too large, thin septa (no interstitial thickening) |
| Subtypes |
centriacinar (centrilobular) emphysema, panacinar (panlobular) emphysema, distal (paraseptal) acinar emphysema, irregular emphysema |
| Gross | usually upper lobe predominant - blebs, bullae |
| Site | lung |
|
| |
| Associated Dx | +/-pneumothorax |
| Syndromes | Alpha-1 antitrypsin deficiency, others |
|
| |
| Clinical history | +/-smoking |
| Signs | barrel chest |
| Symptoms | shortness of breath |
| Prevalence | common |
| Radiology | hyperinflation |
| Prognosis | dependent on underlying cause |
| Treatment | stop smoking, bullectomy |
Emphysema is a common medical lung disease strongly associated with smoking.
- Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, abbreviated COPD, redirects here.
General
- Usually due to smoking.
- Often lumped together with chronic bronchitis and called chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD).[1]
Causes of emphysema other than smoking:[2]
Pathologic classification
Based on morphology:[3]
- Centriacinar (centrilobular) emphysema - associated with heavy smoking.
- Panacinar (panlobular) emphysema - associated with alpha-1 antitrypsin deficiency.
- Distal (paraseptal) acinar emphysema - associated with spontaneous pneumothorax.
- Irregular emphysema - usu. insignificant.
- Q. Why does smoking lead to centriacinar emphysema?
- A. The bad stuff from smoking gets enters the acinus at the centre; ergo, this is the location of the most damage.
Gross
- Holes (blebs, bullae), usually upper lung field predominant.
- Lungs may overlap the heart.[4]
Notes:
Microscopic
Features:[4]
- Large alveoli.
- Thin septa (no interstitial thickening).
Images
See also
References
- ↑ Mitchell, Richard; Kumar, Vinay; Fausto, Nelson; Abbas, Abul K.; Aster, Jon (2011). Pocket Companion to Robbins & Cotran Pathologic Basis of Disease (8th ed.). Elsevier Saunders. pp. 368. ISBN 978-1416054542.
- ↑ Lee, P.; Gildea, TR.; Stoller, JK. (Dec 2002). "Emphysema in nonsmokers: alpha 1-antitrypsin deficiency and other causes.". Cleve Clin J Med 69 (12): 928-9, 933, 936 passim. PMID 12546267.
- ↑ Mitchell, Richard; Kumar, Vinay; Fausto, Nelson; Abbas, Abul K.; Aster, Jon (2011). Pocket Companion to Robbins & Cotran Pathologic Basis of Disease (8th ed.). Elsevier Saunders. pp. 368. ISBN 978-1416054542.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 Mitchell, Richard; Kumar, Vinay; Fausto, Nelson; Abbas, Abul K.; Aster, Jon (2011). Pocket Companion to Robbins & Cotran Pathologic Basis of Disease (8th ed.). Elsevier Saunders. pp. 369. ISBN 978-1416054542.
- ↑ URL: http://dictionary.reference.com/browse/bleb. Accessed on: 3 August 2011.
- ↑ URL: http://dictionary.reference.com/browse/bulla. Accessed on: 3 August 2011.
