Difference between revisions of "Germ cell neoplasia in situ"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
(redirect w/ cat.) |
(split out) |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
'''Intratubular germ cell neoplasia''', abbreviated '''ITGCN''', is a premalignant lesion of the [[testis]]. | |||
==General== | |||
*Considered the precursor lesion for germ cell tumours. | |||
*Not all germ cell tumours (GCTs) arise from ''intratubular germ cell neoplasia''. | |||
The following testicular GCTs do not arise from ITGCN: | |||
*[[Spermatocytic seminoma]].<ref>{{cite journal |author=Müller J, Skakkebaek NE, Parkinson MC |title=The spermatocytic seminoma: views on pathogenesis |journal=Int. J. Androl. |volume=10 |issue=1 |pages=147–56 |year=1987 |month=February |pmid=3583416 |doi= |url=}}</ref> | |||
*[[Yolk sac tumour]]s (endodermal sinus tumour).<ref>{{cite journal |author=Manivel JC, Simonton S, Wold LE, Dehner LP |title=Absence of intratubular germ cell neoplasia in testicular yolk sac tumors in children. A histochemical and immunohistochemical study |journal=Arch. Pathol. Lab. Med. |volume=112 |issue=6 |pages=641–5 |year=1988 |month=June |pmid=2837162 |doi= |url=}}</ref> | |||
*Teratoma.{{Fact}} | |||
Classification:<ref name=pmid11900581/> | |||
*Undifferentiated ITGCN. | |||
*Differentiated ITGCN.<ref name=pmid17592271>{{Cite journal | last1 = Lau | first1 = SK. | last2 = Weiss | first2 = LM. | last3 = Chu | first3 = PG. | title = Association of intratubular seminoma and intratubular embryonal carcinoma with invasive testicular germ cell tumors. | journal = Am J Surg Pathol | volume = 31 | issue = 7 | pages = 1045-9 | month = Jul | year = 2007 | doi = 10.1097/PAS.0b013e31802b8712 | PMID = 17592271 }}</ref> | |||
**''Intratubular embryonal carcinoma''. | |||
**''Intratubular seminoma.'' | |||
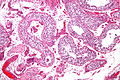
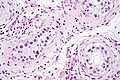
==Microscopic== | |||
Features:<ref>URL: [http://www.webpathology.com/image.asp?case=30&n=1 http://www.webpathology.com/image.asp?case=30&n=1]. Accessed on: 18 May 2010.</ref><ref name=pmid3328244>{{Cite journal | last1 = Gondos | first1 = B. | last2 = Migliozzi | first2 = JA. | title = Intratubular germ cell neoplasia. | journal = Semin Diagn Pathol | volume = 4 | issue = 4 | pages = 292-303 | month = Nov | year = 1987 | doi = | PMID = 3328244 }}</ref> | |||
*"Large" round ''or'' polygonal nuclei. | |||
**Size in relation to normal often not defined. | |||
***Rakheja ''et al.'' say >= 5x a lymphocyte for intratubular embryonal carcinoma.<ref name=pmid11900581>{{Cite journal | last1 = Rakheja | first1 = D. | last2 = Hoang | first2 = MP. | last3 = Sharma | first3 = S. | last4 = Albores-Saavedra | first4 = J. | title = Intratubular embryonal carcinoma. | journal = Arch Pathol Lab Med | volume = 126 | issue = 4 | pages = 487-90 | month = Apr | year = 2002 | doi = 10.1043/0003-9985(2002)1260487:IEC2.0.CO;2 | PMID = 11900581 | url = http://www.archivesofpathology.org/doi/full/10.1043/0003-9985(2002)126%3C0487:IEC%3E2.0.CO;2 }}</ref> | |||
**Polygonal nuclei = squared-off nuclear membrane. | |||
*Prominent nucleoli - '''key feature'''. | |||
*Clear cytoplasm. | |||
*+/-Cells fill the tubule. | |||
DDx: | |||
*Sertoli cell-only syndrome - Sertoli cells also have nucleoli, wind swept appearance.<ref>URL: [http://www.webpathology.com/image.asp?n=3&Case=28 http://www.webpathology.com/image.asp?n=3&Case=28]. Accessed on: 25 March 2013.</ref> | |||
===Images=== | |||
<gallery> | |||
Image: Intratubular germ cell neoplasia - intermed mag.jpg | ITGCN - intermed. mag. | |||
Image: Intratubular germ cell neoplasia - high mag.jpg | ITGCN - high mag. | |||
Image: Intratubular germ cell neoplasia - very high mag.jpg | ITGCN - very high mag. | |||
Image: Intratubular germ cell neoplasia - 2 - very high mag.jpg | ITGCN - very high mag. | |||
</gallery> | |||
<gallery> | |||
Image:Intratubular_germ_cell_neoplasia_high_mag_cropped.jpg | ITGCN - cropped. (WC/Nephron) | |||
Image:Intratubular_germ_cell_neoplasia_high_mag.jpg | ITGCN. (WC/Nephron) | |||
</gallery> | |||
www: | |||
*[http://www.webpathology.com/image.asp?case=30&n=1 ITGCN (webpathology.com)]. | |||
*[http://www.archivesofpathology.org/na101/home/literatum/publisher/pinnacle/journals/content/arpa/2002/15432165-126.4/0003-9985%282002%29126%3C0487%3Aiec%3E2.0.co%3B2/production/images/large/i1543-2165-126-4-487-f01.jpeg Intratubular embryonal carcinoma (archivesofpathology.org)].<ref name=pmid11900581/> | |||
==IHC== | |||
Features:<ref name=pmid15221945>{{Cite journal | last1 = Honecker | first1 = F. | last2 = Stoop | first2 = H. | last3 = de Krijger | first3 = RR. | last4 = Chris Lau | first4 = YF. | last5 = Bokemeyer | first5 = C. | last6 = Looijenga | first6 = LH. | title = Pathobiological implications of the expression of markers of testicular carcinoma in situ by fetal germ cells. | journal = J Pathol | volume = 203 | issue = 3 | pages = 849-57 | month = Jul | year = 2004 | doi = 10.1002/path.1587 | PMID = 15221945 }}</ref> | |||
*PLAP +ve.<ref>{{Cite journal | last1 = Schreiber | first1 = L. | last2 = Lifschitz-Mercer | first2 = B. | last3 = Paz | first3 = G. | last4 = Yavetz | first4 = H. | last5 = Elliott | first5 = DJ. | last6 = Kula | first6 = K. | last7 = Slowikowska-Hilczer | first7 = J. | last8 = Maymon | first8 = BB. | title = Double immunolabeling by the RBM and the PLAP markers for identifying intratubular (in situ) germ cell neoplasia of the testis. | journal = Int J Surg Pathol | volume = 11 | issue = 1 | pages = 17-20 | month = Jan | year = 2003 | doi = | PMID = 12598912 }}</ref> | |||
*CD117 +ve. | |||
**Disputed: doesn't differentiate neoplastic from non-neoplastic according to Biermann ''et al''.<ref name=pmid22340755>{{Cite journal | last1 = Biermann | first1 = K. | last2 = Stoop | first2 = H. | last3 = Looijenga | first3 = L. | title = c-KIT protein expression does not discriminate neoplastic from non-neoplastic intratubular germ cells. | journal = Histopathology | volume = 60 | issue = 6 | pages = 1017-9 | month = May | year = 2012 | doi = 10.1111/j.1365-2559.2011.04157.x | PMID = 22340755 }}</ref> | |||
*OCT3/4 +ve. | |||
Note: | |||
*Normal testis PLAP -ve, CD117 -ve.<ref name=pmid9104938>{{Cite journal | last1 = Hawkins | first1 = E. | last2 = Heifetz | first2 = SA. | last3 = Giller | first3 = R. | last4 = Cushing | first4 = B. | title = The prepubertal testis (prenatal and postnatal): its relationship to intratubular germ cell neoplasia: a combined Pediatric Oncology Group and Children's Cancer Study Group. | journal = Hum Pathol | volume = 28 | issue = 4 | pages = 404-10 | month = Apr | year = 1997 | doi = | PMID = 9104938 }}</ref> | |||
==See also== | |||
*[[Testis]]. | |||
*[[Germ cell tumours]]. | |||
==References== | |||
{{Reflist|2}} | |||
[[Category:Diagnosis]] | [[Category:Diagnosis]] | ||
[[Category:Testis]] | |||
Revision as of 20:24, 25 December 2013
Intratubular germ cell neoplasia, abbreviated ITGCN, is a premalignant lesion of the testis.
General
- Considered the precursor lesion for germ cell tumours.
- Not all germ cell tumours (GCTs) arise from intratubular germ cell neoplasia.
The following testicular GCTs do not arise from ITGCN:
- Spermatocytic seminoma.[1]
- Yolk sac tumours (endodermal sinus tumour).[2]
- Teratoma.[citation needed]
Classification:[3]
- Undifferentiated ITGCN.
- Differentiated ITGCN.[4]
- Intratubular embryonal carcinoma.
- Intratubular seminoma.
Microscopic
- "Large" round or polygonal nuclei.
- Size in relation to normal often not defined.
- Rakheja et al. say >= 5x a lymphocyte for intratubular embryonal carcinoma.[3]
- Polygonal nuclei = squared-off nuclear membrane.
- Size in relation to normal often not defined.
- Prominent nucleoli - key feature.
- Clear cytoplasm.
- +/-Cells fill the tubule.
DDx:
- Sertoli cell-only syndrome - Sertoli cells also have nucleoli, wind swept appearance.[7]
Images
www:
IHC
Features:[8]
- PLAP +ve.[9]
- CD117 +ve.
- Disputed: doesn't differentiate neoplastic from non-neoplastic according to Biermann et al.[10]
- OCT3/4 +ve.
Note:
- Normal testis PLAP -ve, CD117 -ve.[11]
See also
References
- ↑ Müller J, Skakkebaek NE, Parkinson MC (February 1987). "The spermatocytic seminoma: views on pathogenesis". Int. J. Androl. 10 (1): 147–56. PMID 3583416.
- ↑ Manivel JC, Simonton S, Wold LE, Dehner LP (June 1988). "Absence of intratubular germ cell neoplasia in testicular yolk sac tumors in children. A histochemical and immunohistochemical study". Arch. Pathol. Lab. Med. 112 (6): 641–5. PMID 2837162.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 Rakheja, D.; Hoang, MP.; Sharma, S.; Albores-Saavedra, J. (Apr 2002). "Intratubular embryonal carcinoma.". Arch Pathol Lab Med 126 (4): 487-90. doi:10.1043/0003-9985(2002)1260487:IEC2.0.CO;2. PMID 11900581. http://www.archivesofpathology.org/doi/full/10.1043/0003-9985(2002)126%3C0487:IEC%3E2.0.CO;2.
- ↑ Lau, SK.; Weiss, LM.; Chu, PG. (Jul 2007). "Association of intratubular seminoma and intratubular embryonal carcinoma with invasive testicular germ cell tumors.". Am J Surg Pathol 31 (7): 1045-9. doi:10.1097/PAS.0b013e31802b8712. PMID 17592271.
- ↑ URL: http://www.webpathology.com/image.asp?case=30&n=1. Accessed on: 18 May 2010.
- ↑ Gondos, B.; Migliozzi, JA. (Nov 1987). "Intratubular germ cell neoplasia.". Semin Diagn Pathol 4 (4): 292-303. PMID 3328244.
- ↑ URL: http://www.webpathology.com/image.asp?n=3&Case=28. Accessed on: 25 March 2013.
- ↑ Honecker, F.; Stoop, H.; de Krijger, RR.; Chris Lau, YF.; Bokemeyer, C.; Looijenga, LH. (Jul 2004). "Pathobiological implications of the expression of markers of testicular carcinoma in situ by fetal germ cells.". J Pathol 203 (3): 849-57. doi:10.1002/path.1587. PMID 15221945.
- ↑ Schreiber, L.; Lifschitz-Mercer, B.; Paz, G.; Yavetz, H.; Elliott, DJ.; Kula, K.; Slowikowska-Hilczer, J.; Maymon, BB. (Jan 2003). "Double immunolabeling by the RBM and the PLAP markers for identifying intratubular (in situ) germ cell neoplasia of the testis.". Int J Surg Pathol 11 (1): 17-20. PMID 12598912.
- ↑ Biermann, K.; Stoop, H.; Looijenga, L. (May 2012). "c-KIT protein expression does not discriminate neoplastic from non-neoplastic intratubular germ cells.". Histopathology 60 (6): 1017-9. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2559.2011.04157.x. PMID 22340755.
- ↑ Hawkins, E.; Heifetz, SA.; Giller, R.; Cushing, B. (Apr 1997). "The prepubertal testis (prenatal and postnatal): its relationship to intratubular germ cell neoplasia: a combined Pediatric Oncology Group and Children's Cancer Study Group.". Hum Pathol 28 (4): 404-10. PMID 9104938.