Difference between revisions of "Dermal cysts"
| Line 246: | Line 246: | ||
*[http://path.upmc.edu/cases/case674/images/fig03.jpg Steatocystoma (upmc.edu)].<ref>URL: [http://path.upmc.edu/cases/case674.html http://path.upmc.edu/cases/case674.html]. Accessed on: 29 January 2012.</ref> | *[http://path.upmc.edu/cases/case674/images/fig03.jpg Steatocystoma (upmc.edu)].<ref>URL: [http://path.upmc.edu/cases/case674.html http://path.upmc.edu/cases/case674.html]. Accessed on: 29 January 2012.</ref> | ||
==Digital mucous cyst== | ==Digital mucous cyst== | ||
*[[AKA]] ''digital synovial cyst''.<ref name=dermpedia>URL: [http://www.dermpedia.org/dermpedia-textbook/digital-mucous-myxoid-cyst http://www.dermpedia.org/dermpedia-textbook/digital-mucous-myxoid-cyst]. Accessed on: 17 January 2012.</ref> | |||
*[[AKA]] ''digital myxoid pseudocyst''.<ref name=dermpedia/> | |||
===General=== | ===General=== | ||
*Dome-shaped [[papule]]. | *Dome-shaped [[papule]]. | ||
Revision as of 16:48, 5 July 2013
Dermal cysts, also skin cysts, are common in dermatopathology. Dermatopathologists can diagnose 'em.
Overview
Common types:[1]
- Epidermal cyst (sebaceous cyst) -- most common.
- Pilar (trichilemmal) cyst.
- Dermoid cyst.
- Ganglion cyst.
- Milicem.
Epidermal necrosis
- This may be cystic. It is covered in the epidermal necrosis article, which covers erythema multiforme, Steven-Johnson syndrome and toxic epidermal necrolysis.
Common cysts
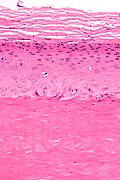
Venous lake
General
- Dilated vein.
Clinical:
- Blanch with pressure.[2]
Gross
- Purple/blue spot.
Images:
Microscopic
Features:[4]
- Lined by endothelium.
- Blood in lumen.
- +/-Fibrin in lumen.
- +/-Solar elastosis - very common.[5]
DDx:
- Angiokeratoma.
- Ectatic superficial dermal vessels.
- Irregular acanthosis.
- Longer rete ridges.
- Cherry hemangioma.[5]
Images:
- Venous lake (jhmi.edu).[3]
- Venous lake (dermpedia.org).[6]
- Venous lake (surgical pathologyatlas.com).
Sign out
SKIN LESION, RIGHT CHEEK, BIOPSY: - VENOUS LAKE. - SOLAR ELASTOSIS. - NEGATIVE FOR NEVUS.
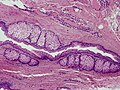
Epidermal inclusion cyst
- Abbreviated EIC.
- AKA epidermal cyst.
- AKA epidermoid cyst.[7]
- AKA follicular cyst, infundibular type.
General
- Very common.
- The clinical term is sebaceous cyst.
- This is a misnomer as they contain keratin (not sebum).[8][9]
- The term may be used to refer to a pilar cyst.
Gross
Features:[10]
- Nodule.
- +/-Yellowish colour.
DDx:
- Pilar cyst - indistinguishable on gross.[8]
- Melanoma.[9]
Image
Microscopic
Features:
- Cyst lining has a granular layer - key feature.[11]
- Trapped collagen bundles at edge of lesion with surrounded by fibroblasts.
- Keratin.
- +/-Granulomatous inflammation due to rupture.
DDx:
- Pilar cyst - no granular layer.
- Eccrine hidrocystoma - eyelid lesion; same histology.[12]
- Dermoid cyst - has adnexal structures, i.e. hair follicle, sebaceous glands, sweat glands.
- Cystic squamous cell carcinoma.[13]
- Keratoacanthoma.[7]
- Dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans - if lesion is large.
- Hybrid epidermoid and trichilemmal cyst.[14]
Images
www:
- Epidermal inclusion cyst (flickr.com).
- Epidermal inclusion cyst (ajronline.org).[15]
- Ruptured epidermal inclusion cyst (nih.gov).
Sign out
SKIN CYST, BACK, EXCISION: - EPIDERMAL INCLUSION CYST.
Ruptured
SKIN LESION, RIGHT CHEEK, EXCISION: - RUPTURED EPIDERMAL INCLUSION CYST.
Micro
The sections show hair-bearing skin with a cyst that is lined by squamous epithelium with a granular layer. The cyst contains keratin. The overlying epithelium is unremarkable.
Ruptured
The sections show hair-bearing skin with a cyst that is lined by squamous epithelium with a granular layer. The cyst contains keratin. A mixed inflammatory infiltrate (predominantly lymphocytes and plasma cells) surround the cyst. Neutrophils infiltrate the cyst lining and are admixed with the keratin within its core.
The lesion appears to be completely excised in the plane of section. Hair follicles are adjacent to the lesion; however, they are not inflamed. The overlying epithelium is unremarkable.
Ruptured without epithelium
The section shows a dermal collection of neutrophils with acellular keratin-like material surrounded by histiocytes and fibrosis. The lesion is completely excised in the plane of section. Hair follicles are adjacent to the abscess; however, they are not inflamed.
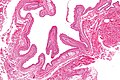
Pilar cyst
- AKA trichilemmal cyst.
General
- Very common.
Gross
- Classic location: head ~90%.[16]
Microscopic
Features:[17]
- Keratin.
- Cyst lining:
- Has no granular layer - key feature.
- Keratohyaline granules (as seen in the granular layer) may be seen focally.
- Inner most cyst lining cells are large cells with abundant eosinophilic cytoplasm.
- Has no granular layer - key feature.
DDx:
- Epidermal cyst - has a granular layer.
Images
www:
Sign out
SKIN CYST, LEFT FLANK, EXCISION: - TRICHILEMMAL CYST (PILAR CYST).
Micro
The sections show a cyst that is lined by squamous epithelium without a granular layer. Focally, keratohyaline granules are seen in the cyst lining cells. The innermost cyst lining cells are large and have abundant eosinophilic cytoplasm. The cyst contains keratin.
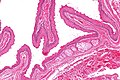
Dermoid cyst
General
- Benign.
- Congenital choristomas.[18]
- May be found in the ovary.
Microscopic
- Cyst lined by normal (keratinized) skin with adnexal structure (hair follicles, sweat glands, sebaceous glands).
DDx:
- Epidermal cyst - no adnexal structures.
Images:
Sign out
OVARY AND UTERINE TUBE, LEFT, UNILATERAL SALPINGO-OOPHORECTOMY: - MATURE TERATOMA. - UTERINE TUBE WITHIN NORMAL LIMITS. - NEGATIVE FOR MALIGNANCY.
Pilonidal cyst
General
- Benign.
- Young adults (late teens, early twenties) - usu. men.[21]
Gross
- Usually at gluteal folds.
- Uncommon: axilla, genital region, umbilicus, scalp.[22]
Microscopic
Features:[22]
- Cyst or pseudocyst into the deep dermis.
- May be lined by squamous epithelium with inflammation +/-pseudoepitheliomatous hyperplasia.
- Neutrophils.
- Granulomatous inflammation.
DDx:
- Squamous cell carcinoma of the skin with inflammation.[23]
- Infection.
Sign out
SKIN LESION (PILONIDAL SINUS), EXCISION: - PILONIDAL SINUS. - NEGATIVE FOR MALIGNANCY.
Micro
The section shows hair-bearing skin with a deep sinus tract containing large clusters of neutrophils, abundant plasma cells, hemosiderin-laden macrophages, eosinophils and multinucleated giant cells. The core of the lesion is, focally, well-vascularized. At the edge of the lesion is fibrotic tissue with plump fibroblasts. Benign, fibrofatty tissue with scant inflammation completely surrounds the tract, in the plane of section; however, it is focally fragmented. There is no squamous lining within the sinus. No nuclear atypia is identified.
Alternate
The section shows hair-bearing skin with a deep sinus containing large clusters of neutrophils, abundant plasma cells, hemosiderin-laden macrophages and multinucleated giant cells. Benign fibrofatty tissue with scant inflammation completely surrounds the lesion in the plane of section. There is no squamous lining within the sinus. No nuclear atypia is identified.
Less common
Steatocystoma
General
- Benign.
- Typically adults.
- Usually on the trunk.
- May be genetic; known as steatocystoma multiplex.[24]
- Classically autosomal dominant.[25]
Microscopic
Features:[26]
- Cyst lined by squamous epithelium with:
- Corrugated eosinophilic lining - key feature.
- Similar appearance to compact keratin (hyperkeratosis).
- Described as a hyaline cuticle.[27]
- No granular cell layer.
- Corrugated eosinophilic lining - key feature.
Images
www:
Digital mucous cyst
General
- Dome-shaped papule.
Microscopic
Features:[29]
- Mucous in superficial dermis - key feature.
- No epithelial lining; it is a pseudocyst.
Note:
- Mucin = glycolated proteins; may be part of mucous.
- Mucous = slippery secretion.
DDx:
Images:
Sign out
LESION, LEFT INDEX FINGER, EXCISION: - BENIGN DIGITAL MUCOUS CYST.
Apocrine cystadenoma
General
- Uncommon.
Microscopic
Features:[33]
- Multiloculated.
- Apocrine differentiation: columnar epithelium +/- apical snouts.
- Solid areas of epithelial proliferation.
- Papillary projections into the cyst.
Images:
See also
References
- ↑ Greenwald, J.; Heng, M. (2007). Toronto Notes for Medical Students 2007 (2007 ed.). The Toronto Notes Inc. for Medical Students Inc.. pp. D5. ISBN 978-0968592878.
- ↑ URL: http://dermatlas.med.jhmi.edu/derm/IndexDisplay.cfm?ImageID=-969536424. Accessed on: 13 August 2012.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 URL: http://dermatlas.med.jhmi.edu/derm/result.cfm?Diagnosis=605386295. Accessed on: 13 August 2012.
- ↑ Weedon's Skin Pathology. 3rd Ed. P.895.
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 Busam, Klaus J. (2009). Dermatopathology: A Volume in the Foundations in Diagnostic Pathology Series (1st ed.). Saunders. pp. 551. ISBN 978-0443066542.
- ↑ URL: http://www.dermpedia.org/case/70-year-old-woman-with-nose-lesion. Accessed on: 21 June 2013.
- ↑ 7.0 7.1 Busam, Klaus J. (2009). Dermatopathology: A Volume in the Foundations in Diagnostic Pathology Series (1st ed.). Saunders. pp. 302. ISBN 978-0443066542.
- ↑ 8.0 8.1 URL: http://www.dermis.net/dermisroot/en/36946/diagnose.htm. Accessed on: 2 November 2012.
- ↑ 9.0 9.1 Venus, MR.; Eltigani, EA.; Fagan, JM. (Sep 2007). "Just another sebaceous cyst?". Ann R Coll Surg Engl 89 (6): W19-21. doi:10.1308/147870807X227791. PMC 2121251. PMID 18201468. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2121251/..
- ↑ URL: http://dermatlas.med.jhmi.edu/derm/result.cfm?diagnosis=128. Accessed on: 2 November 2012.
- ↑ URL: http://emedicine.medscape.com/article/1058907-diagnosis. Accessed on: 18 March 2011.
- ↑ Adams, SP. (Feb 1999). "Dermacase. Eccrine hydrocystoma.". Can Fam Physician 45: 297, 306. PMC 2328272. PMID 10065300. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2328272/.
- ↑ Lin, CY.; Jwo, SC. (Apr 2002). "Squamous cell carcinoma arising in an epidermal inclusion cyst.". Chang Gung Med J 25 (4): 279-82. PMID 12079164.
- ↑ Brownstein, MH. (Dec 1983). "Hybrid cyst: a combined epidermoid and trichilemmal cyst.". J Am Acad Dermatol 9 (6): 872-5. PMID 6643785.
- ↑ Crystal, P.; Shaco-Levy, R. (Mar 2005). "Concentric rings within a breast mass on sonography: lamellated keratin in an epidermal inclusion cyst.". AJR Am J Roentgenol 184 (3 Suppl): S47-8. PMID 15728019.
- ↑ URL: http://emedicine.medscape.com/article/1058907-overview. Accessed on: 15 April 2012.
- ↑ Busam, Klaus J. (2009). Dermatopathology: A Volume in the Foundations in Diagnostic Pathology Series (1st ed.). Saunders. pp. 309. ISBN 978-0443066542.
- ↑ 18.0 18.1 18.2 Gandhi N, Syed NA, Alen R. Dermoid Cyst. EyeRounds.org. posted July 26, 2010; Available from: http://www.EyeRounds.org/cases/115-dermoid-cyst.htm. Accessed on: 22 September 2011.
- ↑ Mitchell, Richard; Kumar, Vinay; Fausto, Nelson; Abbas, Abul K.; Aster, Jon (2011). Pocket Companion to Robbins & Cotran Pathologic Basis of Disease (8th ed.). Elsevier Saunders. pp. 596. ISBN 978-1416054542.
- ↑ URL: http://emedicine.medscape.com/article/788127-overview. Accessed on: 10 September 2012.
- ↑ URL: http://www.nhs.uk/conditions/Pilonidal-sinus/Pages/Introduction.aspx. Accessed on: 10 September 2012.
- ↑ 22.0 22.1 Busam, Klaus J. (2009). Dermatopathology: A Volume in the Foundations in Diagnostic Pathology Series (1st ed.). Saunders. pp. 326. ISBN 978-0443066542.
- ↑ Chatzis, I.; Noussios, G.; Katsourakis, A.; Chatzitheoklitos, E.. "Squamous cell carcinoma related to long standing pilonidal-disease.". Eur J Dermatol 19 (4): 408-9. doi:10.1684/ejd.2009.0705. PMID 19482585.
- ↑ Online 'Mendelian Inheritance in Man' (OMIM) 184500
- ↑ URL: http://path.upmc.edu/cases/case674/dx.html. Accessed on: 29 January 2012.
- ↑ Busam, Klaus J. (2009). Dermatopathology: A Volume in the Foundations in Diagnostic Pathology Series (1st ed.). Saunders. pp. 312. ISBN 978-0443066542.
- ↑ URL: http://path.upmc.edu/cases/case674/dx.html. Accessed on: 29 January 2012.
- ↑ URL: http://path.upmc.edu/cases/case674.html. Accessed on: 29 January 2012.
- ↑ 29.0 29.1 29.2 29.3 URL: http://www.dermpedia.org/dermpedia-textbook/digital-mucous-myxoid-cyst. Accessed on: 17 January 2012.
- ↑ URL: http://dictionary.reference.com/browse/mucous. Accessed on: 8 January 2012.
- ↑ URL: http://dictionary.reference.com/browse/mucus. Accessed on: 8 January 2012.
- ↑ URL: http://www.dermpedia.org/case/digital-mucous-cyst-ganglion-type. Accessed on: 5 July 2013.
- ↑ Busam, Klaus J. (2009). Dermatopathology: A Volume in the Foundations in Diagnostic Pathology Series (1st ed.). Saunders. pp. 316. ISBN 978-0443066542.