Difference between revisions of "Embryonal carcinoma"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
(→Gross: ref) |
(→Microscopic: +MGCT) |
||
| Line 57: | Line 57: | ||
DDx: | DDx: | ||
*[[Mixed germ cell tumour]]. | |||
*[[Yolk sac tumour]]. | *[[Yolk sac tumour]]. | ||
Revision as of 23:23, 13 July 2013
| Embryonal carcinoma | |
|---|---|
| Diagnosis in short | |
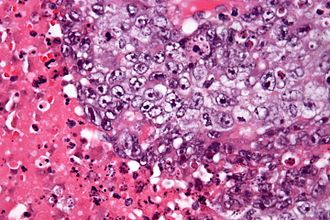 Embryonal carcinoma. H&E stain. | |
|
| |
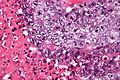
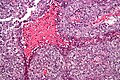
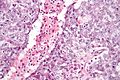
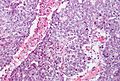
| LM | vesicular nuclei, nuclear overlap, necrosis (common), mitoses, variable architecture (tubulopapillary, glandular, solid, embryoid bodies) |
| LM DDx | seminoma, mixed germ cell tumour, other carcinomas |
| IHC | CD30 +ve, AE1/AE3 +ve |
| Site | testis, ovary, mediastinum |
|
| |
| Signs | testicular mass, pelvic mass |
Embryonal carcinoma is a type of germ cell tumour. It is commonly as a component of mixed germ cell tumours.
General
- Affects young adults.
- May be seen in women.
Gross
- Typically a testicular mass.
- May be seen in the mediastinum.[1]
Microscopic
Features:[2]
- Nucleoli - key feature.
- Vesicular nuclei (clear, empty appearing nuclei) - key feature.
- Nuclei overlap.
- Necrosis - common.
- Not commonly present in seminoma.
- Indistinct cell borders
- Mitoses - common.
- Variable architecture:
- Tubulopapillary.
- Glandular.
- Solid.
- Embryoid bodies - ball of cells in surrounded by empty space on three sides.
Notes:
- Cytoplasmic staining variable (eosinophilic to basophilic).
DDx:
Images
IHC
- AE1/AE3 +ve.
- CD30 +ve.
See also
References
- ↑ Yalçın, B.; Demir, HA.; Tanyel, FC.; Akçören, Z.; Varan, A.; Akyüz, C.; Kutluk, T.; Büyükpamukçu, M. (Oct 2012). "Mediastinal germ cell tumors in childhood.". Pediatr Hematol Oncol 29 (7): 633-42. doi:10.3109/08880018.2012.713084. PMID 22877235.
- ↑ Zhou, Ming; Magi-Galluzzi, Cristina (2006). Genitourinary Pathology: A Volume in Foundations in Diagnostic Pathology Series (1st ed.). Churchill Livingstone. pp. 549. ISBN 978-0443066771.