Difference between revisions of "Invasive ductal carcinoma of the pancreas"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
(redirect w/ cat.) |
(split out) |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
# | '''Invasive ductal carcinoma of the pancreas''' is the most common type of [[pancreas|pancreatic]] [[cancer]]. | ||
It is typically gland forming and thus also referred to as '''ductal adenocarcinoma''', '''pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma''' and '''pancreatic adenocarcinoma'''. | |||
==General== | |||
*Most common type of pancreatic cancer.<ref name=Ref_WMSP>{{Ref WMSP|237}}</ref> | |||
*Location: usually in the head ~60%. | |||
**15% in the body, 5% tail, 20% diffuse (head, body & tail).<ref name=Ref_PBoD950>{{Ref PBoD|950}}</ref> | |||
*Abysmal prognosis. | |||
Risk factors:<ref name=Ref_PCPBoD8_471>{{Ref PCPBoD8|471}}</ref> | |||
*Smoking (RR ~ 2). | |||
*Pancreatitis. | |||
*Family history, esp. BRCA2. | |||
*[[Diabetes mellitus]] - modest risk increase. | |||
Molecular characteristics:<ref name=Ref_PCPBoD8_470-1>{{Ref PCPBoD8|470-1}}</ref><ref name=pmid19896096>{{Cite journal | last1 = Furukawa | first1 = T. | title = Molecular pathology of pancreatic cancer: implications for molecular targeting therapy. | journal = Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol | volume = 7 | issue = 11 Suppl | pages = S35-9 | month = Nov | year = 2009 | doi = 10.1016/j.cgh.2009.07.035 | PMID = 19896096 }}</ref> | |||
#KRAS (oncogene) mutation in ~ 90% of cases. | |||
#CDKN2A<ref name=omim600160>{{OMIM|600160}}</ref> ([[AKA]] p16) inactivation ~ 95% of cases. | |||
#TP53 (AKA p53). | |||
#SMAD4. | |||
==Microscopic== | |||
Features:<ref name=Ref_PBoD951>{{Ref PBoD|951}}</ref> | |||
*Often glandular, may be solid. | |||
*Nuclei. | |||
**May be bland - little pleomorphism. | |||
**Often small nuclei. | |||
**Sometimes [[coffee-bean nuclei|coffee-bean]] appearance. | |||
*Cytoplasm - granular, abundant. | |||
*Quasi endocrine look. | |||
**May stain positive for endocrine markers. | |||
Other features: | |||
*+/-Necrosis. | |||
*+/-Myxoid degeneration. | |||
*+/-Cells around vessels. | |||
DDx: | |||
*[[Chronic pancreatitis]].<ref name=pmid16273946>{{Cite journal | last1 = Adsay | first1 = NV. | last2 = Bandyopadhyay | first2 = S. | last3 = Basturk | first3 = O. | last4 = Othman | first4 = M. | last5 = Cheng | first5 = JD. | last6 = Klöppel | first6 = G. | last7 = Klimstra | first7 = DS. | title = Chronic pancreatitis or pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma? | journal = Semin Diagn Pathol | volume = 21 | issue = 4 | pages = 268-76 | month = Nov | year = 2004 | doi = | PMID = 16273946 }}</ref> | |||
*[[Cholangiocarcinoma]]. | |||
===Images=== | |||
<gallery> | |||
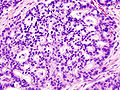
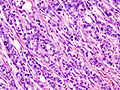
Image:Pancreas_adenocarcinoma_(3)_Case_01.jpg | Pancreatic adenocarcinoma (WC) | |||
Image:Pancreas_adenocarcinoma_(2)_Case_01.jpg | Pancreatic adenocarcinoma (WC) | |||
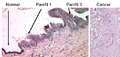
Image:Pancreas_neoplasia_carcinoma_sequence.png | Normal pancreas, pancreatic intraepithelial neoplasia and pancreatic carcinoma (WC) | |||
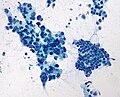
Image:Pancreas_FNA;_adenocarcinoma_vs._normal_ductal_epithelium_(200x).jpg| Pancreatic adenocarcinoma - cytopathology (WC) | |||
</gallery> | |||
www: | |||
*[http://path.upmc.edu/cases/case384.html Pancreatic adenocarcinoma - several images (upmc.edu)]. | |||
==IHC== | |||
Features:<ref name=Ref_Lester3>{{Ref Lester3|94}}</ref> | |||
*CD7 +ve. | |||
*CD20 +ve. | |||
*SMAD4 -ve ~55% of cases -- stomach usually +ve. | |||
*CDX2 -ve/+ve. | |||
*CEA +ve.<ref name=pmid16183479>{{Cite journal | last1 = Adsay | first1 = NV. | last2 = Basturk | first2 = O. | last3 = Cheng | first3 = JD. | last4 = Andea | first4 = AA. | title = Ductal neoplasia of the pancreas: nosologic, clinicopathologic, and biologic aspects. | journal = Semin Radiat Oncol | volume = 15 | issue = 4 | pages = 254-64 | month = Oct | year = 2005 | doi = 10.1016/j.semradonc.2005.04.001 | PMID = 16183479 }}</ref> | |||
==Sign out== | |||
<pre> | |||
MASS, PANCREAS, CORE BIOPSY: | |||
- ADENOCARCINOMA, MODERATELY DIFFERENTIATED. | |||
</pre> | |||
Note: | |||
*On biopsy, it isn't easy to separate from [[cholangiocarcinoma]]. Thus, it is better to stay vague. | |||
==See also== | |||
*[[Pancreas]]. | |||
==References== | |||
{{Reflist|2}} | |||
[[Category:Diagnosis]] | [[Category:Diagnosis]] | ||
[[Category:Pancreas]] | |||
Revision as of 10:44, 5 March 2014
Invasive ductal carcinoma of the pancreas is the most common type of pancreatic cancer.
It is typically gland forming and thus also referred to as ductal adenocarcinoma, pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma and pancreatic adenocarcinoma.
General
- Most common type of pancreatic cancer.[1]
- Location: usually in the head ~60%.
- 15% in the body, 5% tail, 20% diffuse (head, body & tail).[2]
- Abysmal prognosis.
Risk factors:[3]
- Smoking (RR ~ 2).
- Pancreatitis.
- Family history, esp. BRCA2.
- Diabetes mellitus - modest risk increase.
Molecular characteristics:[4][5]
- KRAS (oncogene) mutation in ~ 90% of cases.
- CDKN2A[6] (AKA p16) inactivation ~ 95% of cases.
- TP53 (AKA p53).
- SMAD4.
Microscopic
Features:[7]
- Often glandular, may be solid.
- Nuclei.
- May be bland - little pleomorphism.
- Often small nuclei.
- Sometimes coffee-bean appearance.
- Cytoplasm - granular, abundant.
- Quasi endocrine look.
- May stain positive for endocrine markers.
Other features:
- +/-Necrosis.
- +/-Myxoid degeneration.
- +/-Cells around vessels.
DDx:
Images
www:
IHC
Features:[9]
- CD7 +ve.
- CD20 +ve.
- SMAD4 -ve ~55% of cases -- stomach usually +ve.
- CDX2 -ve/+ve.
- CEA +ve.[10]
Sign out
MASS, PANCREAS, CORE BIOPSY: - ADENOCARCINOMA, MODERATELY DIFFERENTIATED.
Note:
- On biopsy, it isn't easy to separate from cholangiocarcinoma. Thus, it is better to stay vague.
See also
References
- ↑ Humphrey, Peter A; Dehner, Louis P; Pfeifer, John D (2008). The Washington Manual of Surgical Pathology (1st ed.). Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. pp. 237. ISBN 978-0781765275.
- ↑ Cotran, Ramzi S.; Kumar, Vinay; Fausto, Nelson; Nelso Fausto; Robbins, Stanley L.; Abbas, Abul K. (2005). Robbins and Cotran pathologic basis of disease (7th ed.). St. Louis, Mo: Elsevier Saunders. pp. 950. ISBN 0-7216-0187-1.
- ↑ Mitchell, Richard; Kumar, Vinay; Fausto, Nelson; Abbas, Abul K.; Aster, Jon (2011). Pocket Companion to Robbins & Cotran Pathologic Basis of Disease (8th ed.). Elsevier Saunders. pp. 471. ISBN 978-1416054542.
- ↑ Mitchell, Richard; Kumar, Vinay; Fausto, Nelson; Abbas, Abul K.; Aster, Jon (2011). Pocket Companion to Robbins & Cotran Pathologic Basis of Disease (8th ed.). Elsevier Saunders. pp. 470-1. ISBN 978-1416054542.
- ↑ Furukawa, T. (Nov 2009). "Molecular pathology of pancreatic cancer: implications for molecular targeting therapy.". Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol 7 (11 Suppl): S35-9. doi:10.1016/j.cgh.2009.07.035. PMID 19896096.
- ↑ Online 'Mendelian Inheritance in Man' (OMIM) 600160
- ↑ Cotran, Ramzi S.; Kumar, Vinay; Fausto, Nelson; Nelso Fausto; Robbins, Stanley L.; Abbas, Abul K. (2005). Robbins and Cotran pathologic basis of disease (7th ed.). St. Louis, Mo: Elsevier Saunders. pp. 951. ISBN 0-7216-0187-1.
- ↑ Adsay, NV.; Bandyopadhyay, S.; Basturk, O.; Othman, M.; Cheng, JD.; Klöppel, G.; Klimstra, DS. (Nov 2004). "Chronic pancreatitis or pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma?". Semin Diagn Pathol 21 (4): 268-76. PMID 16273946.
- ↑ Lester, Susan Carole (2010). Manual of Surgical Pathology (3rd ed.). Saunders. pp. 94. ISBN 978-0-323-06516-0.
- ↑ Adsay, NV.; Basturk, O.; Cheng, JD.; Andea, AA. (Oct 2005). "Ductal neoplasia of the pancreas: nosologic, clinicopathologic, and biologic aspects.". Semin Radiat Oncol 15 (4): 254-64. doi:10.1016/j.semradonc.2005.04.001. PMID 16183479.